Paul I Šubić of Bribir
| Paul I Šubić of Bribir | |
|---|---|
|
Ban of Croatia Lord of all of Bosnia | |
|
Paul from the 14th century Chest of Saint Simeon | |
| Ban of Croatia | |
| Reign | 1275–1312 |
| Predecessor | Nicholas Gutkeled |
| Successor | Mladen II. Šubić |
| Lord of all of Bosnia | |
| Reign | 1305 - 1312 |
| Successor | Mladen II. Šubić |
| Spouse | Ursa |
| Issue |
Mladen II. Juraj II. Pavao II. Grgur IV. Marko IV. |
| House | House of Šubić |
| Father | Stephen II |
| Mother | Unnamed Árpád woman |
| Born |
c. 1245 Croatia |
| Died |
1 May 1312 Bribir, Croatia |
| Burial | Church of St. Mary, Bribir, Croatia |
| Religion | Roman Catholic |
Paul I Šubić of Bribir (Croatian: Pavao I Šubić Bribirski; Hungarian: bribiri I. Subics Pál) (c. 1245 – 1 May 1312) was a Croatian leader and most outstanding member of the Šubić noble family from Bribir. He was the Ban of Croatia from 1275 and Lord of all of Bosnia from 1305 until his death in 1312. He ruled from his seat in the fortified town of Bribir, where he erected, along with his castle, the three-aisled basilica of St. Mary inside the Franciscan convent.[1]
After the extinction of the Arpad dynasty, Paul had the Angevins brought to the throne, although their power over the Šubić land was merely nominal until 1322. Paul took extensive campaigns and significantly expanded his dominion eastward, over Bosnia and Hum, and also warred successfully against the Republic of Venice, taking the Dalmatian capital Zadar. He was the most powerful Croatian noble at the end of the 13th century and beginning of the 14th century. He reigned during the Árpád and Anjou struggle which secured him power over the whole central part of Croatia. He issued his own money and secured de facto independence.
Biography
Background
The exact date of his birth is unknown, but the year is estimated around 1245. He was the oldest son of the Bribirian noble Stephen II and his wife, who was probably a descendant of the Arpad noble dynasty. Paul was also a brother of Mladen I Šubić of Bribir and George.
The first mention of his name occurs in 1272, when he held the title of Count of Bribir, from which he took his name. Paul became ban of Croatia and was already Duke of Split in 1273 and ruled until his death. At the time of his death, he ruled over most of Dalmatia, Slavonia and Bosnia,[2] lands once ruled by the early Croatian kings.
The first action he undertook to establish his goals, was against the city of Trogir in 1273. He ignored the kings' warning and had his followers attack the royal residence of Klis during winter. The siege failed, as the soldiers of Trogir successfully repelled the attack. Despite these initial failures, Paul subjugated Trogir in spring the following year. These events caused the temporary deposition of Paul as a Ban of Croatia, but was re-established in summer of 1275.[3]
During a civil war between the Árpád and Anjou dynasties for the crown of Hungary and Croatia, he supported Charles I, who named him master of the lands between the Gvozd and Neretva rivers in 1292. In Dalmatia, he appointed his brothers as commissars of Dalmatian cities. He gave Split to his brother Mladen I, and Šibenik, Nin, Trogir and Omiš to his brother Juraj I. He united large parts of Dalmatia and Slavonia. The following year, king Andrew III gave him and his family jurisdiction over the whole Banovina. However, the king also asked to recognize his mother, Tomasina Morosini as the duchess of Slavonia, which Paul rejected and in 1293 proclaimed himself as "ban of the Croats" (Latin: banus Croatorum).
By the time of the death of Andrew III and extinction of the Árpád dynasty (1301), Paul I Šubić became one of the most powerful oligarchs in the Croato-Hungarian kingdom, who ruled de facto independently their dominions. Paul governed whole Croatia and the cities of Dalmatia independently of the central power.[4]
Reign
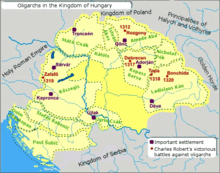
In 1299 he conquered Bosnia, and ruled from the Adriatic sea to the Drava river on the north, and to the Drina river to the east. After conquering Bosnia, Paul I Šubić declared himself as "Dominus of Bosnia" in 1299,[5] and gave his brother Mladen I Šubić the title of Bosnian Ban. Although he did not have himself crowned, he was the de facto sovereign ruler of these territories.
The death of his brother Mladen I in June 1304, who had been reportedly murdered by the supporters of Stephen Kotroman (who Paul had expelled from his lands), compelled Paul I Šubić to lead an army in Bosnia again to crush the resistance and reaffirm his authority. After this he took the title of Lord of all of Bosnia (Latin: totius Bosniae dominus) and passed the title of Ban of Bosnia to his eldest son Mladen II Šubić, who ruled over Bosnia as a Ban under his father. However, after Paul I Šubić's death in 1312, Mladen II tried to maintain his hold over Bosnia and the other Croatian clans, but wasn't successful like his father, so in 1322 he lost control over Bosnia. During 1304. Paul also invaded Serbia to take advantage of the civil war, conquering the area of Hum and reaching as far as today's Montenegro. He appointed his son, Mladen as a governor of these lands as well. However during these conflicts, Mladen was captured and imprisoned by the opposing army. The Serb ruler sent envoys to Paul in Skradin in order to negotiate a meeting. The subject and the briefing of these negotiations are dubious, but it is known that they met in Vrulja,[6] which resulted in concluding peace and securing Mladen's freedom. The details of the agreement between Paul and the Serb king remain unknown.[7]
Paul eventually sided with the Anjou dynasty and sent his brother George I to Naples so he coulf safely transport Charles I over the Adriatic to Hungary. At the death of king Andrew III, Charles I was taken to Zagreb, and from there he went to Esztergom so he could be crowned as the new king. Despite the coronation, Charles wasn't fully recognized for another 10 years and his power in Croatia was only nominal. In 1305 Paul's third son, Paul II, was elected as Prince of Split. During these years Paul I Šubić usually made no reference to the king in his charters, showing that Paul was practically an independent ruler within his realm.[8]
Later years and death

He made several diplomatic interventions and maintained close connection with the nobility of Zadar and Venice as a preliminary move to his expansion over the city. Paul started to assemble an army in the vicinity of Zadar during 1310, and remained stationary until an uprising against Venice broke out in the city in March 1311. The rebels took control of Zadar and arrested the Venetian authorities. The Doge responded by sending a large fleet to recover the city. The siege lasted through two battles that ended favorably for the defender. Troops of Paul Šubić also participated in the defense of the city. Diplomatic actions began in March 1312. The negotiations were handled by the second son of Paul, Juraj II, and it dragged on after Paul's death. Citizens of Zadar, after King Charles I approved their requests, elected Paul's son Mladen II as their prince.[3][8]
Paul died on 1 May 1312 and was buried in the franciscan church of St. Mary in Bribir. Ban Paul was a nearly sovereign monarch, who reigned over most of territories that were originally under former Croatian kings and also issued his own coin.[9] He was succeeded by his son Mladen II during which the power of the Šubić family starts to fade.
Family

Paul Šubić was married to Ursa and had five sons:
- Mladen II. (c. 1275 - c. 1341) - Ban of Croatia and Bosnia (1312–1322), Lord of Hum, Duke of Dalmatia and Zadar (1311–1313), Duke of Split (1294)
- Juraj II. (III.) (c. 1290 - 1328) - Duke of Split (1300), Duke of Tropolje (1301), Duke of the Dalmatian cities (1303)
- Pavao II. (c. 1295 - 1346) - Duke of Trogir (1305–1315), Duke of Ostrovica (1333–1346)
- Grgur IV. - Duke of Šibenik (1320.), Duke of Ostrovica (1346–1347)
- Marko IV. - Duke of Bribir (1322–1345)
Legacy
An important avenue in Zagreb, the Pavao Šubić Avenue is named after him.
See also
References
- ↑ http://hakave.org/index.php?option=com_content&task=view&id=2525&Itemid=151
- ↑ http://www.camo.ch/grbovibhvlastele.htm
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 http://www.scribd.com/doc/32884339/%C5%A0ubi%C4%87i-Bribirski-do-gubitka-nasljedne-banske-%C4%8Dasti-1322
- ↑ Engel, Pál (2001): The Realm of St Stephen: A History of Medieval Hungary, 895-1526. I.B. Tauris Publishers. p. 125.
- ↑ Fine, John Van Antwerp (1994). The Late Medieval Balkans: A Critical Survey from the Late Twelfth Century to the Ottoman Conquest. Michigan: The University of Michigan Press. p. 276. ISBN 0-472-08260-4.
- ↑ Vladimir Ćorović, „Istorija srpskog naroda“ (rukopis iz 1941) Beograd 1989. ISBN 86-13-00389-8
- ↑ Željko Fajfrić, „Sveta loza Stefana Nemanje“, Šid 1998.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 John V. A. Fine: The Late Medieval Balkans: A Critical Survey from the Late Twelfth Century to the Ottoman Conquest, 1994, p. 210
- ↑ http://numizmatika.antikviteti.net/pojma/s1.html
External links
- Damir Karbić, Zlatni vijek Bribira, Matica Hrvatska
- Zvonko Madunić, Šubići u središtu, Hrvatska revija, Matica Hrvatska
- Remains of the palace of Ban Pavao Šubić Of Bribir
- MVEP-Andrija III. daje banu Pavlu Šubiću čitavu južnu Hrvatsku
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Paul I Šubić of Bribir. |
| Paul I Šubić of Bribir House of Šubić Born: c. 1245 Died: 1 May 1312 | ||
| Regnal titles | ||
|---|---|---|
| Preceded by Nicholas II Gutkeled |
Ban of Croatia 1275 – 1312 |
Succeeded by Mladen II Šubić |
| Preceded by Stjepan I Kotroman |
Ban of Bosnia 1299 |
Succeeded by Mladen I Šubić |
| New title | Lord of all of Bosnia 1305 – 1312 |
Succeeded by Mladen II Šubić |