Nizhny Novgorod Metro
 | |||
|
A type 81-717/714 train at Moskovskaya station | |||
| Overview | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Native name |
Нижегородский метрополитен Nizhegorodsky metropoliten | ||
| Locale | Nizhny Novgorod, Russia | ||
| Transit type | Rapid transit | ||
| Number of lines | 2 | ||
| Number of stations | 14[1] | ||
| Daily ridership | 109,500 (daily, 2013)[2] | ||
| Website | Nizhny Novgorod Metro | ||
| Operation | |||
| Began operation | 1985 | ||
| Technical | |||
| System length | 18.8 km (11.7 mi)[1] | ||
| |||
The Nizhny Novgorod Metro (Russian: Нижегородское метро), formerly known as Gorky Metro (Russian: Горьковское Метро) is a rapid-transit system that serves the city of Nizhny Novgorod, Russia. Opened in 1985, it consists of 14 stations[1] and is 18.8 kilometres (11.7 mi) long.[1]
History
Nizhny Novgorod (known in the Soviet times as Gorky) is a large city on the middle Volga. In the mid 1970s the population of the place exceeded a million thus meeting the Soviet requirements to develop a rapid-transit system. Construction began on December 17, 1977 and the network was opened to the public on November 20, 1985 becoming the third such system in Russia, and the tenth in the former Soviet Union.
City layout
Unlike other Soviet time Metros, Nizhny Novgorod does not feature the traditional triangle layout of three line, six radii intersecting under city centre. This is because of the unusual layout of the city. Nizhny Novgorod is located on the right bank of the Volga River, and at the confluence of the Oka River. Over the 20th century, the city developed in a polycentric manner. The historical city centre, including the Nizhny Novgorod Kremlin bears most of administrative, cultural and educational functions and is located on the high hilly right bank of the Oka, whilst the low flat left bank hosts city's most industries and some major residential districts grouped around the three centers in Kanavino (where the city's central railway station and the largest urban transport hubs are located), Sormovo (with the largest industry being the Krasnoye Sormovo plant) and Avtozavod (GAZ).


Metro layout
Faced with such a physical dislocation, the planners adopted a design that would feature two lines with four radii opened in a series of stages (and each stage in segments). The main hub of the system, the Moskovskaya Station, located next to Nizhny Novgorod's main railway station, would feature a four track two island platform arrangement offering a cross-platform transfer.
- Stage 1
The first stage would be Avtozavodskaya Line, following south along the left bank of the Oka, through residential and industrial zones of Leninsky district, the massive GAZ automobile plant and into the Avtozavod residential districts.
- Stage 2
The second stage would be the Sormovskaya Line which would go from Moskovskaya west into the Sormovo districts.
- Stage 3
The third stage would feature a combined auto and Metro bridge across the Oka taking the Avtozavodskaya into the city centre.
- Stage 4
The fourth and final stage would be the Sormovskaya passing into the Meshcherskoye Ozero residential area north-west of the Railway station, on the bank of the Volga. All of this would be finished by the late 1990s and the system would be a total of 25 kilometres long with above 20 stations.
- Order of opening
The order in which the stages was opened was influenced by the industry-centric flows of passengers of the Soviet period, and the depot placement issue. Cross-river traffic used not to be as intense as it is today. GAZ was not only the dominating employer of the Avtozavodsky district, but also consumed a lot of workforce from the Northern parts of the city. The only suitable plot for the train depot was found near the automobile plant, too.
Dissolution of the Soviet Union
Whilst the pace of Metro construction in the Soviet Union was impressive, it did not, and could not foresee the events that would happen when the Soviet Union dissolved and how the financial and social implications would make the Nizhny Novgorod Metro a system with a very difficult future. So, when the first stage was completed in 1989, construction began on the second one...and that was the state in which the Gorky Metro embraced the 1990s. The dissolution of the Soviet Union had devastating effects on the economy and people's lives. Aided with a hyperinflation, almost all funding of expansion of Metros, save Moscow and Saint Petersburg was cut. Those segments that did open in the early 1990s were mostly completed already and the bankrupt companies and workers struggled to finish them off. In late 1993 the first two station segment of the Sormovskaya Line was opened in Nizhny Novgorod.
Timeline
| Segment | Date opened | Length |
|---|---|---|
| Moskovskaya - Proletarskaya | November 20, 1985 | 7.8 km |
| Proletarskaya - Komsomolskaya | August 8, 1987 | 2.4 km |
| Komsomolskaya - Park Kultury | November 15, 1989 | 2.2 km |
| Moskovskaya - Burnakovskaya | December 20, 1993 | 2.6 km |
| Burnakovskaya - Burevestnik | September 9, 2002 | 1.3 km |
| Moskovskaya - Gorkovskaya | November 4, 2012 | 3.5 km |
| Total: | 14 stations | 18.9 km |
Lines
| Livery and # | Name | Name in Cyrillic script | Date of first station opening | Most recent station opening | Length (km) | Number of stations | Ride time (end stn. to end stn.) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Line 1 (Avrozavodskaya) |
Линия 1 (Автозаводская) |
20 November 1985 | 4 November 2012 | 15.1 | 11 | 18 minutes | |
| Line 2 (Sormovskaya) |
Линия 2 (Сормовская) |
20 November 1985 | 9 September 2002 | 3.8 | 4 | 8 minutes | |
| Total: | 18.9 | 14 | |||||
Operation
| Nizhny Novgorod Metro | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Legend | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||


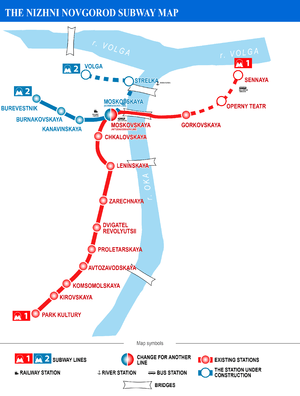
The Nizhny Novgorod Metro has two lines and 14 stations.
All but one of the thirteen stations are underground, and all are shallow level designs. Moskovskaya is the former USSR's unique pillar-fivespan, Chkalovskaya, Leninskaya, Park Kultury and Kanaviskaya are the standard single-vaults, and the rest are the standard pillar-trispans. The station Burevestnik is an exception as it is a surface station with side-platform layout.
The rolling stock of the Metro is provided by the Proletarskoye depot and a total of 80 81-717/714 models are in use. The length of each train is four cars long. Thus formally it is possible to make 20 trains, however there are never that many in operation, and the train interval is about 7½–8 min long in midday.
Future
Gorkovskaya station – the first station on the right bank of Oka – was opened in November 2012 , allowing the Nizhny Novgorod Metro to become the transport artery that it was designed to be.
Before 2012 extension the biggest problem was that despite being the longest of its "new" Russian Metro rivals (new refers to Novosibirsk, Samara and Yekaterinburg) it had a passenger traffic that was one of the lowest – 16.8 million annual ridership in 2004. For comparison, the Novosibirsk system was almost double that.
The root of this problem was not the layout but the Soviet priorities on stage openings, over the past decade, the new Russian population's social structure greatly changed. Many chose to abandon the factories and, particularly the younger generation, in favour of a career in commerce. For Nizhny Novgorod this had a great effect on the daily transport pattern, where the city centre became a nexus for the region's business. Many agree that it was a grave mistake not to link up the two banks of the Oka river prior to continuing the expansion into the residential districts.
Construction of Metrobridge began in 1995. It was built in November 2009.
After extension to the historical centre of the city, there are three major suggestions for further development:
1. Extension of Sormovskaya Line with construction of station Strelka, it will be constructed near planned new Stadium for 2018 FIFA World Cup.
2. Extension of Sormovskaya Line to Sormovo. At present Sormovoskaya Line is quite a mess. Neither the first segment of the line, nor its one extension to a surface station — Burevestnik actually reach Sormovo proper and ends amid an industrial zone. Many commuters thus choose not to use the Metro altogether as they would be forced to switch to land transport anyway. It was chosen to use part of the surface railway's tracks for completion of the line. The northern extension of the Sormovskaya Line began at the same time when the station pit was dug up for the future Yarmarka station, but since it has been disbanded and covered up.
3. Eastern extension of the line in the city centre with construction of stations Operny teatr (Opera house) and Sennaya. Still there is fear that the first station on the right bank — Gorkovskaya would not be able to deal with the massive passenger traffic, meaning that the right bank will have to open with several stations.
See also
- List of Nizhny Novgorod metro stations
- List of rapid transit systems
References
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Nizhny Novgorod Metro. |
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 МЕТРОПОЛИТЕНЫ РОССИИ за 2012 год [METROS of Russia in 2012]. Новосибирский метрополитен (in Russian). Novosibirsk metro. 2012. Retrieved 2013-09-03.
- ↑ "Основные технико-эксплуатационные характеристики метрополитенов за 2013 год" (PDF). международная ассоциация «Метро». Retrieved 2014-04-19.
External links
- Urbanrail.net
- (Russian) Metroworld site - Extensive information
- (Russian) Metrowalks - Extensive image collection and station description
- Nizhny Novgorod Metro Travel and business guide to Nizhny Novgorod
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
_(6584679035).jpg)