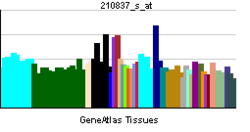
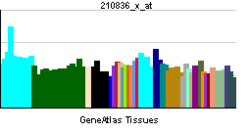
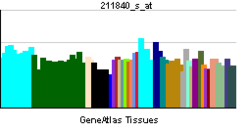
PDE4D
cAMP-specific 3',5'-cyclic phosphodiesterase 4D is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PDE4D gene.
The PDE4D gene is complex and has at least 9 different isoforms that encode functional proteins. These proteins degrade the second messenger cAMP, which is a key signal transduction molecule in multiple cell types, including vascular cells (Dominiczak and McBride, 2003).[supplied by OMIM][1]
Interactions
PDE4D has been shown to interact with myomegalin[2] and GNB2L1.[3][4]
Clinical relevance
Mutations in this gene have been associated to cases od acrodysostosis.[5]
This is the subtype of PDE4 that appears to be involved in the emetic and antidepressant effects of PDE4 inhibitors.[6]
References
- ↑ "Entrez Gene: PDE4D phosphodiesterase 4D, cAMP-specific (phosphodiesterase E3 dunce homolog, Drosophila)".
- ↑ Verde I, Pahlke G, Salanova M, Zhang G, Wang S, Coletti D, Onuffer J, Jin SL, Conti M (April 2001). "Myomegalin is a novel protein of the golgi/centrosome that interacts with a cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase". J. Biol. Chem. 276 (14): 11189–98. doi:10.1074/jbc.M006546200. PMID 11134006.
- ↑ Yarwood SJ, Steele MR, Scotland G, Houslay MD, Bolger GB (May 1999). "The RACK1 signaling scaffold protein selectively interacts with the cAMP-specific phosphodiesterase PDE4D5 isoform". J. Biol. Chem. 274 (21): 14909–17. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.21.14909. PMID 10329691.
- ↑ Steele MR, McCahill A, Thompson DS, MacKenzie C, Isaacs NW, Houslay MD, Bolger GB (July 2001). "Identification of a surface on the beta-propeller protein RACK1 that interacts with the cAMP-specific phosphodiesterase PDE4D5". Cell. Signal. 13 (7): 507–13. doi:10.1016/S0898-6568(01)00167-X. PMID 11516626.
- ↑ Michot, C; Le Goff, C, Goldenberg, A, Abhyankar, A, Klein, C, Kinning, E, Guerrot, AM, Flahaut, P, Duncombe, A, Baujat, G, Lyonnet, S, Thalassinos, C, Nitschke, P, Casanova, JL, Le Merrer, M, Munnich, A, Cormier-Daire, V (Mar 28, 2012). "Exome Sequencing Identifies PDE4D Mutations as Another Cause of Acrodysostosis.". American Journal of Human Genetics 90 (4): 740–5. doi:10.1016/j.ajhg.2012.03.003. PMID 22464250.
- ↑ Zhang, HT (2009). "Cyclic AMP-Specific Phosphodiesterase-4 as a Target for the Development of Antidepressant Drugs". Current Pharmaceutical Design 15 (14): 1688–1698. doi:10.2174/138161209788168092. PMID 19442182.
Further reading
- Wang Q (2005). "Molecular genetics of coronary artery disease". Curr. Opin. Cardiol. 20 (3): 182–8. doi:10.1097/01.hco.0000160373.77190.f1. PMC 1579824. PMID 15861005.
- Swinnen JV, Joseph DR, Conti M (1989). "The mRNA encoding a high-affinity cAMP phosphodiesterase is regulated by hormones and cAMP". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 86 (21): 8197–201. doi:10.1073/pnas.86.21.8197. PMC 298247. PMID 2554303.
- Milatovich A, Bolger G, Michaeli T, Francke U (1994). "Chromosome localizations of genes for five cAMP-specific phosphodiesterases in man and mouse". Somat. Cell Mol. Genet. 20 (2): 75–86. doi:10.1007/BF02290677. PMID 8009369.
- Baecker PA, Obernolte R, Bach C et al. (1994). "Isolation of a cDNA encoding a human rolipram-sensitive cyclic AMP phosphodiesterase (PDE IVD)". Gene 138 (1–2): 253–6. doi:10.1016/0378-1119(94)90818-4. PMID 8125310.
- Bolger G, Michaeli T, Martins T et al. (1993). "A family of human phosphodiesterases homologous to the dunce learning and memory gene product of Drosophila melanogaster are potential targets for antidepressant drugs". Mol. Cell. Biol. 13 (10): 6558–71. PMC 364715. PMID 8413254.
- Sette C, Conti M (1996). "Phosphorylation and activation of a cAMP-specific phosphodiesterase by the cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Involvement of serine 54 in the enzyme activation". J. Biol. Chem. 271 (28): 16526–34. doi:10.1074/jbc.271.28.16526. PMID 8663227.
- Némoz G, Zhang R, Sette C, Conti M (1996). "Identification of cyclic AMP-phosphodiesterase variants from the PDE4D gene expressed in human peripheral mononuclear cells". FEBS Lett. 384 (1): 97–102. doi:10.1016/0014-5793(96)00300-6. PMID 8797812.
- Bolger GB, Erdogan S, Jones RE et al. (1998). "Characterization of five different proteins produced by alternatively spliced mRNAs from the human cAMP-specific phosphodiesterase PDE4D gene". Biochem. J. 328 (Pt 2): 539–48. PMC 1218953. PMID 9371713.
- Hoffmann R, Baillie GS, MacKenzie SJ et al. (1999). "The MAP kinase ERK2 inhibits the cyclic AMP-specific phosphodiesterase HSPDE4D3 by phosphorylating it at Ser579". EMBO J. 18 (4): 893–903. doi:10.1093/emboj/18.4.893. PMC 1171182. PMID 10022832.
- Yarwood SJ, Steele MR, Scotland G et al. (1999). "The RACK1 signaling scaffold protein selectively interacts with the cAMP-specific phosphodiesterase PDE4D5 isoform". J. Biol. Chem. 274 (21): 14909–17. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.21.14909. PMID 10329691.
- Beard MB, O'Connell JC, Bolger GB, Houslay MD (1999). "The unique N-terminal domain of the cAMP phosphodiesterase PDE4D4 allows for interaction with specific SH3 domains". FEBS Lett. 460 (1): 173–7. doi:10.1016/S0014-5793(99)01335-6. PMID 10571082.
- MacKenzie SJ, Baillie GS, McPhee I et al. (2000). "ERK2 mitogen-activated protein kinase binding, phosphorylation, and regulation of the PDE4D cAMP-specific phosphodiesterases. The involvement of COOH-terminal docking sites and NH2-terminal UCR regions". J. Biol. Chem. 275 (22): 16609–17. doi:10.1074/jbc.275.22.16609. PMID 10828059.
- Miró X, Casacuberta JM, Gutiérrez-López MD et al. (2000). "Phosphodiesterases 4D and 7A splice variants in the response of HUVEC cells to TNF-alpha(1)". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 274 (2): 415–21. doi:10.1006/bbrc.2000.3146. PMID 10913353.
- Verde I, Pahlke G, Salanova M et al. (2001). "Myomegalin is a novel protein of the golgi/centrosome that interacts with a cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase". J. Biol. Chem. 276 (14): 11189–98. doi:10.1074/jbc.M006546200. PMID 11134006.
- Zauli G, Milani D, Mirandola P et al. (2001). "HIV-1 Tat protein down-regulates CREB transcription factor expression in PC12 neuronal cells through a phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/AKT/cyclic nucleoside phosphodiesterase pathway". FASEB J. 15 (2): 483–91. doi:10.1096/fj.00-0354com. PMID 11156964.
- Dodge KL, Khouangsathiene S, Kapiloff MS et al. (2001). "mAKAP assembles a protein kinase A/PDE4 phosphodiesterase cAMP signaling module". EMBO J. 20 (8): 1921–30. doi:10.1093/emboj/20.8.1921. PMC 125429. PMID 11296225.
- Steele MR, McCahill A, Thompson DS et al. (2001). "Identification of a surface on the beta-propeller protein RACK1 that interacts with the cAMP-specific phosphodiesterase PDE4D5". Cell. Signal. 13 (7): 507–13. doi:10.1016/S0898-6568(01)00167-X. PMID 11516626.
- Gretarsdottir S, Sveinbjörnsdottir S, Jonsson HH et al. (2002). "Localization of a Susceptibility Gene for Common Forms of Stroke to 5q12". Am. J. Hum. Genet. 70 (3): 593–603. doi:10.1086/339252. PMC 384939. PMID 11833004.
- Moon E, Lee R, Near R et al. (2002). "Inhibition of PDE3B augments PDE4 inhibitor-induced apoptosis in a subset of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia". Clin. Cancer Res. 8 (2): 589–95. PMID 11839681.
- Le Jeune IR, Shepherd M, Van Heeke G et al. (2002). "Cyclic AMP-dependent transcriptional up-regulation of phosphodiesterase 4D5 in human airway smooth muscle cells. Identification and characterization of a novel PDE4D5 promoter". J. Biol. Chem. 277 (39): 35980–9. doi:10.1074/jbc.M204832200. PMID 12121997.
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||