Molisch's test
| Classification | Colorimetric method |
|---|---|
| Analytes | Carbohydrates |
Molisch's test (named after Austrian botanist Hans Molisch) is a sensitive chemical test for the presence of carbohydrates, based on the dehydration of the carbohydrate by sulfuric acid or hydrochloric acid to produce an aldehyde, which condenses with two molecules of phenol (usually α-naphthol, though other phenols (e.g. resorcinol, thymol) also give colored products), resulting in a red- or purple-colored compound.
Procedure
The test solution is combined with a small amount of Molisch's reagent (α-naphthol dissolved in ethanol) in a test tube. After mixing, a small amount of concentrated sulfuric acid is slowly added down the sides of the sloping test-tube, without mixing, to form a layer. A positive reaction is indicated by appearance of a purple ring at the interface between the acid and test layers.
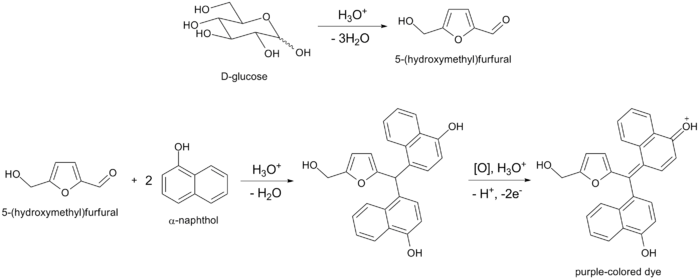
Reaction
All carbohydrates – monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides – should give a positive reaction, and nucleic acids and glycoproteins also give a positive reaction, as all these compounds are eventually hydrolyzed to monosaccharides by strong mineral acids. Pentoses are then dehydrated to furfural, while hexoses are dehydrated to 5-hydroxymethylfurfural. Either of these aldehydes, if present, will condense with two molecules of naphthol to form a purple-colored product, as illustrated below by the example of glucose: