Montmartre Funicular
| Montmartre funicular | |
|---|---|
|
A cabin descending to the lower station | |
| Overview | |
| Stations | 2 |
| Ridership | 2 million journeys per year |
| Operation | |
| Opening | 1900 |
| Rolling stock | 2 cabins |
| Technical | |
| Line length | 0.108 km (0.067 mi) |
| Track gauge | 1,435 mm (4 ft 8 1⁄2 in) |
The Montmartre funicular is an automatic funicular railway serving the Montmartre neighbourhood of Paris, in the Eighteenth arrondissement. It is operated by the RATP, the Paris transport authority. It was opened on 13 July 1900 and was entirely rebuilt in 1935 and again in 1991.
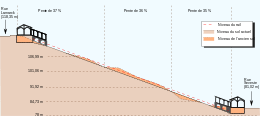
The funicular carries passengers between the foot of the butte (outlier) of Montmartre and its summit, near the foot of the Sacré-Cœur basilica. It provides an alternative to the multiple stairways of more than 300 steps that lead to the top of the Butte Montmartre. At 108 m (354 ft) long, the funicular climbs and drops the 36 m (118 ft) in under a minute and a half. It carries two million passengers a year.
Characteristics

The funicular is open every day from 6 am until 12.45 am, transporting 6,000 people a day, or around 2 million a year, mostly tourists and pilgrims en route to the Sacré-Cœur, and also Parisians and those who love the ambience of the Place du Tertre.[1]
The lower station was built between the Place Saint-Pierre and the Place Suzanne-Valadon, and the upper one on the Rue du Cardinal-Dubois. The funicular runs alongside the Rue Foyatier, a wide 220-step staircase.
Current funicular
Constructed by Schindler Group, the new funicular with electrical traction entered service on 1 June 1991. It has two independent cabins with sixty places each. Its capacity is 2,000 passengers per hour in each direction. A trip in either direction, which covers a vertical distance of 36 m (118 ft) over a track distance of 108 m (354 ft), takes less than 90 seconds. The funicular is double track at standard gauge of 1,435 mm (4 ft 8 1⁄2 in) and the gradient is as high as 35.2% (a little steeper than 1:3).
The technology of the funicular is derived from that of standard elevators, which allows each car to function independently, with its own hoist and cables. This allows one car to remain in service if the other must be taken out of service for maintenance. At busy times, both cabins can ascend at the same time (usually, more passengers use the funicular to ascend than to descend).[2]
The see-through stations were designed by the architect François Deslaugiers, while the new cabins with their distinctive glass sections were by the industrial designer Roger Tallon, who also designed the carriages of the TGV Atlantique. The cabin roofs are partly glazed, which allows a view while in transit of the Montmartre Basilica or the panorama over Paris.[2]
History

The Paris city government voted to construct the Montmartre funicular in 1891. Initially, operation of the funicular was subcontracted to Decauville through a concession that ended in 1931.[3] Thereafter, the Société des transports en commun de la région parisienne (STCRP) took control, and this was nationalized together with the Compagnie du chemin de fer métropolitain de Paris (CMP) to form the Régie autonome des transports parisiens (RATP), which continues to operate the funicular today.
The original funicular was water-powered, using a system of cisterns of 5 m3 (180 cu ft) each that were filled or emptied to move the cars and to compensate for passenger load. In 1935, the system was converted to electricity. The funicular was completely rebuilt by the RATP in 1990–1991.
The funicular was shut down after a minor accident during tests by the RATP in December 2006. It reopened in July 2007.
Chronology
- 5 June 1891: Decision to create a funicular at Montmartre
- 12 or 13 July 1900: Inauguration of the first water-driven funicular
- 1 November 1931: Closure of the water-driven funicular
- 2 February 1935: Opening of the electric funicular
- 1 October 1990: Closure of the funicular for the second renovation
- 5 October 1991: Opening of the modern funicular
- 7 December 2006: Accident during a brake load test, without passengers
Origins
The construction of the Montmartre funicular was decided upon by the Paris municipal council in 1891. It was built to serve the Sacré-Cœur Basilica at the summit of the outlier of Montmartre and was inaugurated on 5 June 1891. If built according to the plan of the project selected initially the funicular would have used electrical traction and had a much longer route, serving six stations as well as two termini.[4] It ended up being far more modest with only two terminal stations, and using water-filled counterweights for motion.
The funicular entered service on 12[5] or 13 July (sources vary), and its operation was handed over to the Decauville company with a contract lasting until 1931. However, lacking the necessary authorisation from the Paris Prefecture of Police to run the service, the company had to close the funicular from 24 November 1900[6] until 22 May 1901.[7]
The funicular was of double track at standard gauge, using the Strub rack system for braking. The rails were supported by sleepers made of structural steel, supported on concrete pedestals.[8]
The system was powered by two sealed water tanks with a capacity of 5 m3 (180 cu ft) placed underneath the floor of each cabin. The cabin's tank was refilled at the upper station which allowed its descent under gravity with the combined weight of the passengers and the water, enabling the other carriage to ascend. A steam engine situated at the lower station worked the filling pumps at the upper station. The cabins had a capacity of forty-eight passengers in four closed compartments arranged like a staircase; the two end platforms were reserved for the driver and brakeman. These were retained for a brake system established on the rack railway. This system transported a million passengers a year for some thirty years.
First renovation, 1931
When the contract expired, the Mayor of Paris and the Seine Department charged the Société des transports en commun de la région parisienne (STCRP) with running the service and modernising the infrustructure. The rack system was deemed too dangerous and so the initial system was shut down; operations ceased on 1 November 1931. The water-driven system was replaced by two electrically driven cabins and reopened on 2 February 1935 after an interruption of more than three years.[9] Traction was provided by a winch driven by a 50 hp (37 kW) electric motor, allowing a cabin holding fifty people to make the journey in 70 seconds at a speed of 2 m/s (4.5 mph). The cabins were no longer arranged like a staircase but composed of a single compartment with a horizontal floor.
By 1955, the line was in service from 7 am until 9 pm in winter and until 11 pm in summer, entry to the station being made by cancelling a bus ticket.[10] In 1962, the funicular transported 1,600,000 passengers and operations were suspended for some weeks for a new renovation. The line was opened in the presence of "poulbots" (Parisian illustrators) and Émile Kérembrun, the President of the République de Montmartre, a philanthropic society.[11]
Second renovation, 1991
After fifty-five years of operation, transporting two million passengers annually, the funicular was in need of renovation. A novel idea was proposed by the RATP and the Mairie de Paris: lengthen the line with a tunnel to the Anvers métro station. The idea was abandoned due to its high cost.
The RATP entirely rebuilt the funicular in 1990–1991 on the same design. Operations ceased on 1 October 1991, being substituted with a minibus service, the "Montmartrobus", between the Place Pigalle and the top of the butte, until the new funicular entered service on 5 October 1991. The old stations were demolished and rebuilt to the designs of the architect François Deslaugiers, being largely of glass and transparent. The works were undertaken by Schindler Group, a lift manufacturer, and cost 43.1 million francs.[12]
Since its latest renovation, the funicular uses angled lift technology with electrical traction and is no longer a funicular in the proper sense: it no longer functions with the traditional alternative movement of funiculars (where the descending cabin acts as a counterweight to the ascending one). The machinery resides in the higher station; it is composed of two totally independent AKROS winches powered by 130 kW (170 hp) motors. The cabins each weigh 6 tonnes (5.9 long tons; 6.6 short tons) unladen, 10 tonnes (9.8 long tons; 11 short tons) when full. They have a service brake and an emergency brake. The carriages and chassis were made by Skirail, and the electrics by Poma.
Operation is entirely automatic: The presence and number of passengers are detected by a system combining electronic balance scales mounted in the cabin floor, and radar in the stations. A computer determines the cabin's departure, indicated with a display board in the cabin. According to the amount of passenger traffic, it chooses between the two possible operating speeds, 2 m/s (6.6 ft/s) or 3.5 m/s (11 ft/s). For safety, the platform edge doors open only when a cabin is present, as on the Paris Métro Line 14 and some stations on London's Jubilee line.[13]
On 7 December 2006 at 5.50 pm, a cabin crashed down the slope during a brake system test by the RATP.[14][15] The terminal of the lifting cable broke. The service was suspended, adding to the problems of the residents and traders on the butte, the first having to make do with a less-frequent replacement bus service, the second seeing their trading levels fall (20–30% lower than for December 2006 [sic]) from having fewer tourists. One of the two cabins was put back in service on 30 June 2007,[16] the other on 2 August 2008.[17]
Operation

The funicular is considered to be part of the Paris Métro network,[18] and so has similar pricing. The two stations each have turnstiles which can read magnetic tickets and Navigo passes. They thus allow access via all RATP payment methods, including the single-journey Ticket "t", Paris Visite combination transport/museum pass and other RATP weekly and monthly passes.
There is no direct transport interchange, except with the "Montmartrobus" which has a stop in the Rue du Cardinal-Dubois in front of the upper station and offers a free interchange. Nevertheless, two métro stations are within easy walking distance of the lower station: Anvers on Line 2 about 200 m (220 yd) to the south and Abbesses on Line 12 about 350 m (380 yd) to the west.
The funicular is considered a special line not coming under the Ticket T+ fare rules for interchanges; a passenger coming from the Métro with an already-cancelled Ticket T+ must use a second ticket for the funicular, and vice versa.[19]
The Codes d'oblitération ("Allocation codes") of the lower and upper stations are respectively 31-02 and 31-03. Code 31 corresponds to the Quartier Pigalle, or FUNB and FUNH.[20]
Finance

The RATP finances the line's operation (maintenance, infrastructure and cost of personnel). Fares are set by political decisions which do not cover the true cost of transportation. The loss is made good by the controlling authority, the Syndicat des transports d'Île-de-France (STIF), which since 2005 has been under the control of the Conseil régional d'Île-de-France ("Île-de-France Regional Council") and composed of local representatives. It defines the general conditions of operation and the duration and frequency of services. Losses are made good by an annual block grant to regional transport operators funded by the versement transport ("Transport payment"), a tax raised on companies with more than nine employees. Public bodies also contribute.[21]
Projects
Given the interest in the technical solution provided by the funicular for public passenger transport over relatively short and extremely steep routes, studies have called for the RATP to build similar systems, notably at Issy-les-Moulineaux, in the renovation project of the Fort d'Issy quarter, and to link the Meudon-sur-Seine station on Paris Tramway Line 2 with the Gare de Bellevue, which would recreate the old Bellevue funicular at Meudon, demolished in 1934.
Popular culture
The funicular is an essential element in Paris life, and thus appears in many films and television series having Montmartre as a theme. One of the most famous is Ripoux contre ripoux (1990), starring Thierry Lhermitte and Philippe Noiret,[22][23] and it also appears in Les Randonneurs (1997),[24] El Tourbini (2006)[25] and Louise (take 2) (1998).[23]
In the first pilot episode of the police series Capitaine Casta, a chase takes place on the Rue Foyatier steps alongside the funicular; the character played by Jean-Pierre Castaldi runs up it to catch the crooks. Similarly in the film Une affaire d'État (2009), Michel Fernandez (Thierry Frémont) flees by the stairs, chased by Nora Chahyd (Rachida Brakni) who takes the funicular.[26]
Jean-Pierre Melville opened his film Bob le flambeur (1956) with a tracking shot around the Montmartre quarter where the film is set, and voiceover then says "c'est tout à la fois le ciel [shot over the Basilique du Sacré-Coeur] et... [bird's eye view of the funicular descending, with music poco a poco fortissimo] ... l'enfer [Shot of the Place Pigalle]" ("It is at one and the same time heaven ... and ... hell").[27]
The funicular figures in an eponymous work by Jean Marchand (1883–1940), on view at the Musée d'Art Moderne de la Ville de Paris.[28] It appears in literature in a short story by Boileau-Narcejac titled L’énigme du funiculaire ("The enigma of the funicular"), published in 1971 in the review Manigances, and also in the works of Jacques Charpentreau who, in a poem entitled Le funiculaire de Montmartre, compares the cabins to two contrary brothers: Quand l'un s'envole dans les airs/ L'autre se précipite en bas/ Et lan lan la ("When one flies into the air, the other falls to the ground/ And la, la la").[29]
It appears in the video game Midnight Club 2 (2003).
In October 2006, at the request of the website la Blogothèque for its "concerts à emporter" ("concerts to download"), the singer Cali made an appearance in one of the funicular's cabins surrounded by passengers, singing her song La Fin du monde pour dans 10 minutes ("The end of the world in ten minutes") from the album Menteur as it ascended.[30]
The funicular appears, next to the Sacré-Cœur, in many miniature parks, such as France Miniature at Élancourt (where it was added twice) and Mini-Europe at Brussels.
See also
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Funiculaire de Montmartre. |
- Funicular
- Inclined railway
- List of Paris metro stations
- Montmartre
- RATP
See also
References
- ↑ Buffier, Dominique (8 July 2007). "Le funiculaire de Montmartre a repris son service" [Montmartre funicular resumes service]. Le Monde (in French).
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Andrew Ayers (2004). The architecture of Paris: an architectural guide. Axel Menges. p. 257. ISBN 978-3-930698-96-7.
- ↑ Philippe Mellot (2006). Paris au temps des fiacres [Paris at the time of hackney carriages] (in French). Editions de Borée. p. 10. ISBN 978-2-84494-432-0.
- ↑ Figuier, Louis, ed. (1893). "Projet de chemin de fer funiculaire de Montmartre à traction électrique" [Montmartre funicular railway project with electrical traction]. L'Année scientifique et industrielle ("The year in science and industry") (in French) (Bibliothèque nationale de France) (36th (1892)): 219–220. Retrieved 8 August 2010.
- ↑ Maïstre, Henri (1901). "12 July entry in the Chronique de l'année 1900". Bulletin de la Société de l'histoire de Paris et de l'Île-de-France ("Bulletin of the Paris and Île-de-France History Society") (in French) (Bibliothèque nationale de France): 176. Retrieved 9 August 2010.
- ↑ Maïstre, Henri (1901). "24 November entry in the Chronique de l'année 1900". Bulletin de la Société de l'histoire de Paris et de l'Île-de-France (in French) (Bibliothèque nationale de France): 180. Retrieved 9 August 2010.
- ↑ Maïstre, Henri (1901). "22 March entry in the Chronique de l'année 1901". Bulletin de la Société de l'histoire de Paris et de l'Île-de-France (in French) (Bibliothèque nationale de France): 152. Retrieved 9 August 2010.
- ↑ Robert 1992, p. 207.
- ↑ "Humpbacked Cars Used On Incline". Popular Science Monthly: 32. July 1935. Retrieved 14 March 2012.
- ↑ Patrimoine 1996, p. 218.
- ↑ Gennesseaux 1992, p. 33.
- ↑ Gennesseaux 1992, p. 34.
- ↑ Gennesseaux 1992, p. 35.
- ↑ "Communiqué de la RATP – Interruption du funiculaire de Montmartre" (PDF) (in French). RATP. Retrieved 10 August 2010.
- ↑ "The Montmartre funicular is still stopped!". Funimag.com (in English and French). 7 January 2007. Retrieved 10 August 2010.
- ↑ "Communiqué de la RATP – Reprise de l’exploitation le 30 juin 2007 sur une cabine" (PDF) (in French). RATP. Archived from the original (PDF) on 27 October 2007. Retrieved 10 August 2010.
- ↑ "Communiqué de la RATP – Funiculaire de Montmartre: Reprise de l'exploitation de la 2ème cabine" (PDF) (in French). RATP. Retrieved 10 August 2010.
- ↑ "Cahier des charges de la Régie autonome des transports parisiens" [Specifications of the RATP] (PDF). stif.info (in French). STIF. 22 November 2005. p. 18. Retrieved 10 August 2010.
|chapter=ignored (help) - ↑ Decision 2007/463 of 28 June 2007 by the Director-General of the SITF. "Relative aux conditions génerales de vente et de utilisation du ticket t+" [Relating to the general conditions of sale and use of the Ticket T+] (PDF) (in French). STIF. 28 June 2007. p. 2. Retrieved 10 August 2010.
|chapter=ignored (help) - ↑ Baro, Aurélien. "Les codes d'oblitération du métro" [Métro allocation codes]. Personal website. Retrieved 10 August 2010.
- ↑ "Le financement des transports franciliens" [Île-de-France transport funding] (in French). STIF. 2007. Retrieved 10 August 2010.
- ↑ "Ripoux contre ripoux". l2tc.com (in French and English). Retrieved 10 August 2010.
- ↑ 23.0 23.1 Lemonier, Marc (2008). Paris des films cultes: Les films qui y sont tournés, les acteurs qui en foulent les pavés [Paris in cult films: Films made there, the actors who walk its streets]. Le Guide (in French). Bonneton. pp. 175–176. ISBN 978-2-86253-436-7.
- ↑ "Les Randonneurs". l2tc.com (in French and English). Retrieved 10 August 2010.
- ↑ "El Tourbini". l2tc.com (in French and English). Retrieved August 2010.
- ↑ Chapuys, Sébastien (24 November 2009). "Que de la gueule: Une affaire d'État" [Word of mouth: Une affaire d'Etat]. Critikat.com (in French). Retrieved 10 August 2010.
- ↑ Nichols, Jay (29 January 2002). "Pierre Melville: Bob le flambeur" (in French). Retrieved 10 August 2010. Transcription on a viewer's personal website
- ↑ Marchand, Jean (1956 (acquisition)). "Funiculaire de Montmartre" (in French). Réunion des musées nationaux ("National Museums Association"). Retrieved 10 August 2010. Check date values in:
|date=(help) - ↑ "Transcription in a document from the Brisbane Alliance française" (PDF). Retrieved 10 August 2010.
- ↑ "Les concerts à emporter: No. 31 Cali". La Blogothèque (in English and French). 15 January 2007. Retrieved 10 August 2010.
Sources
- Various (1996). Le patrimoine de la RATP [Heritage of the RATP]. Le patrimoine des institutions économiques ("Heritage of economic institutions") (in French). Charenton-le-Pont: Flohic. ISBN 978-2-84234-007-0.
- Gennesseaux, Jean (1992). Funiculaires et crémaillères de France [French funiculars and rack railways] (in French). Paris: La Vie du Rail. ISBN 978-2-902808-42-7.
- Robert, Jean (1992). Les tramways parisiens [Paris tramways] (3rd ed.). ASIN B00175PCGO.
External links
- Virtual tour in 360 degrees Use the mouse to turn around.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
