New Zealand parrot
| New Zealand parrot | |
|---|---|
 | |
| New Zealand kaka, North Island subspecies (Nestor meridionalis septentrionalis) at Auckland Zoo, New Zealand | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Psittaciformes |
| Superfamily: | Strigopoidea Bonaparte, 1849 |
| Families | |
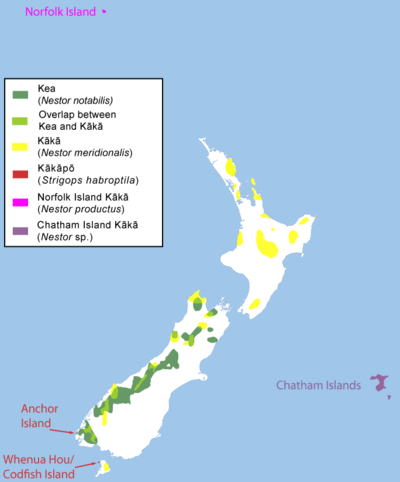
The New Zealand parrot superfamily (Strigopoidea)[1] consists of three genera of parrots, Nestor, Strigops and the fossil Nelepsittacus.[2][3] The genus Nestor consists of the kea, kaka, Norfolk Island kaka and Chatham Island kaka,[4][5] while the genus Strigops contains the iconic kākāpō.[4] All extant species are endemic to New Zealand. The species of the genus Nelepsittacus were endemics of the main islands, while the two extinct species of the genus Nestor were found at the nearby oceanic islands like Chatham Island of New Zealand, and Norfolk Island and Phillip Island of Australia. The modern common species names, kea, kākā and kākāpō, are the same as the original Māori names.[6]
The Norfolk kaka and the Chatham kaka have become extinct in recent times,[5][7] while the extinct species of the genus Nelepsittacus have been extinct for 16 million years. All extant species, the kākāpō, kea, and the two subspecies of the kākā, are threatened.[8][9][10] Human activity caused the two extinctions and the decline of the other three species. Settlers introduced invasive species, such as pigs and possums, which eat the eggs of ground nesting birds, and additional declines have been caused by hunting for food, killing as agricultural pests, habitat loss, and introduced wasps.[11][12][13]
The family diverged from the other parrots around 82 million years ago when New Zealand broke off from Gondwana, while the ancestors of the genera Nestor and Strigops diverged from each other between 60 and 80 million years ago.[14][15]
Systematics
No consensus existed regarding the taxonomy of Psittaciformes until recently. Consequently, the placement of the Strigopoidea species has been variable in the past.[16] This superfamily is one of three superfamilies in the order Psittaciformes; the other two families are Cacatuoidea (cockatoos) and Psittacoidea (true parrots).[17] The family is subdivided in two families, Nestoridae with two genera (Nestor and Nelepsittacus) and Strigopidae with a single genus, (Strigops). Traditionally, the species of the superfamily Strigopoidea were placed in the superfamily Psittacoidea, but several studies confirmed the unique placement of this group at the base of the parrot tree.[14][17][18][19] Most authors now recognize this group as its own taxon.[2][17][20] with two separate families: Nestoridae and Strigopidae.[17][21]
Phylogeography
A hypothesis for the phylogeography of this group has been proposed and this provides a nice example of various speciation mechanisms at work. In this scenario, ancestors of this group became isolated from the remaining parrots when New Zealand broke away from Gondwana about 82 million years ago, resulting in a physical separation of the two groups.[14][15] This mechanism is called allopatric speciation. Over time, ancestors of the two surviving genera, Nestor and Strigops, adapted to different ecological niches. This led to reproductive isolation, an example of ecological speciation.[15] In the Pliocene, around five million years ago, the formation of the Southern Alps diversified the landscape and provided new opportunities for speciation within the genus Nestor. Around three million years ago, two lineages adapted to high altitude and low altitude, respectively. The high altitude lineage gave rise to the modern kea, while the low altitude lineage gave rise to the various kākā species.[15] Island species diverge rapidly from mainland species once a few vagrants arrive at a suitable island. Both the Norfolk kākā as well as the Chatham kākā are the result of migration of a limited number of individuals to islands and subsequent adaptation to the habitat of those islands.[15] The lack of DNA material for the Chatham kākā makes it difficult to establish precisely when those speciation events occurred. Finally, in recent times, the kākā populations at the North Island and South Island became isolated from each other due to the rise in sea levels when the continental glaciers melted at the end of the Pleistocene.[15]
Until modern times New Zealand and the surrounding Islands were not inhabited by four-legged mammals, an environment that enabled some birds to adapt to make nests on the ground and others to become flightless.
The parakeet species belonging to the genus Cyanoramphus (kākārikis) belong to the true parrot family Psittacidae and are closely related to the endemic genus Eunymphicus from New Caledonia. They reached New Zealand between 450,000 and 625,000 years ago from mainland Australia by way of New Caledonia.[22]
Species
Nestoridae
There are two surviving species and at least one well documented extinct species of the Nestoridae family. Very little is known about the Chatham kākā. The genus Nelepsittacus consists of three described and one undescribed species recovered from early Miocene deposits in Otago.[3]
| Nestorini | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Common name (binomial name) status |
Image | Description | Range and habitat |
| Kea (Nestor notabilis) |
_-on_ground-8.jpg) |
48 cm (19 in) long. Mostly olive-green with scarlet underwings and rump. Dark-edged feathers. Dark brown beak, iris, legs, and feet. Male has longer bill.[23] | New Zealand: South Island High-level forests and subalpine scrublands 850–1400 m AMSL.[24] |
| South Island kaka (Nestor meridionalis meridionalis) |
 |
Similar to the North Island kaka, but slightly smaller, brighter colours, the crown is almost white, and the bill is longer and more arched in males.[25] | New Zealand: South Island Unbroken tracts of Nothofagus and Podocarpus forests 450–850 m AMSL in summer and 0–550 m in winter.[24] |
| North Island kaka (Nestor meridionalis septentrionalis) |
 |
About 45 cm (18 in) long. Mainly olive-brown with dark feather edges. Crimson underwings, rump, and collar. The cheeks are golden/brown. The crown is greyish.[25] | New Zealand: North Island Unbroken tracts of Nothofagus and Podocarpus forests between 450–850 m AMSL in summer and 0–550 m in winter.[24] |
| Norfolk kaka |
 |
About 38 cm long. Mostly olive-brown upperparts, (reddish-)orange cheeks and throat, straw-coloured breast, thighs, rump and lower abdomen dark orange.[4] | Formerly endemic on Norfolk Island and Phillip Island of Australia[26] Rocks and trees[4] |
| Chatham kaka (Nestor sp.) |
Appearance unknown, but bones indicate reduced flight capability. | Only known from subfossil bones.[5] | Formerly endemic on Chatham Island of New Zealand Forests[5] |
Strigopidae
The kakapo is the only member of the Strigopidae family.
| Strigopini | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Common name (binomial name) status |
Image | Description | Range and habitat |
| Kakapo (Strigops habroptila) |
 |
Large rotund parrots 58–64 cm (23–25 in) long; males are larger than females and weigh 2–4 kg (4.5–9 lb) at maturity. Mostly green with brown and yellow mottled barring, the underparts being greenish-yellow. Its face is pale and owl-like.[27] | New Zealand: Maud, Chalky, Codfish and Anchor Islands Climax Nothofagus (beech) and Podocarpus (conifer) forests, regenerating subalpine scrub, snow tussock Danthonia grassland 10–1400 m AMSL.[24] |
Common names
All common names for species in this family are the same as the traditional Māori names.[6] The word kākā derives from the ancient Proto-Polynesian word meaning parrot.[28] Kākāpō is a logical extension of that name as pō means night, resulting in kākā of the night or night parrot, reflecting the species' nocturnal behaviour.[29] The etymology of kea in Māori is less clear, and might be onomatopoeic of its call kee-aah.[4][30]
In the anglicized versions of the names, the long versions of the vowels with diacritic marks, ā and ō, are replaced by a or o. In the Māori language, this changes the meaning of kākā from parrot to dress or clothing.[31][32]
Ecology
_-Mount_Cook_-NZ-6.jpg)
The isolated location of New Zealand has made it difficult for mammals to reach the island. This is reflected in the absence of land mammals other than bats. The main predators were birds: eagles (Eyles' harrier, kāhu and Haast's eagle ), falcons (kārearea) and owls (whēkau and ruru). Many of the adaptations found in the avifauna reflect the unique context in which they evolved. This unique balance was disrupted with the arrival of the Polynesians, who introduced the Polynesian rat and the kurī (Polynesian dog) to the island. Later, Europeans introduced many more species, including large herbivores and mammalian predators.
The three extant species of this family occupy rather different ecological niches, a result of the phylogeographical dynamics of this family. The kākāpō is a flightless, nocturnal species, well camouflaged to avoid the large diurnal birds of prey on the island, while the local owls are too small to prey on the kākāpō at night. The kākāpō is the only flightless bird in the world to use a lek-breeding system. Usually, they breed only every 3–5 years when certain podocarp trees like rimu (Dacrydium cupressinum) mast abundantly.
The kea is well adapted to life at high altitudes, and they are regularly observed in the snow at ski resorts. As trees are absent in the alpine zone, they breed in hollows in the ground instead of in tree hollows like most parrot species.
Relationship with humans
Importance to the Māori
The parrots were important to the Māori in various ways. They hunted them for food, kept them as pets and used their feathers in weaving[33] such items as their kahu huruhuru (feather cloak).[34] Feathers were also used to decorate the head of the taiaha, a Māori weapon, but were removed prior to battle.[35] The skins of the kākāpō with the feathers attached were used to make cloaks (kākahu) and dress capes (kahu kākāpō), especially for the wives and daughters of chiefs.[35] Māori like to refer to the kākā in the tauparapara, the incantation to begin their mihi (tribute), because their voice (reo) is continuous.[36][37]
Status
Of the five species, the Norfolk kākā[7][26] and Chatham kākā[5] became extinct in recent history. The last known Norfolk kākā died in captivity in London sometime after 1851,[38] and only between seven[39] and 20[40] skins survive. The Chatham kākā went extinct between 1550 and 1700 in pre-European times, after Polynesians arrived at the island, and is only known from subfossil bones.[5] Of the surviving species, the kākāpō is critically endangered,[8][27] with only 126[41] living individuals. The mainland New Zealand kaka is listed as endangered,[9][25] and the kea is listed as vulnerable.[10][23]
Threats
The fauna of Aotearoa (Māori for New Zealand) evolved for a long time in the absence of humans and other mammals. Only a few bat species and sea mammals were present prior to colonisation by humans, and the only predators were birds of prey that hunt by sight. These circumstances influenced the evolution of New Zealand's parrots, for example, the adaptations to flightlessness of the kākāpō and the ground breeding of the kea.[35] Polynesians arrived at Aotearoa between 800 and 1300 CE,[42] and introduced the kurī (dog) to the islands.[35] This was disastrous for the native fauna, because mammalian predators can locate prey by scent, and the native fauna had not evolved a defence against them.[35]
The kākāpō was hunted for its meat, skin and plumage. When the first European settlers arrived, the kākāpō was already declining but still widespread.[35] The large scale clearance of forests and bush destroyed its habitat while introduced predators like rats, cats, and stoats found the flightless ground-nesting birds easy prey.[11]
The New Zealand kākā is a species that needs large tracts of forest to thrive, and the continued fragmentation of forests due to agriculture and logging has a devastating effect on this species. Another threat comes from competition with introduced species for food, for example with possums for the endemic mistletoe and rātā and with wasps for shimmering honeydew, an excretion of scale insects. Females, young and eggs are particularly vulnerable in the tree hollows they nest in.[12]
The kea nests in holes in the ground, again making it vulnerable to introduced predators. Another major threat, resulting from development of the alpine zone, is their opportunistic reliance on human food sources as their natural food sources dwindle.[13]
Conservation
Recovery programs for the kākāpō[43][44] and the kākā[45] have been established, while the kea is also closely monitored.[46] The 126[41] living kākāpō are all in a breeding and conservation program. Each one has been individually named.
See also
- Kākāriki, New Zealand parakeets
- Fauna of New Zealand
References
- ↑ Nestoridae and Strigopidae are described in the same article, Bonaparte, C.L. (1949) Conspectus Systematis Ornithologiae. Therefore, under rules of the ICZN, the first reviser determines priority, which is Bonaparte, C.L. (1850), Conspectus Generum Avium, E.J. Brill, Leyden.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Christidis L, Boles WE (2008). Systematics and Taxonomy of Australian Birds. Canberra: CSIRO Publishing. p. 200. ISBN 978-0-643-06511-6.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Worthy, Trevor H.; Tennyson, Alan J. D.; Scofield, R. Paul (2011). "An early Miocene diversity of parrots (Aves, Strigopidae, Nestorinae) from New Zealand". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology 31 (5): 1102–16. doi:10.1080/02724634.2011.595857.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 Forshaw, Joseph M.; Cooper, William T. (1981) [1973, 1978]. Parrots of the World (corrected second edition ed.). David & Charles, Newton Abbot, London. ISBN 0-7153-7698-5.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 5.5 5.6 Millener, P. R. (1999). "The history of the Chatham Islands’ bird fauna of the last 7000 years – a chronicle of change and extinction. Proceedings of the 4th International meeting of the Society of Avian Paleontology and Evolution (Washington, D.C., June 1996).". Smithsonian Contributions to Paleobiology 89: 85–109.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 "Maori Bird Names". Kiwi Conservation Club. Retrieved 12 December 2012.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 BirdLife International (2008). Nestor productus. In: IUCN 2008. IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Retrieved 24 December 2008. Database entry includes a range map and justification for why this species is endangered.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 BirdLife International (2008). Strigops habroptila. In: IUCN 2008. IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Retrieved 24 December 2008. Database entry includes a range map and justification for why this species is endangered,
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 9.3 BirdLife International (2008). Nestor meridionalis. In: IUCN 2008. IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Retrieved 24 December 2008. Database entry includes a range map and justification for why this species is endangered.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 BirdLife International (2008). Nestor notabilis. In: IUCN 2008. IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Retrieved 24 December 2008. Database entry includes a range map and justification for why this species is endangered.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 "Threats to Kākāpō". Department of Conservation Te Papa Atawbai. Retrieved 2008-12-31.
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 "Threats to Kākā". Department of Conservation Te Papa Atawbai. Retrieved 2008-12-31.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 "Threats to Kea". Department of Conservation Te Papa Atawbai. Retrieved 2008-12-31.
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 14.2 Wright, T.F.; Schirtzinger E. E., Matsumoto T., Eberhard J. R., Graves G. R., Sanchez J. J., Capelli S., Muller H., Scharpegge J., Chambers G. K. & Fleischer R. C. (2008). "A Multilocus Molecular Phylogeny of the Parrots (Psittaciformes): Support for a Gondwanan Origin during the Cretaceous". Mol Biol Evol 25 (10): 2141–2156. doi:10.1093/molbev/msn160. PMC 2727385. PMID 18653733.
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 15.2 15.3 15.4 15.5 Grant-Mackie, E.J.; J.A. Grant-Mackie, W.M. Boon & G.K. Chambers (2003). "Evolution of New Zealand Parrots". NZ Science Teacher 103.
- ↑ For a discussion about older taxonomic positions, see Sibley, Charles Gald; Jon E. Ahlquist (1991). Phylogeny and Classification of Birds. Yale University Press. For more recent taxonomies, see Christides.
- ↑ 17.0 17.1 17.2 17.3 Leo Joseph, Alicia Toon, Erin E. Schirtzinger, Timothy F. Wright & Richard Schodde. (2012) A revised nomenclature and classification for family-group taxa of parrots (Psittaciformes). Zootaxa 3205: 26–40
- ↑ Tokita, M; Kiyoshi T and Armstrong KN (2007). "Evolution of craniofacial novelty in parrots through developmental modularity and heterochrony". Evolution & Development 9: 590–601. doi:10.1111/j.1525-142X.2007.00199.x. PMID 17976055.
- ↑ de Kloet, RS; de Kloet SR (2005). "The evolution of the spindlin gene in birds: Sequence analysis of an intron of the spindlin W and Z gene reveals four major divisions of the Psittaciformes". Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution 36 (3): 706–721. doi:10.1016/j.ympev.2005.03.013. PMID 16099384.
- ↑ Livezey, B. C.; R. L. Zusi (2007). "Higher-order phylogeny of modern birds (Theropoda, Aves: Neornithes) based on comparative anatomy: II. – Analysis and discussion". Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society 149: 1–94. doi:10.1111/j.1096-3642.2006.00293.x. PMC 2517308. PMID 18784798.
- ↑ Homberger, DG (2006). "Classification and the status of wild populations of parrots". In Luescher AU. Manual of parrot behavior. Ames (IA): Blackwell Publishing. pp. 3–11. ISBN 978-0-8138-2749-0.
- ↑ Boon, W. M.; Kearvell, J.; Daugherty, C. H.; Chambers, G. K. (2001). "Molecular systematics and conservation of kakariki (Cyanoramphus spp.)". Science for Conservation 176.
- ↑ 23.0 23.1 "Kea - BirdLife Species Factsheet". BirdLife International. 2008.
- ↑ 24.0 24.1 24.2 24.3 24.4 Juniper, Tony; Mike Parr (1998). Parrots: A Guide to Parrots of the World. Yale University Press. ISBN 978-0300074536.
- ↑ 25.0 25.1 25.2 "Kaka - BirdLife Species Factsheet". BirdLife International. 2008.
- ↑ 26.0 26.1 "Norfolk Island Kaka - BirdLife Species Factsheet". BirdLife International. 2008.
- ↑ 27.0 27.1 "Kakapo - BirdLife Species Factsheet". BirdLife International. 2008.
- ↑ "Kaakaa". Polynesian Lexicon Online. Retrieved 2012-02-29.
- ↑ "kakapo". The American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language: Fourth Edition. 2000. Retrieved 2008-12-31.
- ↑ "kea". The American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language: Fourth Edition. 2000. Retrieved 2008-12-31.
- ↑ "The Māori Language - Ko Te Reo". Retrieved 2009-01-01.
- ↑ "Māori dictionary". Retrieved 2009-01-02.
- ↑ Evans, Miriama; Ranui Ngarimu; Creative New Zealand; Norman Heke (2005). The Art of Māori Weaving. Wellington, N.Z.: Huia Publishers. ISBN 978-1-86969-161-5.
- ↑ "Kahu huruhuru (feather cloak)". Museum of New Zealand Te Papa Tongarewa. Retrieved 2008-12-31.
- ↑ 35.0 35.1 35.2 35.3 35.4 35.5 Tipa, Rob (2006). "Kakapo in Maori lore". Notornis 53: 193–194.
- ↑ "Putting Together a Mihi for a Hui". maori.org.nz Main Maori Site on the Net!. Retrieved 2009-01-02.
- ↑ "Slideshow: Manu - Birds". maori.org.nz Main Maori Site on the Net!. Retrieved 2009-01-02.
- ↑ Greenway, James Cowan (1967). Extinct and Vanishing Birds of the World (2nd ed.). New York: Dover Publications.
- ↑ "Nestor productus - Norfolk Island Kaka specimen(s) in the ZMA". Nlbif.eti.uva.nl. Retrieved 2008-12-28.
- ↑ "Naturalis - Extinct bird: Nestor productus (Norfolk Island Kaka)". Nlbif.eti.uva.nl. Retrieved 2008-12-28.
- ↑ 41.0 41.1 "Kakapo Recovery". Kakapo Recovery Program. Retrieved 2014-03-13.
- ↑ Douglas G. Sutton, ed. (1994). The Origins of the First New Zealanders. Auckland: Auckland University Press. ISBN 1-86940-098-4.
- ↑ "Kakapo Recovery Program". Retrieved 2008-12-31.
- ↑ "DOC's work with Kākāpō". Department of Conservation Te Papa Atawbai. Retrieved 2008-12-31.
- ↑ "DOC's work with Kākā". Department of Conservation Te Papa Atawbai. Retrieved 2008-12-31.
- ↑ "DOC's work with Kea". Department of Conservation Te Papa Atawbai. Retrieved 2008-12-31.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Strigopidae. |
| Wikispecies has information related to: Strigopidae |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
