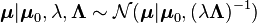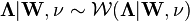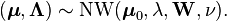Normal-Wishart distribution
| Notation |
 |
|---|---|
| Parameters |
 location (vector of real) location (vector of real)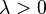 (real) (real)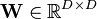 scale matrix (pos. def.) scale matrix (pos. def.)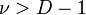 (real) (real) |
| Support |
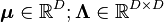 covariance matrix (pos. def.) covariance matrix (pos. def.) |
 |
In probability theory and statistics, the normal-Wishart distribution (or Gaussian-Wishart distribution) is a multivariate four-parameter family of continuous probability distributions. It is the conjugate prior of a multivariate normal distribution with unknown mean and precision matrix (the inverse of the covariance matrix).[1]
Definition
Suppose
has a multivariate normal distribution with mean 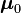 and covariance matrix
and covariance matrix  , where
, where
has a Wishart distribution. Then  has a normal-Wishart distribution, denoted as
has a normal-Wishart distribution, denoted as
Characterization
Probability density function
Properties
Marginal distributions
By construction, the marginal distribution over 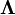 is a Wishart distribution, and the conditional distribution over
is a Wishart distribution, and the conditional distribution over 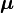 given
given 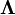 is a multivariate normal distribution. The marginal distribution over
is a multivariate normal distribution. The marginal distribution over 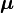 is a multivariate t-distribution.
is a multivariate t-distribution.
Generating normal-Wishart random variates
Generation of random variates is straightforward:
- Sample
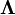 from a Wishart distribution with parameters
from a Wishart distribution with parameters 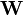 and
and 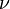
- Sample
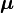 from a multivariate normal distribution with mean
from a multivariate normal distribution with mean 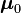 and variance
and variance 
Related distributions
- The normal-inverse Wishart distribution is essentially the same distribution parameterized by variance rather than precision.
- The normal-gamma distribution is the one-dimensional equivalent.
- The multivariate normal distribution and Wishart distribution are the component distributions out of which this distribution is made.
Notes
- ↑ Bishop, Christopher M. (2006). Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning. Springer Science+Business Media. Page 690.
References
- Bishop, Christopher M. (2006). Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning. Springer Science+Business Media.