Mistletoebird
| Mistletoebird | |
|---|---|
.jpg) | |
| Male | |
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Passeriformes |
| Family: | Dicaeidae |
| Genus: | Dicaeum |
| Species: | D. hirundinaceum |
| Binomial name | |
| Dicaeum hirundinaceum (Shaw, 1792) | |
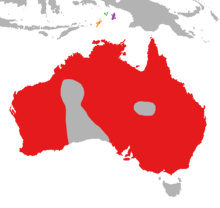 | |
| Distribution map of Dicaeum hirundinaceum hirundinaceum in red, (top-centre:) D. h. keiense in green, D. h. ignicolle in purple, and D. h. fulgidum in orange. | |
The mistletoebird (Dicaeum hirundinaceum), also known as the mistletoe flowerpecker,[2] is a species of flowerpecker native to most of Australia (though absent from Tasmania and the driest desert areas), and also to the eastern Maluku Islands of Indonesia in the Arafura Sea between Australia and New Guinea. They also must live where there are trees and shrubs, so that they can build their nests. The bird eats a variety of different foods such as berries and assorted types of insects.[3]
Taxonomy
Genetic analysis of mitochondrial DNA of 70% of flowerpecker species showed the mistletoebird and red-capped flowerpecker (D. geelvinkianum) to be each other's closest relative.[4]
Subspecies
There are four recognised subspecies, which differ in geographical location and plumage details, primarily of the males:[3]
- Dicaeum hirundinaceum hirundinaceum Shaw & Nodder, 1792 — Australia (extensive red on throat and chest; flanks grey)
- Dicaeum hirundinaceum keiense Salvadori, 1874 — Watubela archipelago, Indonesia (red on chest limited)
- Dicaeum hirundinaceum ignicolle G. R. Gray, 1858 — Aru Islands, Indonesia (flanks yellow-buff)
- Dicaeum hirundinaceum fulgidum P. L. Sclater, 1883 — Tanimbar Islands, Indonesia (flanks buff, red on chest limited, and throat pale buff)
Description
The mistletoebird is small, 9–10 cm long and 7.5–11 g weight. The male is glossy blue-black above, with a red chest and a slight red undertail, and a black centre stripe running down its white belly. The female is dark grey above, with a white throat, light grey underparts, and just a touch of pinkish-red under the tail. The eyes, bill and legs are black; the bill is just over a centimetre long, slender, slightly downcurved and sharply pointed. Immature birds are similar to the female, but have an orange-pink bill instead of black.[3]
Behaviour
Feeding
The mistletoebird eats a variety of different foods. It commonly eats the berries of mistletoes (hence the name) and other plants. The diet also includes nectar, pollen, spiders, and insects.
The species consumes the fruit of Amyema quandang (grey mistletoe)[5] and other mistletoe species. By eating the fruit of the parasitic mistletoe, this bird is able to spread the seeds. When the birds eat the berries, the seeds pass through them, which takes anywhere from 4–25 minutes. Then when the birds excrete the seeds, they are sticky and easily adhere to the branch or trunk of a tree where they soon sprout.
Breeding
The female mistletoebird builds the nest by herself with no help from the male. The nest is made of crushed plants and spider webs, which holds it together and holds it to the tree. She will lay three or four white eggs in the nest and look after them till they hatch. When they have hatched both parents will feed them.
-

Adult female feeding babies in nest south of Perth, Western Australia
-

Three juveniles in the nest near many casuarina trees with mistletoe plants
-

Juvenile leaving the nest for the first time
References
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Dicaeum hirundinaceum. |
| Wikispecies has information related to: Dicaeum hirundinaceum |
- ↑ BirdLife International (2012). "Dicaeum hirundinaceum". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Version 2013.2. International Union for Conservation of Nature. Retrieved 26 November 2013.
- ↑ Pizzey, Graham (1999). The Field Guide to the Birds of Australia (Third ed.). Angus&Robertson. p. 500. ISBN 0 207 19691 5.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 del Hoyo, J. et al., eds. (2008). Handbook of the Birds of the World 13: 388. ISBN 978-84-96553-45-3.
- ↑ Nyária, Árpád S.; Peterson, A. Townsend ; Rice, Nathan H.; Moyle, Robert G. (2009). "Phylogenetic relationships of flowerpeckers (Aves: Dicaeidae): Novel insights into the evolution of a tropical passerine clade". Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution 53 (3): 613–19. doi:10.1016/j.ympev.2009.06.014. PMID 19576993.
- ↑ Reid, Nick (28 July 2006). "Mutualistic interdependence between mistletoes (Amyema quandang), and spiny-cheeked honeyeaters and mistletoebirds in an arid woodland". Austral Ecology (Ecological Society of Australia) 15 (2): 175–190. doi:10.1111/j.1442-9993.1990.tb01526.x.
