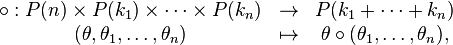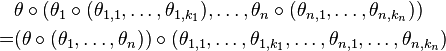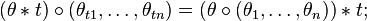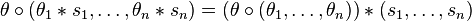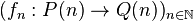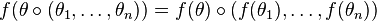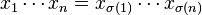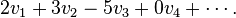Operad theory
Operad theory is a field of abstract algebra concerned with prototypical algebras that model properties such as commutativity or anticommutativity as well as various amounts of associativity. Operads generalize the various associativity properties already observed in algebras and coalgebras such as Lie algebras or Poisson algebras by modeling computational trees within the algebra. Algebras are to operads as group representations are to groups. Originating from work in algebraic topology by Boardman and Vogt, and J. Peter May (to whom their name is due), it has more recently found many applications, drawing for example on work by Maxim Kontsevich on graph homology.
An operad can be seen as a set of operations, each one having a fixed finite number of inputs (arguments) and one output, which can be composed one with others; it is a category-theoretic analog of universal algebra.
The word "operad" was also created by May as a portmanteau of "operations" and "monad" (and also because his mother was an opera singer). Regarding its creation, he wrote: "The name 'operad' is a word that I coined myself, spending a week thinking of nothing else." [1]
Definition
Operad without permutations
An operad without permutations (sometimes called a non-symmetric, non-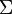 or plain operad) consists of the following:
or plain operad) consists of the following:
- a sequence
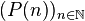 of sets, whose elements are called
of sets, whose elements are called 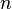 -ary operations,
-ary operations, - an element
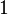 in
in 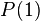 called the identity,
called the identity, - for all positive integers
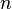 ,
, 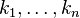
a composition function
satisfying the following coherence axioms:
- identity:
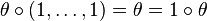
- associativity:
(the number of arguments corresponds to the arities of the operations).
Alternatively, a plain operad is a multicategory with one object.
Operad
An operad is a sequence of sets 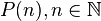 ,
with a right action * of the symmetric group
,
with a right action * of the symmetric group 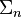 on
on 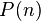 ,
an identity element in
,
an identity element in 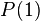 and compositions maps
and compositions maps  satisfying the above associative and identity axioms, as well as
satisfying the above associative and identity axioms, as well as
- equivariance: given permutations
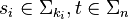 ,
,
The permutation actions in this definition are vital to most applications, including the original application to loop spaces.
A morphism of operads 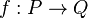 consists of a sequence
consists of a sequence
which:
- preserves the identity:
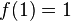
- preserves composition: for every n-ary operation
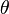 and operations
and operations 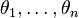 ,
,
- preserves the permutation actions:
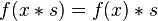 .
.
Associativity axiom
"Associativity" means that composition of operations is associative
(the function  is associative), analogous to the axiom in category theory that
is associative), analogous to the axiom in category theory that  ; it does not mean that the operations themselves are associative as operations.
Compare with the associative operad, below.
; it does not mean that the operations themselves are associative as operations.
Compare with the associative operad, below.
Associativity in operad theory means that one can write expressions involving operations without ambiguity from the omitted compositions, just as associativity for operations allows one to write products without ambiguity from the omitted parentheses.
For instance, suppose that 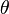 is a binary operation, which is written as
is a binary operation, which is written as 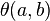 or
or 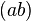 . Note that
. Note that 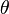 may or may not be associative.
may or may not be associative.
Then what is commonly written 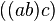 is unambiguously written operadically as
is unambiguously written operadically as 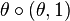 . This sends
. This sends 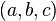 to
to 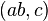 (apply
(apply 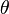 on the first two, and the identity on the third), and then the
on the first two, and the identity on the third), and then the 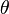 on the left "multiplies"
on the left "multiplies" 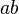 by
by  .
This is clearer when depicted as a tree:
.
This is clearer when depicted as a tree:
which yields a 3-ary operation:
However, the expression 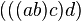 is a priori ambiguous:
it could mean
is a priori ambiguous:
it could mean 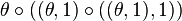 , if the inner compositions are performed first, or it could mean
, if the inner compositions are performed first, or it could mean 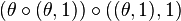 ,
if the outer compositions are performed first (operations are read from right to left).
Writing
,
if the outer compositions are performed first (operations are read from right to left).
Writing 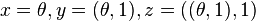 , this is
, this is 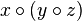 versus
versus 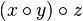 . That is, the tree is missing "vertical parentheses":
. That is, the tree is missing "vertical parentheses":
If the top two rows of operations are composed first (puts an upward parenthesis at the 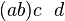 line; does the inner composition first), the following results:
line; does the inner composition first), the following results:
which then evaluates unambiguously to yield a 4-ary operation. As an annotated expression:
If the bottom two rows of operations are composed first (puts a downward parenthesis at the 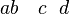 line; does the outer composition first), following results:
line; does the outer composition first), following results:
which then evaluates unambiguously to yield a 4-ary operation:
The operad axiom of associativity is that these yield the same result, and thus that the expression 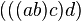 is unambiguous.
is unambiguous.
Identity axiom
The identity axiom (for a binary operation) can be visualized in a tree as:
meaning that the three operations obtained are equal: pre- or post- composing with the identity makes no difference.
Note that, as for categories, 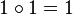 is a corollary of the identity axiom.
is a corollary of the identity axiom.
Examples
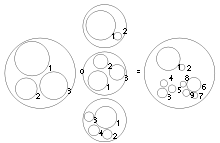

"Little something" operads
A little discs operad or, little balls operad or, more specifically, the little n-discs operad is a topological operad defined in terms of configurations of disjoint n-dimensional discs inside a unit n-disc centered in the origin of Rn. The operadic composition for little 2-discs is illustrated in the figure.[2]
Originally the little n-cubes operad or the little intervals operad (initially called little n-cubes PROPs) was defined by Michael Boardman and Rainer Vogt in a similar way, in terms of configurations of disjoint axis-aligned n-dimensional hypercubes (n-dimensional intervals) inside the unit hypercube.[3] Later it was generalized by May[4] to little convex bodies operad, and "little discs" is a case of "folklore" derived from the "little convex bodies".[5]
Associative operad
Another class of examples of operads are those capturing the structures of algebraic structures, such as associative algebras, commutative algebras and Lie algebras. Each of these can be exhibited as a finitely presented operad, in each of these three generated by binary operations.
Thus, the associative operad is generated by a binary operation 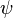 , subject to the condition that
, subject to the condition that
This condition does correspond to associativity of the binary operation 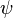 ; writing
; writing 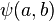 multiplicatively, the above condition is
multiplicatively, the above condition is 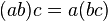 . This associativity of the operation should not be confused with associativity of composition; see the axiom of associativity, above.
. This associativity of the operation should not be confused with associativity of composition; see the axiom of associativity, above.
This operad is terminal in the category of non-symmetric operads, as it has exactly one n-ary operation for each n, corresponding to the unambiguous product of n terms: 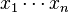 . For this reason, it is sometimes written as 1 by category theorists (by analogy with the one-point set, which is terminal in the category of sets).
. For this reason, it is sometimes written as 1 by category theorists (by analogy with the one-point set, which is terminal in the category of sets).
Terminal symmetric operad
The terminal symmetric operad is the operad whose algebras are commutative monoids, which also has one n-ary operation for each n, with each 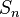 acting trivially; this triviality corresponds to commutativity, and whose n-ary operation is the unambiguous product of n-terms, where order does not matter:
acting trivially; this triviality corresponds to commutativity, and whose n-ary operation is the unambiguous product of n-terms, where order does not matter:
for any permutation 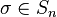 .
.
Operads in topology
In many examples the 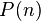 are not just sets but rather topological spaces. Some names of important
examples are the little n-disks, little n-cubes, and linear isometries operads. The idea behind the
little n-disks operad comes from homotopy theory, and the idea is that an element of
are not just sets but rather topological spaces. Some names of important
examples are the little n-disks, little n-cubes, and linear isometries operads. The idea behind the
little n-disks operad comes from homotopy theory, and the idea is that an element of 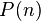 is an arrangement of n disks within the unit disk. Now, the identity is the unit disk as a subdisk of itself, and composition of arrangements is by scaling the unit disk down into the disk that corresponds to the slot in the composition, and inserting the scaled contents there.
is an arrangement of n disks within the unit disk. Now, the identity is the unit disk as a subdisk of itself, and composition of arrangements is by scaling the unit disk down into the disk that corresponds to the slot in the composition, and inserting the scaled contents there.
Operads from the symmetric and braid groups
There is an operad for which each 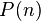 is given by the symmetric group
is given by the symmetric group 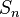 . The composite
. The composite 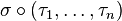 permutes its inputs in blocks according to
permutes its inputs in blocks according to 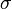 , and within blocks according to the appropriate
, and within blocks according to the appropriate 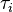 . Similarly, there is an operad for which each
. Similarly, there is an operad for which each 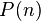 is given by the Artin braid group
is given by the Artin braid group 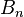 .
.
Linear algebra
In linear algebra, one can consider vector spaces to be algebras over the operad 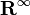 (the infinite direct sum, so only finitely many terms are non-zero; this corresponds to only taking finite sums), which parametrizes linear combinations: the vector
(the infinite direct sum, so only finitely many terms are non-zero; this corresponds to only taking finite sums), which parametrizes linear combinations: the vector 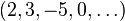 for instance corresponds to the linear combination
for instance corresponds to the linear combination
Similarly, one can consider affine combinations, conical combinations, and convex combinations to correspond to the sub-operads where the terms sum to 1, the terms are all non-negative, or both, respectively. Graphically, these are the infinite affine hyperplane, the infinite hyper-octant, and the infinite simplex. This formalizes what is meant by 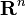 being or the standard simplex being model spaces, and such observations as that every bounded convex polytope is the image of a simplex. Here suboperads correspond to more restricted operations and thus more general theories.
being or the standard simplex being model spaces, and such observations as that every bounded convex polytope is the image of a simplex. Here suboperads correspond to more restricted operations and thus more general theories.
This point of view formalizes the notion that linear combinations are the most general sort of operation on a vector space – saying that a vector space is an algebra over the operad of linear combinations is precisely the statement that all possible algebraic operations in a vector space are linear combinations. The basic operations of vector addition and scalar multiplication are a generating set for the operad of all linear combinations, while the linear combinations operad canonically encode all possible operations on a vector space.
See also
Notes
- ↑ http://www.math.uchicago.edu/~may/PAPERS/mayi.pdf Page 2
- ↑ Giovanni Giachetta, Luigi Mangiarotti, Gennadi Sardanashvily (2005) Geometric and Algebraic Topological Methods in Quantum Mechanics, ISBN 981-256-129-3, pp. 474,475
- ↑ Axiomatic, Enriched and Motivic Homotopy Theory by J. P. C. Greenlees (2004) ISBN 1-4020-1834-7, pp. 154–156
- ↑ J. P. May, "Infinite loop space theory", Bull. Amer. Math. Soc. 83 (1977), 456–494.
- ↑ Jim Stasheff, "Grafting Boardman's Cherry Trees to Quantum Field Theory", 31 March 1998, arXiv:math/9803156v1
References
- Boardman, J. M.; Vogt, R. M. (1973). Homotopy Invariant Algebraic Structures on Topological Spaces. Lecture Notes in Mathematics 347. Springer-Verlag. ISBN 3-540-06479-6.
- Tom Leinster (2004). Higher Operads, Higher Categories. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-53215-9.
- Martin Markl, Steve Shnider, Jim Stasheff (2002). Operads in Algebra, Topology and Physics. American Mathematical Society. ISBN 0-8218-4362-1.
- J. P. May (1972). The Geometry of Iterated Loop Spaces. Springer-Verlag. ISBN 3-540-05904-0.
- Markl, Martin (June 2006). "Operads and PROPs". arXiv:math/0601129 [math].
- Stasheff, Jim (June–July 2004). "What Is...an Operad?" (PDF). Notices of the American Mathematical Society 51 (6): pp.630–631. Retrieved 2008-01-17.
- Loday, Jean-Louis; Vallette, Bruno (2012), Algebraic Operads (PDF), Grundlehren der Mathematischen Wissenschaften 346, Berlin, New York: Springer-Verlag, ISBN 978-3-642-30361-6
- Zinbiel, Guillaume W. (2012), "Encyclopedia of types of algebras 2010", in Bai, Chengming; Guo, Li; Loday, Jean-Louis, Operads and universal algebra, Nankai Series in Pure, Applied Mathematics and Theoretical Physics 9, pp. 217–298, ISBN 9789814365116, Zinbiel is a pseudonym of Jean-Louis Loday