Pamoic acid
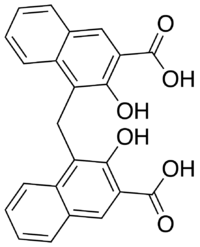 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
4-[(3-Carboxy-2-hydroxynaphthalen-1-yl)methyl]-3-hydroxynaphthalene-2-carboxylic acid | |
| Other names
Embonic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
| 901319 | |
| 130-85-8 | |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:50186 |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL177880 |
| ChemSpider | 8228 |
| EC number | 204-998-0 |
| |
| Jmol-3D images | Image Image |
| MeSH | Pamoic+acid |
| PubChem | 8546 |
| RTECS number | QL2180000 |
| |
| UNII | 7RRQ8QZ38N |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula |
C23H16O6 |
| Molar mass | 388.37 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | ≥300 °C |
| log P | 6.169 |
| Acidity (pKa) | 2.675 |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | Causes skin irritation Causes serious eye irritation |
| EU classification | |
| R-phrases | R36/37/38 |
| S-phrases | S26 S36 |
| Except where noted otherwise, data is given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| Infobox references | |
Pamoic acid, also called embonic acid, is a naphthoic acid derivative. Salts and esters of pamoic acid are known as pamoates or embonates. It can be prepared by the reaction of 2-hydroxy-3-naphthoic acid with formaldehyde. In pharmacology, the salt form of pamoic acid (pamoate ion) can be used as a counter ion of a drug compound to increase the solubility of the drug in water.[3] The presence of multiple oxygen atoms enables significant hydrogen bonding to occur. Hydrogen bonds facilitate the dissolution of compounds in water.
It was demonstrated that pamoic acid has agonist activity for the orphan G protein-coupled receptor GPR35 by which it activates ERK and beta-arrestin2, and causes antinociceptive activity. Although (like other drug salts) it has been considered an inactive compound by the FDA, these recent data suggest that its use may be reexamined.
References
- ↑ Merck Index, 12th Edition, 7136.
- ↑ Zhao, P.; Sharir, H.; Kapur, A.; Cowan, A.; Geller, E. B.; Adler, M. W.; Seltzman, H. H.; Reggio, P. H. et al. (2010). "Targeting of the Orphan Receptor GPR35 by Pamoic Acid: A Potent Activator of Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase and -Arrestin2 with Antinociceptive Activity". Molecular Pharmacology 78 (4): 560–8. doi:10.1124/mol.110.066746. PMC 2981393. PMID 20826425.
- ↑ Saesmaa, T; Tötterman, AM (1990). "Dissolution studies on ampicillin embonate and amoxycillin embonate". Journal of pharmaceutical and biomedical analysis 8 (1): 61–5. doi:10.1016/0731-7085(90)80007-c. PMID 2102266.
External links
- Neubig, Richard R (2010). "Mind your salts: when the inactive constituent isn't". Molecular Pharmacology 78 (4): 558–9. doi:10.1124/mol.110.067645. PMID 20651116.