PON2
| Paraoxonase 2 | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||
| Symbol | PON2 | ||||||||||||
| External IDs | OMIM: 602447 MGI: 106687 HomoloGene: 385 GeneCards: PON2 Gene | ||||||||||||
| EC number | 3.1.1.2, 3.1.1.81 | ||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
| RNA expression pattern | |||||||||||||
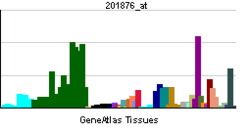 | |||||||||||||
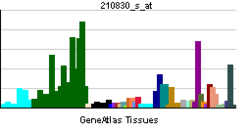 | |||||||||||||
| More reference expression data | |||||||||||||
| Orthologs | |||||||||||||
| Species | Human | Mouse | |||||||||||
| Entrez | 5445 | 330260 | |||||||||||
| Ensembl | ENSG00000105854 | ENSMUSG00000032667 | |||||||||||
| UniProt | Q15165 | Q62086 | |||||||||||
| RefSeq (mRNA) | NM_000305 | NM_183308 | |||||||||||
| RefSeq (protein) | NP_000296 | NP_899131 | |||||||||||
| Location (UCSC) | Chr 7: 95.03 – 95.06 Mb | Chr 6: 5.26 – 5.3 Mb | |||||||||||
| PubMed search | |||||||||||||
Serum paraoxonase/arylesterase 2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PON2 gene.[1][2][3]
This gene encodes a member of the paraoxonase gene family, which includes three known members located adjacent to each other on the long arm of chromosome 7. The encoded protein is ubiquitously expressed in human tissues, membrane-bound, and may act as a cellular antioxidant, protecting cells from oxidative stress. Hydrolytic activity against acylhomoserine lactones, important bacterial quorum-sensing mediators, suggests the encoded protein may also play a role in defense responses to pathogenic bacteria. Mutations in this gene may be associated with vascular disease and a number of quantitative phenotypes related to diabetes. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been described.[3]
References
- ↑ Primo-Parmo SL, Sorenson RC, Teiber J, La Du BN (Sep 1996). "The human serum paraoxonase/arylesterase gene (PON1) is one member of a multigene family". Genomics 33 (3): 498–507. doi:10.1006/geno.1996.0225. PMID 8661009.
- ↑ Mochizuki H, Scherer SW, Xi T, Nickle DC, Majer M, Huizenga JJ, Tsui LC, Prochazka M (Aug 1998). "Human PON2 gene at 7q21.3: cloning, multiple mRNA forms, and missense polymorphisms in the coding sequence". Gene 213 (1–2): 149–57. doi:10.1016/S0378-1119(98)00193-0. PMID 9714608.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 "Entrez Gene: PON2 paraoxonase 2".
Further reading
- Mackness B, Durrington PN, Mackness MI (2003). "The paraoxonase gene family and coronary heart disease". Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 13 (4): 357–62. doi:10.1097/00041433-200208000-00002. PMID 12151850.
- Getz GS, Reardon CA (2005). "Paraoxonase, a cardioprotective enzyme: continuing issues". Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 15 (3): 261–7. doi:10.1097/00041433-200406000-00005. PMID 15166781.
- Ng CJ, Shih DM, Hama SY et al. (2005). "The paraoxonase gene family and atherosclerosis". Free Radic. Biol. Med. 38 (2): 153–63. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2004.09.035. PMID 15607899.
- Hegele RA, Connelly PW, Scherer SW et al. (1997). "Paraoxonase-2 gene (PON2) G148 variant associated with elevated fasting plasma glucose in noninsulin-dependent diabetes mellitus". J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 82 (10): 3373–7. doi:10.1210/jc.82.10.3373. PMID 9329371.
- Sanghera DK, Aston CE, Saha N, Kamboh MI (1998). "DNA polymorphisms in two paraoxonase genes (PON1 and PON2) are associated with the risk of coronary heart disease". Am. J. Hum. Genet. 62 (1): 36–44. doi:10.1086/301669. PMC 1376796. PMID 9443862.
- "Toward a complete human genome sequence". Genome Res. 8 (11): 1097–108. 1999. doi:10.1101/gr.8.11.1097. PMID 9847074.
- Ng CJ, Wadleigh DJ, Gangopadhyay A et al. (2002). "Paraoxonase-2 is a ubiquitously expressed protein with antioxidant properties and is capable of preventing cell-mediated oxidative modification of low density lipoprotein". J. Biol. Chem. 276 (48): 44444–9. doi:10.1074/jbc.M105660200. PMID 11579088.
- Hong SH, Song J, Min WK, Kim JQ (2002). "Genetic variations of the paraoxonase gene in patients with coronary artery disease". Clin. Biochem. 34 (6): 475–81. doi:10.1016/S0009-9120(01)00257-0. PMID 11676977.
- Obineche EN, Frossard PM, Bokhari AM (2002). "An association study of five genetic loci and left ventricular hypertrophy amongst Gulf Arabs". Hypertens. Res. 24 (6): 635–9. doi:10.1291/hypres.24.635. PMID 11768721.
- Janka Z, Juhász A, Rimanóczy A A et al. (2002). "Codon 311 (Cys --> Ser) polymorphism of paraoxonase-2 gene is associated with apolipoprotein E4 allele in both Alzheimer's and vascular dementias". Mol. Psychiatry 7 (1): 110–2. doi:10.1038/sj/mp/4000916. PMID 11803456.
- Kao Y, Donaghue KC, Chan A et al. (2002). "Paraoxonase gene cluster is a genetic marker for early microvascular complications in type 1 diabetes". Diabet. Med. 19 (3): 212–5. doi:10.1046/j.1464-5491.2002.00660.x. PMID 11918623.
- Chen Q, Reis SE, Kammerer CM et al. (2003). "Association between the severity of angiographic coronary artery disease and paraoxonase gene polymorphisms in the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute-sponsored Women's Ischemia Syndrome Evaluation (WISE) study". Am. J. Hum. Genet. 72 (1): 13–22. doi:10.1086/345312. PMC 378617. PMID 12454802.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Hillier LW, Fulton RS, Fulton LA et al. (2003). "The DNA sequence of human chromosome 7". Nature 424 (6945): 157–64. doi:10.1038/nature01782. PMID 12853948.
- Yamada Y, Ando F, Niino N et al. (2003). "Association of polymorphisms of paraoxonase 1 and 2 genes, alone or in combination, with bone mineral density in community-dwelling Japanese". J. Hum. Genet. 48 (9): 469–75. doi:10.1007/s10038-003-0063-x. PMID 12955589.
- Shi J, Zhang S, Tang M et al. (2004). "Possible association between Cys311Ser polymorphism of paraoxonase 2 gene and late-onset Alzheimer's disease in Chinese". Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 120 (2): 201–4. doi:10.1016/j.molbrainres.2003.10.018. PMID 14741412.