Painted Grey Ware culture
.png)
| Outline of South Asian history History of Indian subcontinent | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Soanian people (500,000 BP)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Stone Age (50,000–3000 BC)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Bronze Age (3000–1300 BC)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Iron Age (1200–26 BC)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Classical period (21–1279 AD) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Late medieval period (1206–1596)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Early modern period (1526–1858)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Colonial period (1510–1961)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Other states (1102–1947)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Kingdoms of Sri Lanka
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Nation histories |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Specialised histories |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The Painted Grey Ware culture (PGW) is an Iron Age culture of the Gangetic plain and the Ghaggar-Hakra valley, lasting from roughly 1200 BC to 600 BC.[1][2][3] It is contemporary to, and a successor of the Black and red ware culture. Characterized by a style of fine, grey pottery painted with geometric patterns in black,[4] this culture is associated with village and town settlements (but without large cities like those of the Harappans), domesticated horses, ivory-working, and the advent of iron metallurgy.[5] But this point of view may change as fresh surveys by archaeologist Vinay Kumar Gupta suggest Mathura was the largest PGW site around 375 hectares in area.[6] Among the largest sites is also the recently excavated Ahichatra, with at least 40 hectares of area in PGW times along with evidence of early construction of the fortification which goes back to PGW levels.[7] Total number of PGW sites discovered so far is more than 1100.[8]
It probably corresponds to the middle and late Vedic period, i.e., the Kuru-Panchala kingdom, the first large state in South Asia after the decline of the Indus Valley Civilization.[9][10] It is succeeded by Northern Black Polished Ware from c. 700-500 BC, associated with the rise of the great mahajanapada states and of the Magadha Empire.
Overview
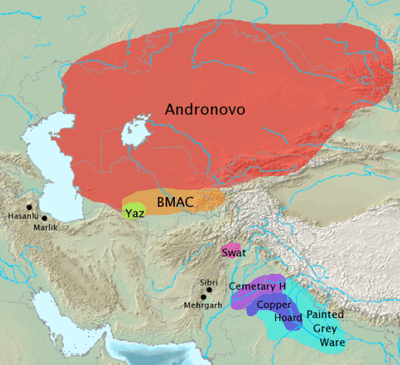
The PGW culture cultivated rice, wheat, and barley, and domesticated cattle, sheep, pigs, and horses. Houses were built of wattle-and-daub, mud, or bricks, ranging in size from small huts to large houses with many rooms. There is a clear settlement hierarchy, with a few central towns that stand out amongst numerous small villages. Some sites, including Jakhera in Uttar Pradesh, demonstrate a “fairly evolved, proto-urban or semi-urban stage” of this culture, with evidence of social organization and trade, including ornaments of gold, copper, ivory, and semi-precious stones, storage bins for surplus grain, stone weights, paved streets, water channels and embankments.[11]
Arts and crafts of the PGW people are represented by ornaments (made from terracotta, stone, faience, and glass), human and animal figurines (made from terracotta) as well as "incised terracotta discs with decorated edges and geometric motifs" which probably had "ritual meaning," perhaps representing symbols of deities.[12] At Bhagwanpura in the Kurukshetra district of Haryana, excavations have revealed an overlap between the late Harappan and Painted Grey Ware cultures, large houses that may have been elite residences, and fired bricks that may have been used in Vedic altars.[13]
In the 1950s, archaeologist B.B. Lal associated Hastinapura, Mathura, Ahichatra, Kampilya, Barnawa, Kurukshetra and other sites of PGW culture with the Mahabharata period and the Aryans. Furthermore, he pointed out that the Mahabharata mentions a flood and a layer of flooding debris was found in Hastinapura. However, B.B. Lal considered his theories to be provisional and based upon a limited body of evidence, and he later reconsidered his statements on the nature of this culture (Kenneth Kennedy 1995). B.B. Lal confirms that Mahabharata is associated with PGW sites in a recent 2012 presentation at the International Seminar on Mahabharata held by Draupadi Trust and gives a date to circa 900 BCE for the War.[14]
The pottery style of this culture is different from the pottery of the Iranian Plateau and Afghanistan (Bryant 2001). In some sites, PGW pottery and Late Harappan pottery are contemporaneous.[15] The archaeologist Jim Shaffer (1984:84-85) has noted that "at present, the archaeological record indicates no cultural discontinuities separating Painted Grey Ware from the indigenous protohistoric culture." However, the continuity of pottery styles may be explained by the fact that pottery was generally made by indigenous craftsmen even after the Indo-Aryan migration.[16] According to Chakrabarti (1968) and other scholars, the origins of the subsistence patterns (e.g. rice use) and most other characteristics of the Painted Grey Ware culture are in eastern India or even Southeast Asia.[note 1]
Towards the end of the period, many of the PGW settlements grew into the large towns and cities of the Northern Black Polished Ware period.[17]
Recently, University of Cambridge and Banaras Hindu University excavated at Alamgirpur near Delhi where sample OxA-21882 showed a calibrated radiocarbon dating from 2136 BC to 1948 BC for PGW levels, overlapping Mature Harappan phase at the site, suggesting PGW early phases are much older than previously thought.[18] Confirmation of this early PGW came when a team of the Archaeological Survey of India led by B.R. Mani and Vinay Kumar Gupta collected charcoal samples from Gosna, a site 6 km east of Mathura across the Yamuna river where two radiocarbon dates from PGW deposit came out to be 2160 BC and 2170 BC.[19]
See also
- Kuru Kingdom
- Panchala
- Mahajanapadas
References
- ↑ http://pubweb.cc.u-tokai.ac.jp/indus/english/3_1_07.html
- ↑ http://books.google.com/books?id=tzU3RIV2BWIC&pg=PA310&dq=Painted+Grey+Ware+culture+1200+bc&as_brr=3&cd=8#v=onepage&q=Painted%20Grey%20Ware%20culture%201200%20bc&f=false "Encyclopedia of Indo-European culture" By J. P. Mallory, Douglas Q. Adams
- ↑ http://books.google.com/books?id=ZR-J6-WOH4QC&pg=PA96&dq=Painted+Grey+Ware+culture+1200+bc&as_brr=3&cd=3#v=onepage&q=Painted%20Grey%20Ware%20culture%201200%20bc&f=false "Malwa Through the Ages" By Kailash Chand Jain
- ↑ http://books.google.com/books?id=WGUz01yBumEC&pg=PA357
- ↑ http://books.google.com/books?id=tzU3RIV2BWIC&pg=PA414
- ↑ https://groups.yahoo.com/neo/groups/IndiaArchaeology/conversations/messages/16569
- ↑ http://www.educationtimes.com/article/290/20130917201309171524062507304cdb3/What-Lies-Beneath.html
- ↑ Vikrama, Bhuvan & Daljeet Singh, 2014."Classification of Motifs on Painted Grey Ware", in Pracyabodha, Indian Archaeology and Tradition, Vol.2, Delhi, pp. 223-229
- ↑ Geoffrey Samuel, (2010) The Origins of Yoga and Tantra: Indic Religions to the Thirteenth Century, Cambridge University Press, pp. 45–51
- ↑ Michael Witzel (1989), Tracing the Vedic dialects in Dialectes dans les litteratures Indo-Aryennes ed. Caillat, Paris, 97–265.
- ↑ Upinder Singh (2009), A History of Ancient and Medieval India: From the Stone Age to the 12th Century, Delhi:Longman, pp. 246–248
- ↑ J.M. Kenoyer (2006), "Cultures and Societies of the Indus Tradition. In Historical Roots" in the Making of ‘the Aryan’, R. Thapar (ed.), pp. 21–49. New Delhi, National Book Trust.
- ↑ Kenoyer (2006)
- ↑ http://es.slideshare.net/sfih108/mahabharata-historicity-prof-b-b-lal
- ↑ Shaffer, Jim. 1993, Reurbanization: The eastern Punjab and beyond. In Urban Form and Meaning in South Asia: The Shaping of Cities from Prehistoric to Precolonial Times, ed. H. Spodek and D.M. Srinivasan.
- ↑ http://www.ejvs.laurasianacademy.com/ejvs0703/ejvs0703article.pdf
- ↑ http://a.harappa.com/sites/g/files/g65461/f/CulturesSocietiesIndusTrad.pdf
- ↑ Singh, R.N., Cameron Petrie et al. (2013)."Recent Excavations at Alamgirpur, Meerut District: A Preliminary Report" in Man and Environment 38(1), pp. 32-54 https://www.academia.edu/8246061/Received_Recent_Excavations_at_Alamgirpur_Meerut_District_A_Preliminary_Report_Indian_Society_for_Prehistoric_and_Quaternary_Studies
- ↑ Gupta, Vinay Kumar, (2014)."Early Settlement of Mathura: An Archaeological Perspective" in History and Society, New Series 41, Nehru Memorial Museum and Library, New Delhi, pp. 1-37 http://www.academia.edu/7025503/Early_Settlement_of_Mathura_An_Archaeological_Perspective_An_Occasional_paper_published_by_Nehru_Memorial_Museum_and_Library_N._Delhi
- Bryant, Edwin (2001). The Quest for the Origins of Vedic Culture. Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-513777-9.
- Chakrabarti, D.K. 1968. The Aryan hypothesis in Indian archaeology. Indian Studies Past and Present 4, 333-358.
- Jim Shaffer. 1984. The Indo-Aryan Invasions: Cultural Myth and Archaeological Reality. In: J.R. Lukak. The People of South Asia. New York: Plenum. 1984.
- Kennedy, Kenneth 1995. “Have Aryans been identified in the prehistoric skeletal record from South Asia?”, in George Erdosy, ed.: The Indo-Aryans of Ancient South Asia, p. 49-54.
Notes
- ↑ See also Indo-Aryan migration#Archaeological evidence.