Nitrophenol

Preparation of 2- and 4-nitrophenol by steam distillation. 2-nitrophenol is yellow, 4-nitrophenol is brown.
Nitrophenols are a family of nitrated phenols with the formula HOC6H4NO2. Three isomeric nitrophenols exist:
- o-Nitrophenol (1-hydroxy-2-nitrobenzene; OH and NO2 groups are neighboring; CAS number: 88-75-5), a yellow crystalline solid (m.p. 46 °C).
- m-Nitrophenol (1-hydroxy-3-nitrobenzene, CAS number: 554-84-7), a yellow solid (m.p. 97 °C) and precursor to the drug mesalazine (5-aminosalicylic acid).
- p-Nitrophenol (1-hydroxy-4-nitrobenzene, CAS number: 100-02-7), yellow crystals (m.p. 114 °C). It is a precursor to the rice herbicide fluorodifen and the pesticide parathion.
The nitrophenols are produced industrially by the reaction of chlorides with sodium hydroxide at temperatures around 200 °C. The mononitrated phenols are often hydrogenated to the corresponding aminophenols that are also useful industrially.[1]
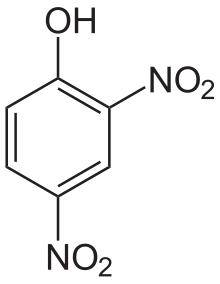
Di- and trinitrophenols
2,4-Dinitrophenol (m.p. 83 °C) is a moderately strong acid (pKa = 4.89). 2,4,6-trinitrophenol is better known as picric acid, which has a well-developed chemistry.
Safety
Nitrophenols are poisonous. Occasionally, nitrophenols contaminate the soil near former explosives or fabric factories and military plants, and current research is aimed at remediation.
References
- ↑ Gerald Booth "Nitro Compounds, Aromatic" in "Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry" 2007; Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. doi:10.1002/14356007.a17_411