Myriocin
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
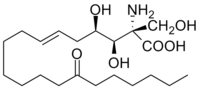
| IUPAC name
2-Amino-3,4-dihydroxy-2-(hydroxymethyl)-14-oxoicos-6-enoic acid | |
| Other names
Antibiotic ISP-1; Thermozymocidin | |
| Identifiers | |
| 5113331 | |
| 35891-70-4 | |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:582124 CHEBI:183131 |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL55076 |
| ChemSpider | 4942874 (2S,3R,4R,6E) 11654743 (6E) 266093 () 21467337 (3S,4S,6E) |
| |
| Jmol-3D images | Image Image |
| KEGG | C19914 |
| PubChem | 6438394 (6E) 301119 () |
| RTECS number | JX3890000 |
| |
| UN number | 2811 |
| Properties | |
| C21H39NO6 | |
| Molar mass | 401.54 g/mol |
| Except where noted otherwise, data is given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Myriocin, also known as antibiotic ISP-1 and thermozymocidin, is an atypical amino acid and an antibiotic derived from certain thermophilic fungi. Among the producing strains are Mycelia sterilia[1] and Isaria sinclairii.
Myriocin is a very potent inhibitor of serine palmitoyltransferase, the first step in sphingosine biosynthesis.[2] Due to this property, it is used in biochemical research as a tool for depleting cells of sphingolipids.
Myriocin was shown to inhibit the proliferation of an IL-2-dependent mouse cytotoxic T cell line.
Myriocin possesses immunosuppressant activity. It is reported to be 10 to 100 fold more potent than ciclosporin.
The multiple sclerosis drug fingolimod was derived from myriocin by using structure–activity relationship studies to determine the parts of the molecule important to its activity.