Ontario Highway 90
| ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | ||||||||||
| Route information | ||||||||||
| Maintained by the Ministry of Transportation of Ontario | ||||||||||
| Length: | 19.0 km[1] (11.8 mi) | |||||||||
| Existed: | October 6, 1937[2] – January 1, 1998[3] | |||||||||
| Major junctions | ||||||||||
| West end: |
Camp Borden Road in Angus (continues south as Simcoe County Road 10) | |||||||||
| Highway 131 | ||||||||||
| East end: |
| |||||||||
| Location | ||||||||||
| Major cities: | Barrie | |||||||||
| Towns: | Angus | |||||||||
| Highway system | ||||||||||
<td width="100%" align=center" colspan="3" style="padding:0;vertical-align:middle;text-align:center">Current highways
| ||||||||||
King's Highway 90, commonly referred to as Highway 90, was a provincially maintained highway in the Canadian province of Ontario. The route connected Barrie with the town of Angus and CFB Borden. The highway was designated in 1937. During the early 1960s, the highway was realigned within Barrie in order to have it interchange with Highway 400; originally the route followed Tiffin Street. At the beginning of 1998, the entire highway was transferred to the City of Barrie and Simcoe County; it is now known as Simcoe County Road 90.
Route description

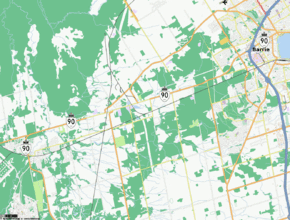
Today, the former routing of Highway 90 is known as Dunlop Street within Barrie and Simcoe County Road 90 outside of the city.[4] The route begins at a split between Cambrai Road, which provides access to Camp Borden, and Simcoe County Road 10, which continues south to Alliston and Tottenham.[5] The four lane Simcoe County Road 90 progresses north through the centre of Angus. North of the Barrie Collingwood Railway overhead, it acts as the principal commercial strip for the town.[6] North of Angus, the highway makes a broad 90 degree turn to the east and skims the southern edge of the Minesing Wetlands, an internationally significant bog.[7]
East of the swamp, the road enters Essa, where it intersects the Sunnidale Road (Simcoe County Road 40). From there to Barrie, the highway passes through a largely rural area. It intersects former Highway 131, now Simcoe County Road 27, then enters Barrie at Miller Drive, curving northeast. East of Ferndale Drive, the route crosses Highway 400 at Exit 96.[5] Shortly thereafter, as it approaches the waterfront of Kempenfelt Bay, the route ends at High Street in downtown Barrie.[1]
Simcoe County Road 90 is two lanes wide between McKinnon Road, north of Angus, and Ferndale Drive in Barrie, although a passing lane is provided for eastbound traffic between Angus and Essa. The road also widens to four lanes briefly at the junction with former Highway 131 west of Barrie, as well as within the city and within Angus. The land use surrounding the route is mixed, with pastures and forests composing the majority of the setting. Residences and small businesses are also scattered throughout the length of the route.[6]
History
Highway 90 was originally assumed by the Department of Highways (DHO), the predecessor to today's Ministry of Transportation of Ontario (MTO), during the late 1930s. The primary purpose for the highway was to connect the CFB Borden military base at Angus with the main north–south routes of central Ontario. At that time, these were Highway 27 and Highway 11. On October 6, 1937, the DHO designated the Barrie to Angus Road as King's Highway 90.[2] The initially unimproved road was paved shortly after the outbreak of World War II; a contract was awarded to Brennan Paving of Hamilton during the autumn of 1939,[8] and work completed by the end of the year.[9]
Initially, Highway 90 followed Tiffin Street through Barrie, ending just short of the waterfront of Kempenfelt Bay at the intersection of Essa Street (Highway 27) and Bradford Street (Highway 11/27).[10] However, during the early 1960s the route was modified so as to provide an interchange with Highway 400. A new interchange was constructed during the late 1950s at what was then known as Elizabeth Street in order to provide better access to downtown Barrie from the freeway. By 1960, Highway 90 had been rerouted northwest along Ferndale Drive and northeast along Elizabeth Street. Though it still ended at Bradford Street, it intersected it 1.5 kilometres (0.93 mi) to the north.[11] By 1961, Elizabeth Street was renamed as Dunlop Street West.[12] By 1964, Dunlop Street was extended southwest of Ferndale Drive to merge with Tiffin Street at Miller Drive (the present city limits).[13]

The highway remained unchanged for over three decades, with the exception of a Connecting Link agreement established between the MTO and the City of Barrie.[1] However, during the late 1990s, the MTO transferred many highways to lower levels of government as a cost-cutting measure. Highway 90 was transferred to Simcoe County on January 1, 1998.[3] The Connecting Link through Barrie was also discontinued. Simcoe County has since renamed its portion of the route as Simcoe County Road 10.[6]
Major intersections
The following table lists the major junctions along Highway 90, as noted by the Ministry of Transportation of Ontario.[1]
| Division | Location | km[1] | mi | Destinations | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Simcoe | Angus | 0.0 | 0.0 | Roadway continues south as Camp Borden Road | |
| 1.8 | 1.1 | ||||
| Essa–Springwater | 7.4 | 4.6 | County Road 56 south | ||
| 12.1 | 7.5 | ||||
| 13.9 | 8.6 | Former Highway 131 south | Now Simcoe County Road 27 | ||
| Essa–Barrie | 14.9 | 9.3 | Barrie city limits; beginning of Connecting Link agreement | ||
| Barrie | |||||
| 17.4 | 10.8 | Exit 96 | |||
| 19.0 | 11.8 | End of Connecting Link agreement | |||
| 1.000 mi = 1.609 km; 1.000 km = 0.621 mi | |||||
References
- Footnotes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 Provincial Highways Distance Table. Ministry of Transportation of Ontario. 1989. p. 80. ISSN 0825-5350.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 "Appendix 3 - Schedule of Assumptions and Reversions of Sections". Annual Report (Report). Department of Highways. March 31, 1938. p. 81.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Highway Transfers List - “Who Does What” (Report). Ministry of Transportation of Ontario. June 20, 2001. p. 14.
- ↑ Transportation and Engineering Department (2005). County Road System (PDF) (Map). Simcoe County. Retrieved September 22, 2011.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Mapart (2010). Ontario Back Road Atlas (Map). Peter Heiler Ltd. pp. 13, 20, 26, 38–39. § Z10–T19. ISBN 978-1-55198-226-7.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 Google (September 7, 2014). "Highway 90 length and route" (Map). Google Maps. Google. Retrieved September 7, 2014.
- ↑ "The Annotated Ramsar List of Wetlands of International Importance - Canada". Ramsar Convention Bureau. Archived from the original on July 15, 2007. Retrieved September 24, 2011.
- ↑ Contracts Awarded. The Canadian Engineer 77 (15) (Monetary Times Print). October 10, 1939. p. 17. Retrieved September 24, 2011.
- ↑ Annual Report (Report). Department of Highways. March 31, 1940. p. 18.
- ↑ Ontario Road Map (Map). Cartography by C.P. Robins. Ontario Department of Highways. 1938–39. § K7.
- ↑ Ontario Road Map (Map). Cartography by C.P. Robins. Ontario Department of Highways. 1960. Barrie inset.
- ↑ Ontario Road Map (Map). Cartography by C.P. Robins. Ontario Department of Highways. 1961. Barrie inset.
- ↑ Ontario Road Map (Map). Cartography by C.P. Robins. Ontario Department of Highways. 1964. Barrie inset.
Route map: Bing
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
