PTPN21
| Protein tyrosine phosphatase, non-receptor type 21 | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||
| Symbols | PTPN21 ; PTPD1; PTPRL10 | ||||||||||||
| External IDs | OMIM: 603271 MGI: 1344406 HomoloGene: 5110 ChEMBL: 4060 GeneCards: PTPN21 Gene | ||||||||||||
| EC number | 3.1.3.48 | ||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
| RNA expression pattern | |||||||||||||
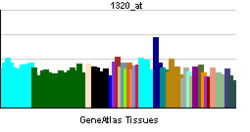 | |||||||||||||
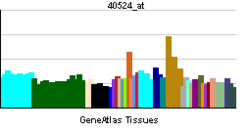 | |||||||||||||
 | |||||||||||||
| More reference expression data | |||||||||||||
| Orthologs | |||||||||||||
| Species | Human | Mouse | |||||||||||
| Entrez | 11099 | 24000 | |||||||||||
| Ensembl | ENSG00000070778 | ENSMUSG00000021009 | |||||||||||
| UniProt | Q16825 | E9PZ70 | |||||||||||
| RefSeq (mRNA) | NM_007039 | NM_001146199 | |||||||||||
| RefSeq (protein) | NP_008970 | NP_001139671 | |||||||||||
| Location (UCSC) | Chr 14: 88.93 – 89.02 Mb | Chr 12: 98.68 – 98.74 Mb | |||||||||||
| PubMed search | |||||||||||||
Tyrosine-protein phosphatase non-receptor type 21 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PTPN21 gene.[1][2]
Function
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the protein tyrosine phosphatase (PTP) family. PTPs are known to be signaling molecules that regulate a variety of cellular processes including cell growth, differentiation, mitotic cycle, and oncogenic transformation. This PTP contains an N-terminal domain, similar to cytoskeletal- associated proteins including band 4.1, ezrin, merlin, and radixin. This PTP was shown to specially interact with BMX/ETK, a member of Tec tyrosine kinase family characterized by a multimodular structures including PH, SH3, and SH2 domains. The interaction of this PTP with BMX kinase was found to increase the activation of STAT3, but not STAT2 kinase. Studies of the similar gene in mice suggested the possible roles of this PTP in liver regeneration and spermatogenesis.[2]
Interactions
PTPN21 has been shown to interact with BMX[3] and KIF1C.[4]
References
- ↑ Møller NP, Møller KB, Lammers R, Kharitonenkov A, Sures I, Ullrich A (Sep 1994). "Src kinase associates with a member of a distinct subfamily of protein-tyrosine phosphatases containing an ezrin-like domain". Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91 (16): 7477–81. doi:10.1073/pnas.91.16.7477. PMC 44424. PMID 7519780.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 "Entrez Gene: PTPN21 protein tyrosine phosphatase, non-receptor type 21".
- ↑ Jui HY, Tseng RJ, Wen X, Fang HI, Huang LM, Chen KY et al. (Dec 2000). "Protein-tyrosine phosphatase D1, a potential regulator and effector for Tec family kinases". J. Biol. Chem. 275 (52): 41124–32. doi:10.1074/jbc.M007772200. PMID 11013262.
- ↑ Dorner C, Ciossek T, Müller S, Møller PH, Ullrich A, Lammers R (Aug 1998). "Characterization of KIF1C, a new kinesin-like protein involved in vesicle transport from the Golgi apparatus to the endoplasmic reticulum". J. Biol. Chem. 273 (32): 20267–75. doi:10.1074/jbc.273.32.20267. PMID 9685376.
Further reading
- Zeitlin AA, Heward JM, Brand OJ, Newby PR, Franklyn JA, Gough SC et al. (2007). "Use of Tag single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) to screen PTPN21: no association with Graves' disease.". Clin. Endocrinol. (Oxf) 65 (3): 380–4. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2265.2006.02608.x. PMID 16918960.
- Kimura K, Wakamatsu A, Suzuki Y, Ota T, Nishikawa T, Yamashita R et al. (2006). "Diversification of transcriptional modulation: large-scale identification and characterization of putative alternative promoters of human genes.". Genome Res. 16 (1): 55–65. doi:10.1101/gr.4039406. PMC 1356129. PMID 16344560.
- Cardone L, Carlucci A, Affaitati A, Livigni A, DeCristofaro T, Garbi C et al. (2004). "Mitochondrial AKAP121 binds and targets protein tyrosine phosphatase D1, a novel positive regulator of src signaling.". Mol. Cell. Biol. 24 (11): 4613–26. doi:10.1128/MCB.24.11.4613-4626.2004. PMC 416429. PMID 15143158.
- Jui HY, Tseng RJ, Wen X, Fang HI, Huang LM, Chen KY et al. (2001). "Protein-tyrosine phosphatase D1, a potential regulator and effector for Tec family kinases.". J. Biol. Chem. 275 (52): 41124–32. doi:10.1074/jbc.M007772200. PMID 11013262.
- Tokuchi H, Higashitsuji H, Nishiyama H, Nonoguchi K, Nagao T, Xue JH et al. (2000). "Expression of protein tyrosine phosphatase PTP-RL10 and its isoform in the mouse testis.". Int. J. Urol. 6 (11): 572–7. doi:10.1046/j.1442-2042.1999.611108.x. PMID 10585123.
- Dorner C, Ciossek T, Müller S, Møller PH, Ullrich A, Lammers R (1998). "Characterization of KIF1C, a new kinesin-like protein involved in vesicle transport from the Golgi apparatus to the endoplasmic reticulum.". J. Biol. Chem. 273 (32): 20267–75. doi:10.1074/jbc.273.32.20267. PMID 9685376.
- Higashitsuji H, Arii S, Furutani M, Imamura M, Kaneko Y, Takenawa J et al. (1995). "Enhanced expression of multiple protein tyrosine phosphatases in the regenerating mouse liver: isolation of PTP-RL10, a novel cytoplasmic-type phosphatase with sequence homology to cytoskeletal protein 4.1.". Oncogene 10 (2): 407–14. PMID 7838537.
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||