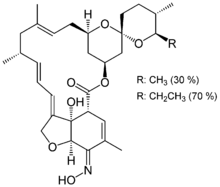
Milbemycin oxime
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Oral | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 5–10% |
| Metabolism | Liver |
| Excretion | Biliary |
| Identifiers | |
|
129496-10-2 | |
| QP54AB01 | |
| Chemical data | |
| Formula |
C31H43NO7 (30%) C32H45NO7 (70%) |
|
541.68 g/mol (30%) 555.702 g/mol (70%) | |
| | |
Milbemycin oxime (trade name Interceptor, marketed by Novartis) is a veterinary drug from the group of milbemycins, used as a broad spectrum antiparasitic. It is active against worms (anthelmintic), insects (insecticide) and mites (miticide).
Mechanism of action
Like avermectins, milbemycins are products of fermentation by Streptomyces species. They have a similar mechanism of action, but a longer half-life than the avermectins. Milbemycin oxime is produced by Streptomyces hygroscopicus aureolacrimosus. It opens glutamate sensitive chloride channels in neurons and myocytes of invertebrates, leading to hyperpolarisation of these cells and blocking of signal transfer.
Uses
Milbemycin oxime is active against a broad spectrum of nematodes. Its miticide spectrum includes Sarcoptes and Demodex. The USA FDA approval for milbemycin oxime as formulated alone does not indicate insecticidal activity.[1]
The drug is used for treatment and prevention of heartworm in dogs and cats, although it is less potent against heartworms than ivermectin.
The substance is often combined with other parasiticides to achieve a broader spectrum of action. Such products include:
- Milbemax (with praziquantel)
- Sentinel Flavor Tabs (with lufenuron)
- Trifexis (with spinosad)
Recently the drug has been used in marine reef aquaria to control parasitic harptacoid copepod (Tegastidae) infestations on captive hard coral colonies. It is an effective full tank treatment for these parasites because it is not toxic to corals in the dosage required to kill the parasites. Shrimps, crabs and other crustaceans should be removed prior to treatment, as they will be killed by the treatment.
Side effects
The drug is tolerated well, even by dogs with multiple drug resistance.
References
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||