Neamine transaminase
| Neamine transaminase | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| EC number | 2.6.1.93 | ||||||||
| Databases | |||||||||
| IntEnz | IntEnz view | ||||||||
| BRENDA | BRENDA entry | ||||||||
| ExPASy | NiceZyme view | ||||||||
| KEGG | KEGG entry | ||||||||
| MetaCyc | metabolic pathway | ||||||||
| PRIAM | profile | ||||||||
| PDB structures | RCSB PDB PDBe PDBsum | ||||||||
| |||||||||
Neamine transaminase (EC 2.6.1.93, glutamate---6'-dehydroparomamine aminotransferase, btrB (gene), neoN (gene), kacL (gene)) is an enzyme with system name neamine:2-oxoglutarate aminotransferase.[1][2][3] This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
- neamine + 2-oxoglutarate
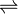 6'-dehydroparomamine + L-glutamate
6'-dehydroparomamine + L-glutamate
The reaction occurs in vivo in the opposite direction.
References
- ↑ Huang, F., Spiteller, D., Koorbanally, N.A., Li, Y., Llewellyn, N.M. and Spencer, J.B. (2007). "Elaboration of neosamine rings in the biosynthesis of neomycin and butirosin". ChemBioChem. 8 (3): 283–288. doi:10.1002/cbic.200600371. PMID 17206729.
- ↑ Clausnitzer, D., Piepersberg, W. and Wehmeier, U.F. (2011). "The oxidoreductases LivQ and NeoQ are responsible for the different 6′-modifications in the aminoglycosides lividomycin and neomycin". J. Appl. Microbiol. 111 (3): 642–651. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2672.2011.05082.x. PMID 21689223.
- ↑ Park, J.W., Park, S.R., Nepal, K.K., Han, A.R., Ban, Y.H., Yoo, Y.J., Kim, E.J., Kim, E.M., Kim, D., Sohng, J.K. and Yoon, Y.J. (2011). "Discovery of parallel pathways of kanamycin biosynthesis allows antibiotic manipulation". Nat. Chem. Biol. 7: 843–852. doi:10.1038/nchembio.671. PMID 21983602.
External links
- Neamine transaminase at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)