N-Acylethanolamine
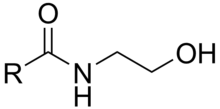
An N-acylethanolamine is a type of fatty acid amide formed when one of several types of acyl group is linked to the nitrogen atom of ethanolamine. These amides conceptually can be formed from a fatty acid and ethanolamine with the release of a molecule of water, but the known biological synthesis uses a specific phospholipase D to cleave the phospholipid unit from N-acylphosphatidylethanolamines.[1] Another route relies on the transesterification of acyl groups from phosphatidylcholine by an N-acyltransferase (NAT) activity. The suffixes -amine and -amide in these names each refer to the single nitrogen atom of ethanolamine that links the compound together: it is termed "amine" in ethanolamine because it is considered as a free terminal nitrogen in that subunit, while it is termed "amide" when it is considered in association with the adjacent carbonyl group of the acyl subunit. Names for these compounds may be encountered with either "amide" or "amine" varying by author.[2]
Examples of N-acylethanolamines include:[3]
- Anandamide (N-arachidonoylethanolamine) is the amide of arachidonic acid (20:4 ω-6) and ethanolamine. It is the ligand of both cannabinoid receptors and vanilloid receptor that attenuates pain sensation.[4][5][6][7]
- N-Palmitoylethanolamine is the amide of palmitic acid (16:0) and ethanolamine. It has anti-inflammatory activity and also attenuates pain sensation.[7][8]
- N-Oleoylethanolamine is the amide of oleic acid (18:1) and ethanolamine. It has anorexic effects and enables fat breakdown by stimulating PPAR-alpha.[9]
- N-Stearoylethanolamine is the amide of stearic acid (18:0) and ethanolamine. It has pro-apoptotic activity. It operates independently of the known cannabinoid and vanilloid receptors targeted by anandamide.[9]
References
- ↑ Okamoto, Y.; Morishita, J.; Tsuboi, K.; Tonai, T.; Ueda, N. (2004). "Molecular characterization of a phospholipase D generating anandamide and its congeners.". The Journal of Biological Chemistry 279 (7): 5298–5305. doi:10.1074/jbc.M306642200. PMID 14634025.
- ↑ For example, note synonyms in PubChem for oleoylethanolamine.
- ↑ The list and references provided are based on background discussion in Okamoto Y, Morishita J, Tsuboi K, Tonai T, Ueda N (February 2004). "Molecular characterization of a phospholipase D generating anandamide and its congeners". J. Biol. Chem. 279 (7): 5298–305. doi:10.1074/jbc.M306642200. PMID 14634025.
- ↑ WA Devane, L Hanus, A Breuer, RG Pertwee, LA Stevenson, G Griffin, D Gibson, A Mandelbaum, A Etinger, and R Mechoulam; Hanus; Breuer; Pertwee; Stevenson; Griffin; Gibson; Mandelbaum; Etinger; Mechoulam (1992). "Isolation and structure of a brain constituent that binds to the cannabinoid receptor". Science 258 (5090): 1946–1949. Bibcode:1992Sci...258.1946D. doi:10.1126/science.1470919. PMID 1470919.
- ↑ Di Marzo (1998). "'Endocannabinoids' and other fatty acid derivatives with cannabimimetic properties: biochemistry and possible physiopathological relevance.". Biochimica et Biophysica Acta 1392 (2–3): 153–75. doi:10.1016/s0005-2760(98)00042-3. PMID 9630590.
- ↑ Di Marzo; De Petrocellis, L; Fezza, F; Ligresti, A; Bisogno, T (2002). "Anandamide receptors". Prostaglandins, leukotrienes, and essential fatty acids 66 (2–3): 377–91. doi:10.1054/plef.2001.0349. PMID 12052051.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Calignano; La Rana, G; Giuffrida, A; Piomelli, D (1998). "Control of pain initiation by endogenous cannabinoids". Nature 394 (6690): 277–81. Bibcode:1998Natur.394..277C. doi:10.1038/28393. PMID 9685157.
- ↑ Lambert; Vandevoorde, S; Jonsson, KO; Fowler, CJ (2002). "The palmitoylethanolamide family: a new class of anti-inflammatory agents?". Current medicinal chemistry 9 (6): 663–74. doi:10.2174/0929867023370707. PMID 11945130.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 Rodríguez De Fonseca; Navarro, M; Gómez, R; Escuredo, L; Nava, F; Fu, J; Murillo-Rodríguez, E; Giuffrida, A; Loverme, J (2001). "An anorexic lipid mediator regulated by feeding". Nature 414 (6860): 209–12. doi:10.1038/35102582. PMID 11700558.