NOAA Commissioned Officer Corps
| National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration Commissioned Officer Corps | |
|---|---|
 Seal of the NOAA Commissioned Officer Corps | |
| Active | May 22, 1917 – present[1][2][3] |
| Country |
|
| Branch |
|
| Type | Uniformed service |
| Size |
379 officers[4] 19 ships, 14 aircraft[5] |
| Part of |
|
| Garrison/HQ | Silver Spring, Maryland, U.S. |
| Nickname | "NOAA Corps" |
| Motto | "Science, service, stewardship."[6] |
| Colors | Blue, White |
| March | "Forward with NOAA"[7] |
| Engagements | |
| Commanders | |
| Deputy Under Secretary for Operations, NOAA | VADM Michael S. Devany |
| Director, NOAA Commissioned Officer Corps[9] | RADM David A. Score |
| Deputy Director, NOAA Commissioned Officer Corps[10] | RDML Anita L. Lopez |
| Director, Office of Coast Survey[11] | RDML Gerd F. Glang |
| Notable commanders |
VADM Henry A. Karo RADM William L. Stubblefield RADM Evelyn J. Fields RADM Samuel P. De Bow, Jr. |
| Insignia | |
| Flag |
 |
| Aircraft flown | |
| Reconnaissance | WP-3D, AC-695A, G-IV, DHC-6 |
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration Commissioned Officer Corps, and known informally as the NOAA Corps, is one of seven federal uniformed services of the United States[note 1] and operates under the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), a scientific agency within the Department of Commerce. The NOAA Corps is one of two uniformed services – the other is the United States Public Health Service Commissioned Corps – that consist only of commissioned officers, with no enlisted or warrant officer ranks.
Established in 1970, the NOAA Corps is the successor to the United States Coast and Geodetic Survey Corps (1917–1965) and the Environmental Science Services Administration Corps (ESSA Corps) (1965–1970).
History
The NOAA Commissioned Officer Corps traces its roots to the United States Coast and Geodetic Survey. The Coast and Geodetic Survey's predecessor, the United States Survey of the Coast – renamed the United States Coast Survey in 1836 – was founded in 1807 under President Thomas Jefferson. Until the American Civil War, the Coast Survey was manned by civilian personnel working with United States Army and United States Navy officers. During the Civil War (1861–1865), Army officers were withdrawn from Coast Survey duty, never to return, while all but two Navy officers also were withdrawn from Coast Survey service for the duration of the war. Since most men of the Survey had Union sympathies, most stayed on with the Survey rather than resigning to serve the Confederate States of America; their work shifted in emphasis to support of the U.S. Navy and Union Army, and these Coast Surveyors are the professional ancestors of today's NOAA Corps. Those Coast Surveyors supporting the Union Army were given assimilated military rank while attached to a specific command, but those supporting the U.S. Navy operated as civilians and ran the risk of being executed as spies if captured by the Confederates while working in support of Union forces. After the war, U.S. Navy officers returned to duty with the Coast Survey, which was given authority over geodetic activities in the interior of the United States in 1871 and accordingly was renamed the United States Coast and Geodetic Survey in 1878.[12][13]
With the outbreak of the Spanish–American War in April 1898, the Navy again withdrew all of its officers from Coast and Geodetic Survey assignments. They returned after the war, but the system of U.S. Navy officers and men crewing the Survey 's ships that had prevailed for most of the 19th century came to an end when the appropriation law approved on June 6, 1900 provided for "all necessary employees to man and equip the vessels" instead of Navy personnel. The law took effect on July 1, 1900; at that point, all Navy personnel assigned to the Survey 's ships remained aboard until the first call at each ship 's home port, where they transferred off, with the Survey reimbursing the Navy for their pay accrued after July 1, 1900.[14]
From July 1900, the Coast and Geodetic Survey continued as an entirely civilian-manned organization until after the United States entered World War I in April 1917. To avoid the dangers that Coast Survey personnel had faced during the Civil War of being executed as spies if captured by the enemy, the Coast and Geodetic Survey Corps was established on May 22, 1917, giving Coast and Geodetic Survey officers a commissioned status so that under the laws of war, they could not be executed as spies if they were captured while serving as surveyors on a battlefield. The creation of the Coast and Geodetic Survey Corps also ensured that in wartime a set of officers with technical skills in surveying could be rapidly assimilated into the United States armed forces so that their skills could be employed in military and naval work essential to the war effort. Before World War I ended in November 1918, over half of all Coast and Geodetic Survey Corps officers had served in the U.S. Army, U.S. Navy, or United States Marine Corps, performing duty as artillery orienteering officers, minelaying officers in the North Sea (where they were involved in the laying of the North Sea Mine Barrage), troop transport navigators, intelligence officers, and on the staff of General John "Black Jack" Pershing.[12]
The Coast and Geodetic Survey Corps returned to peacetime scientific pursuits after the war.[12] Its first flag officer was Rear Admiral Raymond S. Patton, who was promoted from captain to rear admiral in 1936.
When the United States entered World War II in December 1941, the Coast and Geodetic Survey Corps again suspended its peacetime activities to support the war effort, often seeing front-line service. Over half of all Coast and Geodetic Survey officers were transferred to the U.S. Army, U.S. Navy, U.S. Marine Corps, or United States Army Air Forces, seeing duty in North Africa, Europe, and the Pacific as artillery surveyors, hydrographers, amphibious engineers, beachmasters, instructors at service schools, and in a wide variety of technical positions. They also served as reconnaissance surveyors for a worldwide aeronautical charting effort, and a Coast and Geodetic Survey officer was the first commanding officer of the Army Air Forces Aeronautical Chart Plant at St. Louis, Missouri. Three officers who remained in Coast and Geodetic Survey service were killed during the war, as were eleven other Survey personnel.[12]
After the war ended in August 1945, the Coast and Geodetic Survey again returned to peacetime scientific duties, although a significant amount of its work in succeeding years was related to support of military and naval requirements during the Cold War.[12] When the Coast and Geodetic Survey was transferred to the newly established Environmental Science Services Administration on July 13, 1965,[15] control of the corps was transferred from the Survey to ESSA itself, and accordingly the corps was redesignated the Environmental Science Services Administration Corps (ESSA Corps). Rear Admiral H. Arnold Karo was promoted to vice admiral on July 13, 1965 to help lead in the establishment of the new ESSA; he served as the first Deputy Administrator of ESSA, and as a vice admiral he remains the highest-ranking officer in the combined history of the Coast and Geodetic Survey Corps, ESSA Corps, and NOAA Corps. Rear Admiral James C. Tison was the first director of the ESSA Corps.
The ESSA was reorganized and expanded to become the new National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration on October 3, 1970,[16] and the ESSA Corps was redesignated the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration Corps (NOAA Corps). Rear Admiral Harley D. Nygren was appointed as the first director of the new NOAA Corps.
In 1972 the NOAA Corps became the first uniformed service of the U.S. Government to recruit women on the same basis as men.[17]
Directors of the NOAA Corps and predecessor organizations
| Image | Rank | Name | Tenure | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| United States Coast and Geodetic Survey Corps | ||||
 |
Captain | Ernest Lester Jones | 1915–1929 | First Director, Coast and Geodetic Survey Corps[18] |
| Rear Admiral | Raymond Stanton Patton | 1929–1937 | [18] | |
 |
Rear Admiral | Leo Otis Colbert | 1938–1950 | [18] |
| Rear Admiral | Robert Francis Anthony Studds | 1950–1955 | [18] | |
 |
Rear Admiral | Henry Arnold Karo | 1955–1965 | Last Director, Coast and Geodetic Survey Corps. Promoted to vice admiral in 1965 and served as Deputy Administrator, ESSA from 1965 to 1967.[18] |
| Environmental Science Services Administration Commissioned Corps (ESSA Corps) | ||||
 |
Rear Admiral | James C. Tison, Jr | 1965–1968 | First Director, ESSA Corps[18] |
| Rear Admiral | Don A. Jones | 1968–1970 | Last Director, ESSA Corps. Served as Director, National Ocean Survey 1970 – 1972.[18] | |
| National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration Commissioned Corps (NOAA Corps) | ||||
 |
Rear Admiral | Harley D. Nygren | 1970–1980 | First Director, NOAA Commissioned Officer Corps[19] |
| Rear Admiral | Kelly E. Taggart | 1980–1986 | [20] | |
| Rear Admiral | Francis D. Moran | 1986–1990 | [21] | |
| Rear Admiral | Sigmund R. Petersen | 1990–1995 | [22] | |
 |
Rear Admiral | William L. Stubblefield | 1995–1999 | [23] |
 |
Rear Admiral | Evelyn J. Fields | 1999–2003 | [24] |
 |
Rear Admiral | Samuel P. De Bow, Jr. | 2003–2007 | [25] |
 |
Rear Admiral | Jonathan W. Bailey | 2007–2012 | [26] |
 |
Rear Admiral | Michael S. Devany | 2012–2014 | Promoted to vice admiral on January 2, 2014 and currently serves as Deputy Under Secretary for Operations, NOAA.[27] |
 |
Rear Admiral | David A. Score | 2014–present | [28] |
Commissioned officers
The NOAA Corps is one of the seven uniformed services of the United States Government[note 1] and has over 300 commissioned officers and no enlisted or warrant officer ranks. The NOAA Corps today provides a cadre of professionals trained in engineering, earth sciences, oceanography, meteorology, fisheries science, and other related disciplines. NOAA Corps officers operate NOAA ships, fly NOAA aircraft, manage research projects, conduct diving operations, and serve in staff positions throughout NOAA, as well as in positions in the United States Department of Defense, the United States Coast Guard, the National Aeronautics and Space Administration, and the United States Department of State. Like its predecessors, the Coast and Geodetic Survey Corps and the ESSA Corps, the NOAA Corps provides a ready source of technically skilled officers which can be incorporated into the U.S. armed forces in time of war, and in peacetime supports defense requirements in addition to its purely civilian scientific projects.[12]
The NOAA Corps uses the same commissioned officer ranks as the U.S. Navy and U.S. Coast Guard. While the grade of admiral has been established as a rank in the NOAA Corps,[29][29] the rank has not been authorized for use by the United States Congress.[30] Current NOAA Corps ranks rise from ensign to vice admiral,[30] pay grades O-1 through O-9 respectively. NOAA Corps officers are appointed via direct commission and receive the same pay as other members of the uniformed services. They cannot hold a dual commission with another service, but inter-service transfers are sometimes permitted.
| Commissioned officer ranks and abbreviations of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration Commissioned Officer Corps | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vice Admiral |
Rear Admiral | Rear Admiral (lower half) |
Captain | |||||||
| O-9 | O-8 | O-7 | O-6 | |||||||
 |
 |
 |
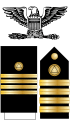 | |||||||
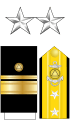
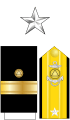
| VADM | RADM | RDML | CAPT | |||||||
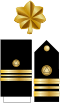
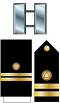
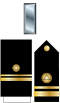
| Commander | Lieutenant Commander |
Lieutenant | Lieutenant (junior grade) |
Ensign |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O-5 | O-4 | O-3 | O-2 | O-1 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
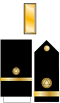 |
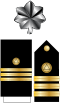
| CDR | LCDR | LT | LTJG | ENS |
Uniforms
For formal service uniforms, the NOAA Corps wears the same Service Dress Blues and Service Dress Whites as the U.S. Navy, but with NOAA Corps insignia in place of U.S. Navy insignia. For daily work uniforms, the NOAA Corps wears the same Operational Dress Uniform (ODU) as the U.S. Coast Guard, but with NOAA Corps insignia in place of U.S. Coast Guard insignia.
-

NOAA Corps Combination Cap Device
-

NOAA Corps Device
-
An ODU uniform ball cap, with LCDR rank insignia
-

Officers wearing the Service Dress Blues
See also
- NOAA ships and aircraft
- Awards and decorations of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration
Notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 The other six uniformed services of the United States Government are the United States Air Force, United States Army, United States Coast Guard, United States Marine Corps, United States Navy, and United States Public Health Service Commissioned Corps.
References
- ↑ "NOAA History A Sea Odyssey".
- ↑ "History of the NOAA Corps".
- ↑ "The Roots of the NOAA Corps".
- ↑ "33 USC 3005: Number of Authorized Commissioned Officers".
- ↑ "New Commander to Direct NOAA's Aircraft Operations".
- ↑ http://celebrating200years.noaa.gov/edufun/book/NOAAintroduction.pdf
- ↑ http://www.noaacorps.noaa.gov/about/song.html
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 History of the NOAA Commissioned Corps
- ↑ Note: Also concurrently serves as Director, Office of Marine and Aviation Operations
- ↑ Note: Also concurrently serves as Deputy Director for Operations, Office of Marine and Aviation Operations
- ↑ Note: Also concurrently serves as the U.S. National Hydrographer
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 12.2 12.3 12.4 12.5 NOAA History: NOAA Corps and the Coast and Geodetic Survey
- ↑ noaa.gov NOAA History: NOAA Legacy Timeline 1807–1899
- ↑ U.S. Coast and Geodetic Survey (1901). Report Of The Superintendent of the Coast And Geodetic Survey Showing The Progress Of Work From July 1, 1900 To June 30, 1901. Washington, D.C.: U.S. Government Printing Office. pp. 15, 17, 109.
- ↑ Reorganization Plan No. 2 of 1965, reprinted in 5 U.S.C. app. at 1517
- ↑ Reorganization Plan No. 4 of 1970, reprinted with amendments in 5 U.S.C. app. at 1557–61. Section 3(d) states: "The Commissioned Officer Corps of the Environmental Science Services Administration shall become the Commissioned Officer Corps of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration."
- ↑ noaa.gov NOAA History: NOAA Legacy Time Line 1970–2000
- ↑ 18.0 18.1 18.2 18.3 18.4 18.5 18.6 "Leaders of Coast Survey" (PDF). National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved August 29, 2013.
- ↑ "C&GS Biographies". Profiles in Time NOAA History. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved 29 August 2013.
- ↑ http://www.presidency.ucsb.edu/ws/?pid=45524
- ↑ http://www.presidency.ucsb.edu/ws/?pid=37470
- ↑ http://www.apnewsarchive.com/1990/Nation-s-Smallest-Service-to-Get-New-Leader/id-b53461e84e2d07795dc5c2b00c93816d
- ↑ http://www.publicaffairs.noaa.gov/pr95/may95/stubble.html
- ↑ http://www.publicaffairs.noaa.gov/releases99/july99/noaa99052.html
- ↑ http://www.publicaffairs.noaa.gov/releases2006/oct06/noaa06-r827.html
- ↑ http://thomas.loc.gov/cgi-bin/query/z?c112:H.RES.792:
- ↑ "RADM Michael S. Devany , NOAA Director, NOAA Commissioned Officer Corps Director, NOAA Office of Marine and Aviation Operations" (PDF). US Department of Commerce, National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved January 10, 2014.
- ↑ "Rear Adm. David A. Score to lead NOAA Corps and Office of Marine and Aviation Operations". US Department of Commerce, National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved January 10, 2014.
- ↑ 29.0 29.1 10 USC 201. Pay grades: assignment to; general rules
- ↑ 30.0 30.1 S.2388 - National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration Commissioned Officer Corps Amendments Act of 2012
External links
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
