Monarchy of Barbados
| Queen of Barbados | |
|---|---|
|
| |
| Incumbent | |
 | |
| Elizabeth II | |
| Details | |
| Style | Her Majesty |
| Heir apparent | Charles, Prince of Wales |
| First monarch | Elizabeth II |
| Formation | 30 November 1966 |
 |
| This article is part of a series on the politics and government of Barbados |
| Constitution |
|
|
|
|
Administrative divisions |
|
|
|
Politics portal |
The monarchy of Barbados is the core of the country's Westminster style parliamentary democracy,[1][2] being the foundation of the executive, legislative, and judicial branches of the government. The current Barbadian monarch, since 6 February 1952, is Queen Elizabeth II. As the sovereign, she is the personal embodiment of the Barbadian Crown. Although the person of the sovereign is equally shared with 15 other independent countries within the Commonwealth of Nations, each country's monarchy is separate and legally distinct. As a result, the current monarch is officially titled Queen of Barbados and, in this capacity, she, her consort, and other members of the Royal Family undertake public and private functions domestically and abroad as representatives of the Barbadian state. However, the Queen is the only member of the Royal Family with any constitutional role. The Queen lives predominantly in the United Kingdom and, while several powers are the sovereign's alone, most of the royal governmental and ceremonial duties in Barbados are carried out by the Queen's representative, the governor-general.
Some of the powers of the Crown are exercisable by the monarch (such as appointing governors-general), others by the governor-general (such as calling parliamentary elections), and some others by either figure (such as giving or withholding Royal Assent to bills). Further, the royal sign-manual is required for letters patent and orders in council. But, the authority for these acts stems from the Barbadian populace and, within the conventional stipulations of constitutional monarchy, the sovereign's direct participation in any of these areas of governance is limited, with most related powers entrusted for exercise (via advice or direction to the monarch or the viceroy) by the elected and appointed parliamentarians, the ministers of the Crown generally drawn from amongst them, and the judges and justices of the peace. The Crown today primarily functions as a guarantor of continuous and stable governance and a nonpartisan safeguard against the abuse of power.
The historical roots of the Barbadian monarchy date back to approximately the early 15th century, when King James IV of Scotland and I of England made the first claims to Barbados. Monarchical governance thenceforth evolved under a continuous succession of British sovereigns and eventually the Barbadian monarchy of today.
International and domestic aspects
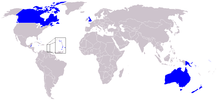
The person who is the Barbadian sovereign is equally shared with 15 other monarchies (a grouping, including Barbados, known informally as the Commonwealth realms) in the 54-member Commonwealth of Nations, with the monarch residing predominantly in the oldest and most populous realm, the United Kingdom, and a viceroy acting as the sovereign's representative in Barbados. This arrangement emerged among the older realms after the end of the First World War and is governed by the Statute of Westminster 1931. Since then, the pan-national Crown has had both a shared and a separate character and the sovereign's role as monarch of Barbados has been, since Barbados' independence in 1966, distinct to his or her position as monarch of any other realm, including the United Kingdom.[n 1][4] Only Barbadian ministers of the Crown may advise the sovereign on all matters of the Barbadian state.[4] The monarchy thus ceased to be an exclusively British institution and in Barbados became a Barbadian, or "domesticated",[5] establishment.
This division is illustrated in a number of ways: The sovereign, for example, holds a unique Barbadian title and, when she is acting in public specifically as a representative of Barbados, she will use, where possible, Barbadian symbols, including the country's national flag, unique royal symbols, and the like. The sovereign similarly only draws from Barbadian coffers for support in the performance of her duties when in Barbados or acting as Queen of Barbados abroad; Barbadians do not pay any money to the Queen, either towards personal income or to support royal residences outside of Barbados. This applies equally to other members of the Royal Family. Normally, tax dollars pay only for the costs associated with the governor-general in the exercise of the powers of the Crown, including travel, security, residences, offices, and ceremonies.
Succession
Succession in Barbados is deferred to the laws of the United Kingdom; whomever is monarch of the UK is automatically also monarch of Barbados. Succession in Britain is, for those born before 28 October 2011, by male-preference primogeniture and, for people born after 28 October 2011, by absolute primogeniture, governed by common law, the Act of Settlement 1701, Bill of Rights 1689, and Succession to the Crown Act 2013. This legislation limits the succession to the natural (i.e. non-adopted), legitimate descendants of Sophia, Electress of Hanover, and stipulates that the monarch cannot be a Roman Catholic and must be in communion with the Church of England upon ascending the throne. Though these constitutional laws still lie within the control of the British parliament, via adopting the Statute of Westminster, the United Kingdom agreed not to change the rules of succession without the unanimous consent of the other realms, unless explicitly leaving the shared monarchy relationship;[6] a situation that applies symmetrically in all the other realms and which has been likened to a treaty among these countries.[7] Barbados last indicated its consent to alteration to the line of succession in 2015, when the Governor-General-in-Council brought into force the Succession to the Throne Act, 2013, which signified the legislature's acquiescence to the British Succession to the Crown Bill 2013.[8]

Upon a demise of the Crown (the death or abdication of a sovereign), the late sovereign's heir immediately and automatically succeeds, without any need for confirmation or further ceremony; hence arises the phrase "The King is dead. Long live the King!" Following an appropriate period of mourning, the monarch is also crowned in the United Kingdom, though this ritual is not necessary for a sovereign to reign; for example, Edward VIII was never crowned, yet was undoubtedly king during his short time on the throne. All incumbent viceroys, judges, civil servants, legislators, military officers, etc., are not affected by the death of the monarch. After an individual ascends the throne, he or she typically continues to reign until death. Monarchs are not allowed to unilaterally abdicate; the only monarch to abdicate, Edward VIII, did so before Barbados was independent and, even then, only with the authorization of the governments of the United Kingdom and the then Dominions and special Acts of Parliament in each, as well as the UK.
Personification of the state
Today the sovereign is regarded as the personification, or legal personality, of the Barbadian state. Therefore, the state is referred to as Her Majesty the Queen in Right of Barbados; the state is referred to as such, or simply Regina, if a lawsuit is filed against the government. The monarch, in his or her position as sovereign, and not as an individual, is thus the owner of all state lands (called Crown land), buildings and equipment (called Crown held property), state-owned companies (called statutory bodies or Crown Corporations), and the copyright for all government publications (called Crown copyright), as well as guardianship of foster children (called Crown wards). Government staff (the Civil Service) are also employed by the monarch, as are the governor-general, judges, members of the Barbados Defence Force, police officers, and parliamentarians. Hence, many employees of the Crown are required by law to recite an oath of allegiance to the monarch before taking their posts, in reciprocation to the sovereign's Coronation Oath, wherein he or she promises "to govern the Peoples of... [Barbados]... according to their respective laws and customs".[9] The oath required by the Director of Public Prosecutions, for example, is: "I, [name], do swear that I will well and truly serve Her Majesty Queen Elizabeth II, Her Heirs and Successors, in the office of Director of Public Prosecutions. So help me God", while that for judges is: "I, [name], do swear that I will well and truly serve Our Sovereign Lady Queen Elizabeth II, Her Heirs and Successors, in the office of Chief Justice/Judge of the Supreme Court and I will do right to all manner of people after the laws and usages of Barbados without fear or favour, affection or ill will. so help me God."[10]
Constitutional role

Barbados' constitution gives the country a similar parliamentary system of government to the other Commonwealth realms, wherein the role of the monarch and governor-general is both legal and practical, but not political. The Crown is regarded as a corporation, in which several parts share the authority of the whole, with the sovereign as the person at the centre of the constitutional construct,[11] meaning all powers of state are constitutionally reposed in the monarch, who is represented by the governor-general, appointed by the monarch on the advice of the Prime Minister of Barbados.[12] The constitution requires most of the Queen's domestic duties to be performed by her viceregal representative.
All institutions of government are said to act under the sovereign's authority; the vast powers that belong to the Crown are collectively known as the Royal Prerogative. Parliamentary approval is not required for the exercise of the Royal Prerogative; moreover, the consent of the Crown must be obtained before either of the houses of parliament may even debate a bill affecting the sovereign's prerogatives or interests. While the Royal Prerogative is extensive, it is not unlimited; for example, the monarch does not have the prerogative to impose and collect new taxes—such an action requires the authorization of an Act of Parliament. The government of Barbados is also thus formally referred to as Her Majesty's Government. Further, the constitution instructs that any change to the position of the monarch, or the monarch's representative in Barbados, requires the consent of two-thirds of the all the members of each house of parliament.[2][13]
Executive (Queen-in-Council)
One of the main duties of the Crown is to appoint a prime minister,[2] who thereafter heads the Cabinet and advises the monarch or governor-general on how to execute their executive powers over all aspects of government operations and foreign affairs;[2] this requirement is constitutionally enshrined in Barbados,[14] unlike in other Commonwealth realms, where it is a matter of convention. Though the monarch's power is still a part of the executive process—the operation of the Cabinet is technically known as the Queen-in-Council (or Governor-in-Council)—the advice tendered is typically binding. Since the death of Queen Anne in 1714, the last monarch to head the British Cabinet, the monarch reigns but does not rule. This means that the monarch's, and thereby the viceroy's, role is almost entirely symbolic and cultural, acting as a symbol of the legal authority under which all governments and agencies operate, while the Cabinet directs the use of the Royal Prerogative, which includes the privilege to declare war, maintain the Queen's peace, and direct the actions of the Barbados Defence Force, as well as to summon and prorogue parliament, and call elections. However, it is important to note that the Royal Prerogative belongs to the Crown, and not to any of the ministers, though it may sometimes appear that way,[11] and the governor-general may unilaterally use these powers in exceptional, constitutional crisis situations. There are also a few duties which must be specifically performed by, or bills that require assent by, the Queen. These include signing the appointment papers of governors-general, the creation of Barbadian honours, and the approval of any change in her Barbadian title.
In accordance with convention, the governor-general, to maintain the stability of government, must appoint as prime minister the individual most likely to maintain the support of the House of Assembly; usually this is the leader of the political party with a majority in that house, but also when no party or coalition holds a majority (referred to as a minority government situation), or other scenarios in which the governor-general's judgement about the most suitable candidate for prime minister has to be brought into play. The governor-general also appoints to Cabinet the other ministers of the Crown, who are, in turn, accountable to the democratically elected House of Assembly and, through it, to the people. The Queen is informed by her viceroy of the acceptance of the resignation of a prime minister and the swearing-in of a new prime minister and other members of the ministry, she remains fully briefed through regular communications from her Barbadian ministers, and she holds audience with them where possible.[4]
Members of various executive agencies and other officials are appointed by the Crown. The commissioning of privy councillors, senators, the Speaker of the Senate, and Supreme Court justices also falls under the Royal Prerogative, though these duties are specifically assigned to the governor-general by the constitution.[15] Public inquiries are also commissioned by the Crown through a Royal Warrant and are called Royal Commissions.
The Royal Prerogative also extends to foreign affairs: the sovereign or governor-general negotiates and ratifies treaties, alliances, and international agreements. As with other uses of the Royal Prerogative, no parliamentary approval is required; however, a treaty cannot alter the domestic laws of Barbados; an Act of Parliament is necessary in such cases. The governor-general, on behalf of the Queen, also accredits Barbadian High Commissioners and ambassadors and receives diplomats from foreign states. In addition, the issuance of passports falls under the Royal Prerogative and, as such, all Barbadian passports are issued in the monarch's name.
Parliament (Queen-in-Parliament)

The sovereign, along with the Senate and the House of Assembly, is one of the three components of parliament,[16] called the Queen-in-Parliament. The authority of the Crown therein is embodied in the mace, which bears a crown at its apex; unlike other realms, however, the Barbados parliament only has a mace for the lower house.[17] Per the constitution, the monarch does not, however, participate in the legislative process; the viceroy does, though only in the granting of Royal Assent.[18] Further, the constitution outlines that the Governor-General alone is responsible for summoning, proroguing, and dissolving parliament,[19] after which the writs for a general election are usually dropped by the Governor-General at Government House. The new parliamentary session is marked by the State Opening of Parliament, during which either the monarch or the Governor-General reads the Speech from the Throne. As the monarch and viceroy cannot enter the House of Assembly, this, as well as the bestowing of Royal Assent, takes place in the Senate chamber; Members of Parliament are summoned to these ceremonies from the Commons by the Crown's messenger, the Usher of the Black Rod, after he knocks on the doors of the lower house that have been slammed closed on him, to symbolise the barring of the monarch from the assembly.
All laws in Barbados are enacted only with the viceroy's, or sovereign's, granting of Royal Assent; usually done by the Governor-General, with the Public Seal. Thus, all bills begin with the phrase "Her Majesty, by virtue and in exercise of the powers vested in Her by section 5 of the Barbados Independence Act 1966 and of all other powers enabling Her in that behalf, is pleased, by and with the advice of Her Privy Council, to order, and it is hereby ordered, as follows..."[20]
Courts (Queen-on-the-Bench)
The sovereign is deemed the fount of justice, and is responsible for rendering justice for all subjects, known in this role as the Queen on the Bench. However, he or she does not personally rule in judicial cases; instead, judicial functions are performed in his or her name. Hence, the common law holds that the sovereign "can do no wrong"; the monarch cannot be prosecuted in his or her own courts for criminal offences. Civil lawsuits against the Crown in its public capacity (that is, lawsuits against the government) are permitted; however, lawsuits against the monarch personally are not cognizable. In international cases, as a sovereign and under established principles of international law, the Queen of Barbados is not subject to suit in foreign courts without her express consent. The sovereign, and by extension the Governor-General, also exercises the prerogative of mercy,[21] and may pardon offences against the Crown, either before, during, or after a trial. In addition, the monarch also serves as a symbol of the legitimacy of courts of justice, and of their judicial authority. An image of the Queen or the Arms of Her Majesty in Right of Barbados is always displayed in Barbadian courtrooms. Judges have a pair of white gloves from the Queen on display on the edge of the bench, and in Barbados this marks the authority of the court similar to the Ceremonial mace of Parliament.
Cultural role
From the beginning of Queen Elizabeth II's reign onwards, royal symbols in Barbados were altered or new ones created to make them distinctly Barbadian, such as the creation of the Royal Arms of Barbados in 1966 (presented on 14 February that year by the Queen to then President of the Senate Sir Grey Massiah),[22][23] and Queen's Royal Standard for Barbados, created in 1975.[24]
The main symbol of the monarchy is the sovereign herself. Thus, her image appears in portraits in public buildings, and on stamps.[25][26] A crown is also used to illustrate the monarchy as the locus of authority, appearing on police force and Barbados Defence Force regimental and maritime badges and rank insignia, as well as Barbadian honours, the system of such created through Letters Patent issued by Queen Elizabeth II in July 1980.[23] The Queen's Personal Barbadian Flag is the symbol of the monarch. Second in precedence is the personal flag of the Governor-General.
Stability
A claim made by supporters of the monarchy is that the Queen "keeps the line of stability open."[27] When Barbados become independent in 1966, the cold war threat meant small islands in the region were unusually vulnerable to coup d'états or invasions by foreign powers.[28] The Queen's continued association to Barbados meant that if the country were ever invaded, the Constitution's provisions for empowering the Monarchy with reserve powers should mean the continuity of the executive authority as the Queen is located safely across the Atlantic Ocean.[29][30][31][32] This is especially useful if the entire government became incapacitated or was unable to function.[33] Such a continuation of the executive authority for Barbados has not been tested; however, it may have helped if the Operation Red Dog-invasion plot which targeted the Commonwealth of Dominica and likely Barbados[34] was not halted. By virtue of the Monarch not being located within Barbados means more difficulty for the entire Barbados government to overthrown. Outside of war, The Constitution also allows such a "period of public emergency" to be called: as a result of "the occurrence of any earthquake, hurricane, flood, fire, outbreak of pestilence, outbreak of infectious disease or other calamity, whether similar to the foregoing or not; or that action has been taken or is immediately threatened by any person of such a nature and on so extensive a scale as to be likely to endanger the public safety or to deprive the community, or any substantial portion of the community, of supplies or services essential to life."[29] During such a period, Parliament (to which the Monarchy is a member) may meet to pass by majority a resolution either extending the period of emergency or terminating it and the issuing of a writ to proceed towards elections for the filling of seats to the Parliament and/or the selecting of a Governor-General.[35]
History
The current Barbadian monarchy can trace its ancestral lineage back to the Anglo-Saxon period and, ultimately, back to the kings of the Angles and the early Scottish kings. The Crown in Barbados has grown over the centuries since the Barbados was claimed under King James VI of Scotland and I of England in 1625, though not colonised until 1627, when, in the name of King Charles I, Governor Charles Wolferstone established the first settlement on the island.[36] By the 18th century, Barbados became one of the main seats of British authority in the British West Indies, though, due to the economic burden of duties and trade restrictions, some Barbadians, including the Clerk of the General Assembly, attempted to declare in 1727 that the Act of Settlement 1701 had expired in the colony, since the Governor, Henry Worsley, had not received a new commission from King George II upon his accession to the throne. Thus, they refused to pay their taxes to a governor they recognised as having no authority. The Attorney and Solicitor General of Great Britain confirmed that Worsley was entitled to collect the dues owed, but, Worsley resigned his post before the directive arrived in Barbados.[37]
After attempting in 1958 a federation with other West Indian colonies, similar to that of fellow Commonwealth realms Canada and Australia, continued as a self-governing colony under the Colonial Office, until independence came with the signing of the Barbados Independence Order by Queen Elizabeth II. In the same year, Elizabeth's cousin, Prince Edward, Duke of Kent, opened the second session of the first parliament of the newly established country,[36] before the Queen herself, along with her husband, Prince Philip, Duke of Edinburgh, toured Barbados, opening Barclays Park,[38] in Saint Andrew, amongst other events. Elizabeth returned for her Silver Jubilee in 1977, after addressing the new session of parliament, she departed on the Concorde, which was the Queen's first supersonic flight.[36] She also was in Barbados in 1989, to mark the 350th anniversary of the establishment of the Barbados parliament, where she sat to receive addresses from both houses.[4][36]
Republicanism
Former Prime Minister Owen Arthur called for a referendum on becoming a republic to be held in 2005.[39] It was announced on 26 November 2007 that the referendum would be held in 2008, together with the general election.[40] On 2 December 2007, reports emerged that this vote was put off due to concerns raised by the Electoral and Boundaries Commission.[41] Following the election, David Thompson replaced Arthur as prime minister.
On 22 March 2015, Prime Minister Freundel Stuart announced his intention to move the country towards a republican form of government "in the very near future".[42] The general secretary of the Democratic Labour Party, George Pilgrim, confirmed the move and said that it is exepected to coincide with the 50th anniversary of Barbadian independence in 2016.[43] According to the country's constitution, a two-thirds majority in parliament is needed to authorize the change; The Democratic Labour Party has a two-thirds majority in the Senate, but not in the House of Assembly, where it would need the support of the opposition Barbados Labour Party to approve the transition. Opposition leader Mia Mottley has not commented on the prime minister's proposal.[44]
See also
- Prime Ministers of Queen Elizabeth II
- List of Commonwealth visits made by Queen Elizabeth II
- Monarchies in the Americas
- List of monarchies
- List of current state leaders by date of assumption of office
Notes
- ↑ The English Court of Appeal ruled in 1982, while "there is only one person who is the Sovereign within the British Commonwealth... in matters of law and government the Queen of the United Kingdom, for example, is entirely independent and distinct from the Queen of Canada."[3]
Citations
- ↑ "Barbados". Caribbean Court of Justice.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 "Barbados: Constitution". Commonwealth Secretariat.
- ↑ R v Foreign Secretary, Ex parte Indian Association (as referenced in High Court of Australia: Sue v Hill [1999] HCA 30; 23 June 1999; S179/1998 and B49/1998), QB 892 at 928 (English Court of Appeal June 1999).
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 Royal Household. "The Queen and Commonwealth > Other Caribbean Realms". Queen's Printer.
- ↑ Mallory, J.R. (August 1956). "Seals and Symbols: From Substance to Form in Commonwealth Equality". The Canadian Journal of Economics and Political Science (Montreal: Blackwell Publishing) 22 (3): 281–291. ISSN 0008-4085. JSTOR 138434.
- ↑ Mackinlay, Andrew (10 Mar 2005). "Early day motion 895: MORGANATIC MARRIAGE AND THE STATUTE OF WESTMINSTER 1931". British Parliament. Retrieved 2011-11-05.
- ↑ Justice Rouleau in a 2003 court ruling wrote that "Union under the ... Crown together with other Commonwealth countries [is a] constitutional principle". O’Donohue v. Canada, 2003 CanLII 41404 (ON S.C.)
- ↑ Elizabeth II (2013), An Act to provide for the Parliament of Barbados to acquiesce to alterations in the law relating to the succession to the Throne of the United Kingdom (PDF), Bridgetown: Government Information Service, retrieved 31 March 2015
- ↑ The Form and Order of Service that is to be performed and the Ceremonies that are to be observed in the Coronation of Her Majesty Queen Elizabeth II in the Abbey Church of St. Peter, Westminster, on Tuesday, the second day of June, 1953
- ↑ Constitution of Barbados; First Schedule
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 Cox, Noel; Murdoch University Electronic Journal of Law: Black v Chrétien: Suing a Minister of the Crown for Abuse of Power, Misfeasance in Public Office and Negligence; Volume 9, Number 3 (September 2002)
- ↑ Constitution of Barbados; Ch. IV.28
- ↑ Parliament of Barbados: The Constitution
- ↑ Constitution of Barbados; Ch. VI.63.1 through 71
- ↑ Constitution of Barbados; various
- ↑ Constitution of Barbados; Ch. V.35
- ↑ The Barbados Parliament: The Mace of the House of Assembly
- ↑ Constitution of Barbados; Ch. V.58.1
- ↑ Constitution of Barbados; Ch. V.61.1 & 61.2
- ↑ Barbados Independence Order; 1966 No. 1455
- ↑ Constitution of Barbados; Ch. VI.78.1 through 78.4
- ↑ National Symbols: Barbados
- ↑ 23.0 23.1 The Barbados Parliament: Independence
- ↑ Flags of the World: Flag of Queen Elizabeth II in Barbados
- ↑ Barbados Postal Service: The Golden Jubilee
- ↑ Barbados Postal Service: The Golden Jubilee Souvenir Sheet
- ↑ Barbados, Anglican Church Worldwide
- ↑ Caribbean Islands-The Postwar Strategic Vacuum Mongabay
- ↑ 29.0 29.1 Constitution of Barbados, Chapter III, Section 25 of the Constitution outlines the powers of the Monarch and their representative the Governor General during a "period of public emergency".
- ↑ Constitution of Barbados, Chapter IV, Section 28–29 of the Constitution. Sections 28–29 speaks of the Governor-General's ability to operate in-place of the Monarch.
- ↑ Constitution of Barbados, Chapter VI, Section 63 (1), (2). Section 63 (1) says "The executive authority of Barbados is vested in Her Majesty." and (2) "Subject to the provisions of this Constitution, the executive authority of Barbados may be exercised on behalf of Her Majesty by the Governor General either directly or through officers subordinate to him."
- ↑ Constitution of Barbados, Chapter V, Part I, Section 35. Section 35 Establishes the composition of Parliament, and expressly establishes the Monarch as a composition of Parliament: "There shall be a Parliament of Barbados which shall consist of Her Majesty, a Senate and a House of Assembly."
- ↑ Constitution of Barbados, Chapter IV, Section 29 (1a), (1b), (1c). Establishes provisions should the office of the Governor-General be vacant, or if the Governor-General is absent.
- ↑ A, C (October 4, 2006). "Tull: Tell us about coup rumours". Nation Newspaper. Archived from the original on 2009-10-04. Retrieved 2009-10-04.
- ↑ Constitution of Barbados, Chapter V, Part I, Section 35. Section 35, (2), (3), (4)
- ↑ 36.0 36.1 36.2 36.3 "Parliament's History". The Barbados Parliament.
- ↑ Schomburgk, Robert Hermann (1848). The History of Barbados. London: Longman, Brown, Green, and Longmans. p. 318.
- ↑ Badbados.org: Barbados Places of Interest: Barclays Park
- ↑ Thomas, Norman "Gus" (7 February 2005). "Barbados to vote on move to republic". Caribbean Net News. Retrieved 2006-06-30.
- ↑ Staff writer (26 November 2007). "Referendum on Republic to be bundled with election". Caribbean Broadcasting Corporation. Archived from the original on 2007-11-28. Retrieved 2007-11-27.
- ↑ Gollop, Chris (2 December 2007). "Vote Off". The Nation. Retrieved 2008-06-17.
- ↑ "PM says Barbados moving towards Republic". Jamaica Observer. 23 March 2015. Retrieved 23 March 2015.
- ↑ "Barbados plans to replace Queen with ceremonial president". The Guardian. 23 March 2015. Retrieved 23 March 2015.
- ↑ "Barbados to remove Queen Elizabeth II as titular head of state". Globe and Mail. Associated Press. 23 March 2015. Retrieved 23 March 2015.
References
- Burleigh, Craig (2008). "Queen Elizabeth II Silver Jubilee in Barbados ends with her first flight on Concorde on a record setting flight back to London Heathrow.". Retrieved 16 January 2010.
- Elizabeth II (January 2010). "Queen and Barbados: Royal visits". Retrieved 16 January 2010.
External links
- Queen's Official website on Barbados
- Diamond Jubilee Celebration for Queen Elizabeth II on YouTube, Visits to Barbados by the Royal Family over the decades
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||


