PTPRR
Protein tyrosine phosphatase receptor-type R is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PTPRR gene.[1][2][3]
Function
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the protein tyrosine phosphatase (PTP) family. PTPs are known to be signaling molecules that regulate a variety of cellular processes including cell growth, differentiation, mitotic cycle, and oncogenic transformation. This PTP possesses an extracellular region, a single transmembrane region, and a single intracellular catalytic domains, and thus represents a receptor-type PTP. The similar gene predominately expressed in mouse brain was found to associate with, and thus regulate the activity and cellular localization of MAP kinases. The rat counterpart of this gene was reported to be regulated by the nerve growth factor, which suggested the function of this gene in neuronal growth and differentiation.[3]
Interactions
PTPRR has been shown to interact with MAPK7.[4]
References
- ↑ Shiozuka K, Watanabe Y, Ikeda T, Hashimoto S, Kawashima H (Nov 1995). "Cloning and expression of PCPTP1 encoding protein tyrosine phosphatase". Gene 162 (2): 279–84. doi:10.1016/0378-1119(95)00306-Q. PMID 7557444.
- ↑ van den Maagdenberg AM, Schepens JT, Schepens MT, Merkx GF, Darroudi F, Wieringa B et al. (Jul 1999). "Assignment1 of the PTP-SL/PTPBR7 gene (Ptprr/PTPRR) to mouse chromosome region 8A2 by in situ hybridization". Cytogenet Cell Genet 84 (3-4): 243–4. doi:10.1159/000015268. PMID 10393441.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 "Entrez Gene: PTPRR protein tyrosine phosphatase, receptor type, R".
- ↑ Buschbeck M, Eickhoff J, Sommer MN, Ullrich A (Aug 2002). "Phosphotyrosine-specific phosphatase PTP-SL regulates the ERK5 signaling pathway". J. Biol. Chem. 277 (33): 29503–9. doi:10.1074/jbc.M202149200. PMID 12042304.
Further reading
- Sharma E, Lombroso PJ (1995). "A neuronal protein tyrosine phosphatase induced by nerve growth factor.". J. Biol. Chem. 270 (1): 49–53. doi:10.1074/jbc.270.1.49. PMID 7814416.
- Ogata M, Sawada M, Fujino Y, Hamaoka T (1995). "cDNA cloning and characterization of a novel receptor-type protein tyrosine phosphatase expressed predominantly in the brain.". J. Biol. Chem. 270 (5): 2337–43. doi:10.1074/jbc.270.5.2337. PMID 7836467.
- Pulido R, Zúñiga A, Ullrich A (1999). "PTP-SL and STEP protein tyrosine phosphatases regulate the activation of the extracellular signal-regulated kinases ERK1 and ERK2 by association through a kinase interaction motif.". EMBO J. 17 (24): 7337–50. doi:10.1093/emboj/17.24.7337. PMC 1171079. PMID 9857190.
- Ogata M, Oh-hora M, Kosugi A, Hamaoka T (1999). "Inactivation of mitogen-activated protein kinases by a mammalian tyrosine-specific phosphatase, PTPBR7.". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 256 (1): 52–6. doi:10.1006/bbrc.1999.0278. PMID 10066421.
- Zúñiga A, Torres J, Ubeda J, Pulido R (1999). "Interaction of mitogen-activated protein kinases with the kinase interaction motif of the tyrosine phosphatase PTP-SL provides substrate specificity and retains ERK2 in the cytoplasm.". J. Biol. Chem. 274 (31): 21900–7. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.31.21900. PMID 10419510.
- Blanco-Aparicio C, Torres J, Pulido R (2000). "A novel regulatory mechanism of MAP kinases activation and nuclear translocation mediated by PKA and the PTP-SL tyrosine phosphatase.". J. Cell Biol. 147 (6): 1129–36. doi:10.1083/jcb.147.6.1129. PMC 2168101. PMID 10601328.
- Augustine KA, Silbiger SM, Bucay N, Ulias L, Boynton A, Trebasky LD et al. (2000). "Protein tyrosine phosphatase (PC12, Br7,S1) family: expression characterization in the adult human and mouse.". Anat. Rec. 258 (3): 221–34. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-0185(20000301)258:3<221::AID-AR1>3.0.CO;2-W. PMID 10705342.
- Bektas A, Hughes JN, Warram JH, Krolewski AS, Doria A (2001). "Type 2 diabetes locus on 12q15. Further mapping and mutation screening of two candidate genes.". Diabetes 50 (1): 204–8. doi:10.2337/diabetes.50.1.204. PMID 11147789.
- Szedlacsek SE, Aricescu AR, Fulga TA, Renault L, Scheidig AJ (2001). "Crystal structure of PTP-SL/PTPBR7 catalytic domain: implications for MAP kinase regulation.". J. Mol. Biol. 311 (3): 557–68. doi:10.1006/jmbi.2001.4890. PMID 11493009.
- Buschbeck M, Eickhoff J, Sommer MN, Ullrich A (2002). "Phosphotyrosine-specific phosphatase PTP-SL regulates the ERK5 signaling pathway.". J. Biol. Chem. 277 (33): 29503–9. doi:10.1074/jbc.M202149200. PMID 12042304.
- Shin BK, Wang H, Yim AM, Le Naour F, Brichory F, Jang JH et al. (2003). "Global profiling of the cell surface proteome of cancer cells uncovers an abundance of proteins with chaperone function.". J. Biol. Chem. 278 (9): 7607–16. doi:10.1074/jbc.M210455200. PMID 12493773.
- Tárrega C, Ríos P, Cejudo-Marín R, Blanco-Aparicio C, van den Berk L, Schepens J et al. (2006). "ERK2 shows a restrictive and locally selective mechanism of recognition by its tyrosine phosphatase inactivators not shared by its activator MEK1.". J. Biol. Chem. 280 (45): 37885–94. doi:10.1074/jbc.M504366200. PMID 16148006.
- Eswaran J, von Kries JP, Marsden B, Longman E, Debreczeni JE, Ugochukwu E et al. (2006). "Crystal structures and inhibitor identification for PTPN5, PTPRR and PTPN7: a family of human MAPK-specific protein tyrosine phosphatases.". Biochem. J. 395 (3): 483–91. doi:10.1042/BJ20051931. PMC 1462698. PMID 16441242.
PDB gallery |
|---|
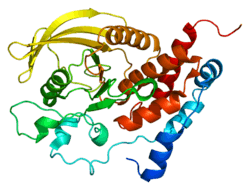
| | 1jln: Crystal structure of the catalytic domain of protein tyrosine phosphatase PTP-SL/BR7 |
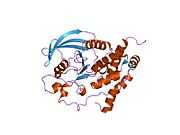
| 2a8b: Crystal Structure of the Catalytic Domain of Human Tyrosine Phosphatase Receptor, Type R |
|
|
|