PDCD4
| Programmed cell death 4 (neoplastic transformation inhibitor) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 PDB rendering based on 2ggf. | |||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||
| Symbols | PDCD4 ; H731 | ||||||||||||
| External IDs | OMIM: 608610 MGI: 107490 HomoloGene: 7879 ChEMBL: 1781868 GeneCards: PDCD4 Gene | ||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
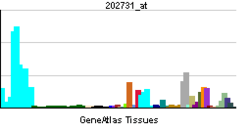
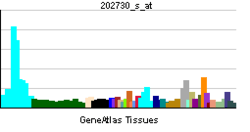
| RNA expression pattern | |||||||||||||
 | |||||||||||||
 | |||||||||||||
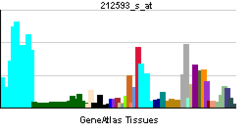 | |||||||||||||
| More reference expression data | |||||||||||||
| Orthologs | |||||||||||||
| Species | Human | Mouse | |||||||||||
| Entrez | 27250 | 18569 | |||||||||||
| Ensembl | ENSG00000150593 | ENSMUSG00000024975 | |||||||||||
| UniProt | Q53EL6 | Q61823 | |||||||||||
| RefSeq (mRNA) | NM_001199492 | NM_001168491 | |||||||||||
| RefSeq (protein) | NP_001186421 | NP_001161963 | |||||||||||
| Location (UCSC) | Chr 10: 112.63 – 112.66 Mb | Chr 19: 53.89 – 53.93 Mb | |||||||||||
| PubMed search | |||||||||||||
Programmed cell death protein 4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PDCD4 gene.[1][2] It is one of the targets of an oncomiR, MIRN21.[3]
Function
This gene encodes a protein localized to the nucleus in proliferating cells. Expression of this gene is modulated by cytokines in natural killer and T cells. The gene product is thought to play a role in apoptosis but the specific role has not yet been determined. Two transcripts encoding different isoforms have been identified.[2]
Interactions
PDCD4 has been shown to interact with RPS13[4] and Ribosomal protein L5.[4]
References
- ↑ Azzoni L, Zatsepina O, Abebe B, Bennett IM, Kanakaraj P, Perussia B (1998). "Differential transcriptional regulation of CD161 and a novel gene, 197/15a, by IL-2, IL-15, and IL-12 in NK and T cells". Journal of immunology 161 (7): 3493–500. PMID 9759869.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 EntrezGene 27250
- ↑ Frankel LB, Christoffersen NR, Jacobsen A, Lindow M, Krogh A, Lund AH (2008). "Programmed cell death 4 (PDCD4) is an important functional target of the microRNA miR-21 in breast cancer cells". The Journal of Biological Chemistry 283 (2): 1026–33. doi:10.1074/jbc.M707224200. PMID 17991735.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Kang MJ, Ahn HS, Lee JY, Matsuhashi S, Park WY (2002). "Up-regulation of PDCD4 in senescent human diploid fibroblasts". Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 293 (1): 617–21. doi:10.1016/S0006-291X(02)00264-4. PMID 12054647.
Further reading
- Göke R, Gregel C, Göke A, Arnold R, Schmidt H, Lankat-Buttgereit B (2004). "Programmed Cell Death Protein 4 (PDCD4) Acts As a Tumor Suppressor in Neuroendocrine Tumor Cells". Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 1014: 220–1. doi:10.1196/annals.1294.024. PMID 15153438. Vancouver style error (help)
- Maruyama K, Sugano S (1994). "Oligo-capping: A simple method to replace the cap structure of eukaryotic mRNAs with oligoribonucleotides". Gene 138 (1–2): 171–4. doi:10.1016/0378-1119(94)90802-8. PMID 8125298.
- Shibahara K, Asano M, Ishida Y, Aoki T, Koike T, Honjo T (1995). "Isolation of a novel mouse gene MA-3 that is induced upon programmed cell death". Gene 166 (2): 297–301. doi:10.1016/0378-1119(95)00607-9. PMID 8543179.
- Suzuki Y, Yoshitomo-Nakagawa K, Maruyama K, Suyama A, Sugano S (1997). "Construction and characterization of a full length-enriched and a 5′-end-enriched cDNA library". Gene 200 (1–2): 149–56. doi:10.1016/S0378-1119(97)00411-3. PMID 9373149.
- Yoshinaga H, Matsuhashi S, Fujiyama C, Masaki Z (1999). "Novel human PDCD4 (H731) gene expressed in proliferative cells is expressed in the small duct epithelial cells of the breast as revealed by an anti-H731 antibody". Pathology International 49 (12): 1067–77. doi:10.1046/j.1440-1827.1999.00995.x. PMID 10632927.
- Soejima, H.; Miyoshi, O.; Yoshinaga, H.; Masaki, Z.; Ozaki, I.; Kajiwara, S.; Niikawa, N.; Matsuhashi, S.; Mukai, T. (1999). "Assignment1 of the programmed cell death 4 gene (PDCD4) to human chromosome band 10q24 by in situ hybridization". Cytogenetic and Genome Research 87: 113–4. doi:10.1159/000015408.
- Kang MJ, Ahn HS, Lee JY, Matsuhashi S, Park WY (2002). "Up-regulation of PDCD4 in senescent human diploid fibroblasts". Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 293 (1): 617–21. doi:10.1016/S0006-291X(02)00264-4. PMID 12054647.
- Chen Y, Knösel T, Kristiansen G, Pietas A, Garber ME, Matsuhashi S et al. (2003). "Loss of PDCD4 expression in human lung cancer correlates with tumour progression and prognosis". The Journal of Pathology 200 (5): 640–6. doi:10.1002/path.1378. PMID 12898601. Vancouver style error (help)
- Yang HS, Cho MH, Zakowicz H, Hegamyer G, Sonenberg N, Colburn NH (2004). "A Novel Function of the MA-3 Domains in Transformation and Translation Suppressor Pdcd4 is Essential for Its Binding to Eukaryotic Translation Initiation Factor 4A". Molecular and Cellular Biology 24 (9): 3894–906. doi:10.1128/MCB.24.9.3894-3906.2004. PMC 387765. PMID 15082783.
- Brill LM, Salomon AR, Ficarro SB, Mukherji M, Stettler-Gill M, Peters EC (2004). "Robust Phosphoproteomic Profiling of Tyrosine Phosphorylation Sites from Human T Cells Using Immobilized Metal Affinity Chromatography and Tandem Mass Spectrometry". Analytical Chemistry 76 (10): 2763–72. doi:10.1021/ac035352d. PMID 15144186.
- Göke R, Barth P, Schmidt A, Samans B, Lankat-Buttgereit B (2004). "Programmed cell death protein 4 suppresses CDK1/cdc2 via induction of p21Waf1/Cip1". AJP: Cell Physiology 287 (6): C1541–6. doi:10.1152/ajpcell.00025.2004. PMID 15317660. Vancouver style error (help)
- Rush J, Moritz A, Lee KA, Guo A, Goss VL, Spek EJ et al. (2004). "Immunoaffinity profiling of tyrosine phosphorylation in cancer cells". Nature Biotechnology 23 (1): 94–101. doi:10.1038/nbt1046. PMID 15592455.
- Rual JF, Venkatesan K, Hao T, Hirozane-Kishikawa T, Dricot A, Li N, Berriz GF, Gibbons FD et al. (2005). "Towards a proteome-scale map of the human protein–protein interaction network". Nature 437 (7062): 1173–8. doi:10.1038/nature04209. PMID 16189514.
- Palamarchuk A, Efanov A, Maximov V, Aqeilan RI, Croce CM, Pekarsky Y (2005). "Akt Phosphorylates and Regulates Pdcd4 Tumor Suppressor Protein". Cancer Research 65 (24): 11282–6. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-3469. PMID 16357133.
- Yang HS, Matthews CP, Clair T, Wang Q, Baker AR, Li CC et al. (2006). "Tumorigenesis Suppressor Pdcd4 Down-Regulates Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Kinase Kinase Kinase 1 Expression to Suppress Colon Carcinoma Cell Invasion". Molecular and Cellular Biology 26 (4): 1297–306. doi:10.1128/MCB.26.4.1297-1306.2006. PMC 1367180. PMID 16449643.
| |||||||||||||||||||