Nyctiphruretus
| Nyctiphruretus Temporal range: Guadalupian | |
|---|---|
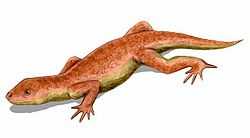 | |
| Nyctiphruretus acudens | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Reptilia |
| Order: | †Procolophonomorpha |
| Suborder: | †Nyctiphruretia Lee, 1997 |
| Family: | †Nyctiphruretidae Lee, 1997 |
| Genus: | †Nyctiphruretus Efremov, 1938 |
| Species | |
Nyctiphruretus (Guardian of the Night) is an extinct genus of ankyramorph parareptile known from the Guadalupian series (middle Permian) of European Russia.[1][2]
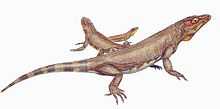
Many fossils of the type species, N. acudens, were found well preserved near the Mezen River of European Russia in various stages of growth. The dentition identified that Nyctiphruretus is a herbivore. Based on the large numbers of individuals found and the sediment that they were found in, it appears that their diet consisted of aquatic plants. Adults discovered averaged 36 cm in length with a 4.4 cm skull that was crushed but recognisable. Nyctiphruretus was first named by Efremov in 1938 and the type species is Nyctiphruretus acudens. In 2002, a second species was named by V. V. Bulanov.[1] N. optabilis is known from a single jaw, also from Russia, Eastern Europe.[3]
Lee (1997) named the order Nyctiphruretia and the family Nyctiphruretidae, to include Nyctiphruretus. While the family was defined to be monotypic, the order was defined to include both nyctiphruretids and nycteroleterids.[4] However, recent cladistic analyses suggest that nycteroleterids are more closely related to the Pareiasauria.[1][5] Therefore, Nyctiphruretus is currently the only known genus of its order.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Laura K. Säilä (2010). "The phylogenetic position of Nyctiphruretus acudens, a parareptile from the Permian of Russia". Journal of Iberian Geology 36 (2): 123–143. doi:10.5209/rev_JIGE.2010.v36.n2.2. ISSN 1698-6180.
- ↑ Marcello Ruta, Juan C. Cisneros, Torsten Liebrect, Linda A. Tsuji and Johannes Muller (2011). "Amniotes through major biological crises: faunal turnover among Parareptiles and the end-Permian mass extinction". Palaeontology 54 (5): 1117–1137. doi:10.1111/j.1475-4983.2011.01051.x.
- ↑ V. V. Bulanov (2002). "New data on procolophons from the Permian of Eastern Europe". Paleontological Journal 36: 525–530.
- ↑ M. S. Y. Lee (1997). "Pareiasaur phylogeny and the origin of turtles". Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society 120: 197–280. doi:10.1111/j.1096-3642.1997.tb01279.x.
- ↑ Linda A. Tsuji, Johannes Müller and Robert R. Reisz (2012). "Anatomy of Emeroleter levis and the Phylogeny of the Nycteroleter Parareptiles". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology 32 (1): 45–67. doi:10.1080/02724634.2012.626004.