Octane
| | |
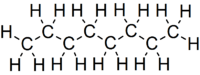 | |
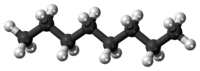 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Octane[1] | |
| Identifiers | |
| 3DMet | B00281 |
| 1696875 | |
| 111-65-9 | |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:17590 |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL134886 |
| ChemSpider | 349 |
| DrugBank | DB02440 |
| EC number | 203-892-1 |
| 82412 | |
| |
| Jmol-3D images | Image |
| KEGG | C01387 |
| MeSH | octane |
| PubChem | 356 |
| RTECS number | RG8400000 |
| |
| UN number | 1262 |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula |
C8H18 |
| Molar mass | 114.23 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colorless liquid |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Density | 0.703 g cm−3 |
| Melting point | −57.1 to −56.6 °C; −70.9 to −69.8 °F; 216.0 to 216.6 K |
| Boiling point | 125.1 to 126.1 °C; 257.1 to 258.9 °F; 398.2 to 399.2 K |
| 0.007 mg dm−3 (at 20°C) | |
| log P | 4.783 |
| Vapor pressure | 1.47 kPa (at 20.0 °C) |
| Henry's law constant (kH) |
29 nmol Pa−1 kg−1 |
| Refractive index (nD) |
1.398 |
| Viscosity | 542 μPa s (at 20 °C) |
| Thermochemistry | |
| Specific heat capacity (C) |
255.68 J K−1 mol−1 |
| Std molar entropy (S |
361.20 J K−1 mol−1 |
| Std enthalpy of formation (ΔfH |
−252.1–−248.5 kJ mol−1 |
| Std enthalpy of combustion (ΔcH |
−5.53–−5.33 MJ mol−1 |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |     |
| GHS signal word | DANGER |
| H225, H304, H315, H336, H410 | |
| P210, P261, P273, P301+310, P331 | |
| EU Index | 601-009-00-8 |
| EU classification | |
| R-phrases | R11, R38, R50/53, R65, R67 |
| S-phrases | (S2), S16, S29, S33 |
| NFPA 704 | |
| Flash point | 13.0 °C (55.4 °F; 286.1 K) |
| 220.0 °C (428.0 °F; 493.1 K) | |
| Explosive limits | 0.96–6.5% |
| Related compounds | |
| Related alkanes |
|
| Except where noted otherwise, data is given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Octane is a hydrocarbon and an alkane with the chemical formula C8H18, and the condensed structural formula CH3(CH2)6CH3. Octane has many structural isomers that differ by the amount and location of branching in the carbon chain. One of these isomers, 2,2,4-trimethylpentane (isooctane) is used as one of the standard values in the octane rating scale.
Octane is a component of gasoline (petrol). As with all low molecular weight hydrocarbons, octane is volatile and very flammable.
Use of the term in gasoline
"Octane" is colloquially used as a short form of "octane rating" (an index of a fuel's ability to resist engine knock at high compression ratios, which is a characteristic of octane's branched-chain isomers, especially isooctane), particularly in the expression "high octane." However, components of gasoline other than isomers of octane can also contribute to a high octane rating, while some isomers of octane can lower it, and n-octane itself has a negative octane rating.[2]
Metaphorical use
Octane became well known in American popular culture in the mid- and late 1960s, when gasoline companies boasted of "high octane" levels in their gasoline advertisements.
These commercials disappeared by the time of the 1973 Oil Crisis, which spared gasoline companies the need to compete in advertising. "Octane" was rarely cited in non-technical contexts over the next two decades.
The compound adjective "high-octane" is recorded in a figurative sense from 1944.[3] By the mid-1990s, the phrase was commonly being used as an intensifier and has found a place in modern English vernacular.
"Octane" is a slang term for trihexyphenidyl, because of its similarity to its trade name Artane.
Isomers
Octane has 18 structural isomers (24 including stereoisomers):
- Octane (n-octane)
- 2-Methylheptane
- 3-Methylheptane (2 enantiomers)
- 4-Methylheptane
- 3-Ethylhexane
- 2,2-Dimethylhexane
- 2,3-Dimethylhexane (2 enantiomers)
- 2,4-Dimethylhexane (2 enantiomers)
- 2,5-Dimethylhexane
- 3,3-Dimethylhexane
- 3,4-Dimethylhexane (2 enantiomers + 1 meso compound)
- 3-Ethyl-2-methylpentane
- 3-Ethyl-3-methylpentane
- 2,2,3-Trimethylpentane (2 enantiomers)
- 2,2,4-Trimethylpentane (isooctane)
- 2,3,3-Trimethylpentane
- 2,3,4-Trimethylpentane
- 2,2,3,3-Tetramethylbutane
References
- ↑ "octane - Compound Summary". PubChem Compound. USA: National Center for Biotechnology Information. 16 September 2004. Identification and Related Records. Retrieved 6 January 2012.
- ↑ eejit's guides – Octane ratings explained
- ↑ Oxford English Dictionary.
External links
- International Chemical Safety Card 0933
- "NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards #0470". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- Dr. Duke's Phytochemical and Ethnobotanical Databases, Octane, http://www.ars-grin.gov/cgi-bin/duke/chemical.pl?OCTANE
| ||||||||||
