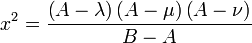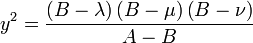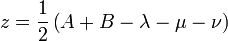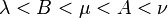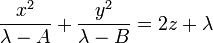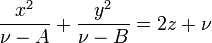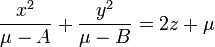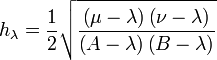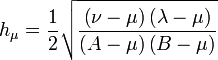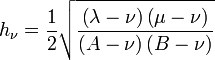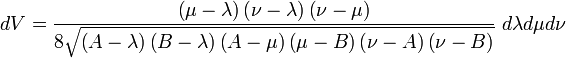Paraboloidal coordinates
Paraboloidal coordinates are a three-dimensional orthogonal coordinate system 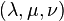 that generalizes the two-dimensional parabolic coordinate system. Similar to the related ellipsoidal coordinates, the paraboloidal coordinate system has orthogonal quadratic coordinate surfaces that are not produced by rotating or projecting any two-dimensional orthogonal coordinate system.
that generalizes the two-dimensional parabolic coordinate system. Similar to the related ellipsoidal coordinates, the paraboloidal coordinate system has orthogonal quadratic coordinate surfaces that are not produced by rotating or projecting any two-dimensional orthogonal coordinate system.
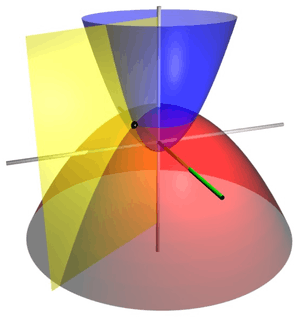
Basic formulae
The Cartesian coordinates 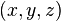 can be produced from the ellipsoidal coordinates
can be produced from the ellipsoidal coordinates
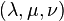 by the equations
by the equations
where the following limits apply to the coordinates
Consequently, surfaces of constant 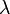 are elliptic paraboloids
are elliptic paraboloids
and surfaces of constant 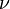 are likewise
are likewise
whereas surfaces of constant 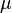 are hyperbolic paraboloids
are hyperbolic paraboloids
Scale factors
The scale factors for the paraboloidal coordinates 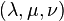 are
are
Hence, the infinitesimal volume element equals
Differential operators such as 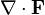 and
and 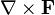 can be expressed in the coordinates
can be expressed in the coordinates 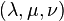 by substituting the scale factors into the general formulae found in orthogonal coordinates.
by substituting the scale factors into the general formulae found in orthogonal coordinates.
References
Bibliography
- Morse PM, Feshbach H (1953). Methods of Theoretical Physics, Part I. New York: McGraw-Hill. p. 664. ISBN 0-07-043316-X. LCCN 52011515.
- Margenau H, Murphy GM (1956). The Mathematics of Physics and Chemistry. New York: D. van Nostrand. pp. 184–185. LCCN 55010911.
- Korn GA, Korn TM (1961). Mathematical Handbook for Scientists and Engineers. New York: McGraw-Hill. p. 180. LCCN 59014456. ASIN B0000CKZX7.
- Arfken G (1970). Mathematical Methods for Physicists (2nd ed.). Orlando, FL: Academic Press. pp. 119–120.
- Sauer R, Szabó I (1967). Mathematische Hilfsmittel des Ingenieurs. New York: Springer Verlag. p. 98. LCCN 67025285.
- Zwillinger D (1992). Handbook of Integration. Boston, MA: Jones and Bartlett. p. 114. ISBN 0-86720-293-9. Same as Morse & Feshbach (1953), substituting uk for ξk.
- Moon P, Spencer DE (1988). "Paraboloidal Coordinates (μ, ν, λ)". Field Theory Handbook, Including Coordinate Systems, Differential Equations, and Their Solutions (corrected 2nd ed., 3rd print ed.). New York: Springer-Verlag. pp. 44–48 (Table 1.11). ISBN 978-0-387-18430-2.
External links
| ||||||||||