Oil and gas industry in New Zealand

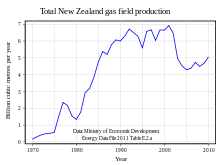
The oil and gas industry in New Zealand explores and develops oil and gas fields, and produces petroleum products and natural gas.
In 2008, New Zealand's self-sufficiency in oil (production divided by consumption) was 47%, i.e. the country imports over half its petroleum product needs (though actual imports are higher, as some of the local product is also exported).[1] In the March 2010 quarter, 28.7 petajoules of crude were produced in New Zealand, 78 pj of petroleum products imported (most of it crude), and 61.6 pj consumed. The difference is exported or used for international travel (aviation fuel and similar).[2]
Oil and gas are produced from 21 petroleum licenses / permits, all in the Taranaki basin.[3] The most important fields are Kapuni, Maui, Pohokura and Kupe. Exploration for oil and gas reserves includes the Great South Basin and offshore areas near Canterbury and Gisborne.
New Zealand has one oil refinery, the Marsden Point Oil Refinery. The major industry body is the Petroleum Exploration and Production Association of New Zealand.
New Zealand has one underground gas storage facility, the Ahuroa Gas Storage Facility.
History
In 1865, the Alpha well was drilled near Mikotahi at New Plymouth.[4] This was the first oil well in what is now the Commonwealth and one of the first in the world. A petroleum industry developed at Moturoa, including producing wells and refineries. The last refinery there was closed in 1972. The field continues to produce small quantities of oil.[5]
Oil and gas fields

Proven and probable (P50) reserves, ultimate and remaining, as at 1 January 2011[1]
Producing fields
| Field | Ultimate oil recoverable (mmbbls) |
Remaining oil reserves (mmbbls) |
Ultimate gas recoverable (PJ) |
Remaining gas reserves (PJ) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maui | 158 | 4 | 3,962 | 101 |
| Kapuni | 68 | 4 | 1,098 | 169 |
| Pohokura | 57 | 38 | 1,185 | 891 |
| Maari | 58 | 46 | ||
| Kupe | 32 | 29 | 287 | 254 |
| Tui | 51 | 21 | ||
| Turangi | 7 | 6 | 193 | 168 |
| Kowhai | 5 | 5 | 160 | 151 |
| Mangahewa | 5 | 4 | 237 | 175 |
| Ngatoro | 13 | 4 | 65 | 37 |
| McKee | 48 | 1 | 226 | 50 |
| Others | 32 | 3 | 175 | 23 |
| Total | 534 | 166 | 7,587 | 2,021 |
Non-producing fields
| Field | Estimated oil recoverable (mmbbls) |
Estimated gas recoverable (PJ) |
|---|---|---|
| Radnor | 0.9 | 5 |
| Total | 0.9 | 5 |
See also
- Energy in New Zealand
- Oil and gas companies in New Zealand
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Energy Data File. MED. July 2011.
- ↑ "New Zealand Energy Quarterly, March 2010". 16 June 2010. Retrieved 8 July 2010.
- ↑ "Petroleum Overview". Crown Minerals, Ministry of Economic Development. 26 June 2008.
- ↑ Lambert, Ron (1995). In Crude State - a History of the Moturoa Oilfield New Plymouth. Methanex New Zealand. ISBN 0-473-03428-X.
- ↑ "Moturoa black gold - "the good oil"". Puke Ariki. 19 November 2004. Retrieved 2009-07-25.