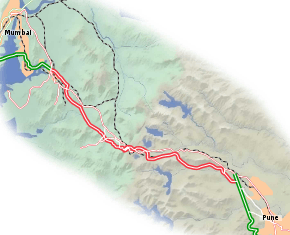
Mumbai Pune Expressway
| Mumbai-Pune Expressway | |
|---|---|
| मुंबई-पुणे द्रुतगती मार्ग | |
|
Yashwantrao Chavan Expressway यशवंतराव चव्हाण द्रुतगती मार्ग | |
|
Expressway map | |
| Route information | |
| Maintained by MSRDC | |
| Length: | 94.5 km (58.7 mi) |
| Existed: | 2002 – present |
| Major junctions | |
| West end: | Kalamboli, Navi Mumbai |
| East end: | Dehu Road, Pune |
| Location | |
| States: | Maharashtra |
| Major cities: | Panvel, Khandala, Lonavala |
| Highway system | |

The Mumbai Pune Expressway, (officially known as the Yashwantrao Chavan Mumbai Pune Expressway) is India's first six-lane concrete, high-speed, access controlled tolled expressway.[1] It spans a distance of 94.5 km (58.7 mi) connecting Mumbai, the administrative capital of Maharashtra and the financial capital of India, with Pune, an industrial and educational hub. The expressway, which was fully operationalized in 2002, introduced new levels of speed and safety in automobile transportation to Indian roads.[2] It is one of India's busiest roads.[3]
The expressway has reduced the travel time between the cities of Mumbai and Pune to approximately two hours. For most practical purposes, it has replaced the older Mumbai-Pune stretch of the Mumbai-Chennai National Highway (NH 4), which had become extremely congested and accident-prone over time but now it is also a fun road to drive, as cars and buses preferring to move on expressway and thus keeping it away from traffic. The expressway starts at Kalamboli (near Panvel), and ends at Dehu Rd. (near Pune). It cleaves through the scenic Sahyadri mountain ranges thru passes and tunnels. It has six interchanges: Shedung, Chowk, Khalapur, Lonavala, Kusgaon and Talegaon.
The expressway has two carriageways with three concrete lanes, each separated by a central divider and a tarmac or concrete shoulder on either side. Vehicles with fewer than four wheels and agricultural tractors are not permitted, although tractor-trailers (semi-trailer rigs) are permitted. The expressway handles about 43,000 PCUs daily,[3] and is designed to handle up to 1,000,000 PCUs.
History

In 1990, the Government of Maharashtra appointed RITES and Scott Wilson Kirkpatrick to carry out feasibility studies for the new expressway to be operated on toll basis. RITES submitted their report in 1994 with the estimated cost of project at ![]() 11.46 billion (US$180 million).
11.46 billion (US$180 million).
The Government of Maharashtra entrusted the work of the construction of Mumbai-Pune expressway to MSRDC in March 1997 on Build-Operate-Transfer basis with permission to collect toll for 30 years. The environmental clearance from the Ministry of Environment and Forests, Government of India was received on 13 October 2007. The Forest Clearance was received on 11 November 1997.
The tender notice was published in leading newspapers all over India and also on the Internet. Due to the wide publicity, 133 tenders were sold and on 18 December 1997, 55 tenders were received. After technical and financial evaluation, tenders were accepted and work orders were given on 1 January 1998 to four contractors. Thereafter tenders for widening of Khandala and Lonavala-Khandala bypass works were invited. The tenders were received on 24 August 1998 and orders were issued on 4 September 1998.
Construction



This six laner project was completed under the stewardship of the Maharashtra State Road Development Corporation (MSRDC).
The expressway cost ![]() 16.3 billion (US$260 million) to construct.
16.3 billion (US$260 million) to construct.
The first sections opened in 2000, and the entire route was completed, opened to traffic and made fully operational from April 2002.
Tunnels
It has five illuminated, ventilated tunnels totalling 5,724 metres. These tunnels were built by the Konkan Railway Corporation Ltd.
These are:
| Tunnel | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Bhatan | This tunnel opened in April 2000. The Mumbai-Pune (North) tube is 1,046 m and the Pune-Mumbai (South) tube is 1,086 m long. |
| 2 | Madap | This tunnel also opened in April 2000. The Mumbai-Pune (North) tube is 295 m and the Pune-Mumbai (South) tube is 351 m long. |
| 3 | Adoshi | This tunnel contains only a half part of the expressway which goes from Pune to Mumbai. The Mumbai-Pune carriageway skirts the eastern edge of the tunnel while the Pune-Mumbai carriageway traverses the 230 m long tunnel. |
| 4 | Khandala | This is a curved pair of tubes. The Mumbai-Pune (North) tube is 320 m and the Pune-Mumbai (South) tube is 360 m long. |
| 5 | Kamshet-1 | The Mumbai-Pune (North) tube is 935 m and the Pune-Mumbai (South) tube is 972 m long. |
| 6 | Kamshet-2 | The Mumbai-Pune (North) tube is 191 m and the Pune-Mumbai (South) tube is 168 m long. |
The entire length of expressway has a single layer of barbed wire fencing to keep out stray cattle.
Distances
| Description | Distance | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Start of Expressway (Mumbai end) (19°01′11.47″N 73°06′13.21″E / 19.0198528°N 73.1036694°E) to Kon-Shedung interchange | 8.5 km (5.3 mi) |
| 2 | Kon-Shedung interchange to Bhatan tunnel | 6.3 km (3.9 mi) |
| 3 | Bhatan tunnel to Madap tunnel | 10.6 km (6.6 mi) |
| 4 | Madap tunnel to Khalapur toll station | 7.3 km (4.5 mi) |
| 5 | Khalapur toll station to Khalapur-Sajgaon gas station & rest area | 1.6 km (0.99 mi) |
| 6 | Khalapur-Sajgaon rest area to Adoshi tunnel. The Mumbai-Pune carriageway skirts the eastern edge of the tunnel while the Pune-Mumbai carriageway traverses the 230 m long tunnel. |
6.9 km (4.3 mi) |
| 7 | Adoshi tunnel to the old British-built Deccan-Konkan stone trestle. This is the site of the old (1830–1928) GIPR reversing station. |
4.5 km (2.8 mi) |
| 8 | Stone trestle to Khandala tunnel | 0.8 km (0.50 mi) |
| 9 | Khandala tunnel to Khandala | 2.7 km (1.7 mi) |
| 10 | Khandala to Tungarli | 3.5 km (2.2 mi) |
| 11 | Tungarli to Kamshet-1 tunnel | 17.1 km (10.6 mi) |
| 12 | Kamshet-1 tunnel to Kamshet-2 tunnel | 1.2 km (0.75 mi) |
| 13 | Kamshet-3 tunnel to Talegaon toll station | 11.1 km (6.9 mi) |
| 14 | Talegaon toll station to Somatne interchange | 3.4 km (2.1 mi) |
| 16 | Somatne interchange to End of Expressway (Pune end) (18°39′45.85″N 73°43′35.61″E / 18.6627361°N 73.7265583°E) | 7.6 km (4.7 mi) |
| Total length of Expressway: Start to End | 93.1 km (57.8 mi) |
Toll Plazas

Toll is collected at Khalapur (Pali Phata) (for the Mumbai-Pune direction) and at Talegaon (for the Pune-Mumbai direction). The toll ranges from ![]() 195 (US$3.10) for private cars, to
195 (US$3.10) for private cars, to ![]() 1750 (US$28) for multi-axle trailer trucks.
1750 (US$28) for multi-axle trailer trucks.
Safety
The Expressway has witnessed a large number of accidents, attributed to human errors and the large volume of traffic. In 10 years there were 1758 accidents, with more than 400 fatalities.[4] Sporadic instances of robbery have also been reported in the highway.[5][6][7]
On 28 May 2012, 27 people were reported to have died, and another 26, injured in a road accident when a speeding tempo hit a stationary bus carrying passengers near Khalapur.[8][9]
On 10 June 2010 people were injured and 30 vehicles were damaged in a pileup near Kamshet which occurred when a MSRTC bus skidded inside a tunnel.[10]
Future Expansion
MSRDC has decided to extend the Mumbai Pune Expressway from the current endpoint of Kalamboli near Panvel and to extend it till Sion in Mumbai. The extended stretch will reduce commuting time between Mumbai and Pune by 30 minutes. Under the plan, the Sion Panvel Expressway corridor will be widened, with dedicated lanes for heavy and light vehicles. Service roads will be built for entry and exit at various points. It will also involve constructing a brand new bridge over the Thane creek parallel to the current Vashi Mankhurd Bridge. MSRDC will undertake the expansion project. Work is expected to commence in March 2009 and complete by September 2011. The new 22-km link is expected to cost ![]() 8 billion (US$130 million).
8 billion (US$130 million).
MSRDC is planning to widen the expressway from current 6 lane to 8 lane.[3] The proposal has been presented in Maharashtra Cabinet for approval.
Naming
The expressway was conceived and the work started when the BJP and Shiv Sena governed Maharashtra. Eventually, in 2009, the ruling coalition (Congress, NCP) named the expressway after the first Chief Minister of Maharashtra, Yashavantrao Chavan who was instrumental in the development of Maharashtra and an early member of the Congress party.
Connecting Cities
Apart from providing faster connectivity from Mumbai to Pune, the expressway has also connected cities like Satara, Sangli, Kolhapur, Belgaum, Hubli and Bangalore with Mumbai and reduced the travel time between these cities.
Gallery
-

-
-

A scenic view of the expressway near the Khandala exit in monsoon.
-
Near Kamshet 2 tunnel
-
Entrance of the Madap tunnel, in the Pune-Mumbai direction
See also
- Expressways in India
- Roads in Pune
References
- ↑ "Mumbai-Pune Expressway, India". Road Traffic Technology. Retrieved 2010-08-21.
- ↑ "Expressway pune mumbai pune , mumbai pune mumbai , express high way nh-4 national highway no4". Punediary.com. Retrieved 2010-08-21.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 "Mumbai-Pune expressway may soon have eight lanes". The Times Of India. 23 February 2013.
- ↑ "A bloody track record". Pune Mirror. 20 July 2010. Retrieved 21 July 2010.
- ↑ "Asiad bus looted on expressway". Times of India. 23 February 2004. Retrieved 21 July 2010.
- ↑ Umbrajkar, Manish (13 May 2009). "MSRDC should handle security on e-way: Bokey". The Times of India. Retrieved 21 July 2010.
- ↑ "Expressway turns into a fast lane for robbers". The Times of India. 25 February 2002. Retrieved 21 July 2010.
- ↑ "26 killed in road accident on Mumbai-Pune expressway". The Times Of India. Retrieved 2012-05-28.
- ↑ "27 killed in accident on Mumbai-Pune expressway". Mumbai: Hindustan Times. 28 May 2012. Retrieved 28 May 2012.
- ↑ "10 injured, 30 vehicles damaged in major pile-up on expressway". Pune: Dainik Bhaskar. 10 June 2012. Retrieved 15 June 2012.
External links
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Mumbai Pune expressway. |