Miglitol
 | |
| Systematic (IUPAC) name | |
|---|---|
|
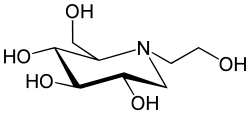
(2R,3R,4R,5S)-1-(2-hydroxyethyl)-2-(hydroxymethyl) piperidine-3,4,5-triol | |
| Clinical data | |
| Trade names | Glyset |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a601079 |
| Licence data | US FDA:link |
| |
| Oral | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | Dose-dependent |
| Protein binding | Negligible (<4.0%) |
| Metabolism | Nil |
| Half-life | 2 hours |
| Excretion | Renal (95%) |
| Identifiers | |
|
72432-03-2 | |
| A10BF02 | |
| PubChem | CID 441314 |
| DrugBank |
DB00491 |
| ChemSpider |
390074 |
| UNII |
0V5436JAQW |
| KEGG |
D00625 |
| ChEMBL |
CHEMBL1561 |
| Chemical data | |
| Formula | C8H17NO5 |
| 207.224 g/mol | |
|
SMILES
| |
| |
| Physical data | |
| Density | 1.458 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 114 °C (237 °F) |
| | |
Miglitol is an oral anti-diabetic drug that acts by inhibiting the ability of the patient to break down complex carbohydrates into glucose. It is primarily used in diabetes mellitus type 2 for establishing greater glycemic control by preventing the digestion of carbohydrates (such as disaccharides, oligosaccharides, and polysaccharides) into monosaccharides which can be absorbed by the body.[1]
Miglitol, and other structurally-related iminosugars, inhibit glycoside hydrolase enzymes called alpha-glucosidases. Since miglitol works by preventing digestion of carbohydrates, it lowers the degree of postprandial hyperglycemia. It must be taken at the start of main meals to have maximal effect.[2] Its effect will depend on the amount of non-monosaccharide carbohydrates in a person's diet.
In contrast to acarbose (another alpha-glucosidase inhibitor), miglitol is systemically absorbed; however, it is not metabolized and is excreted by the kidneys.
See also
References
- ↑ "Migliotl: MedlinePlus Drug Information". MedlinePlus. National Institudes of Health. 1 September 2010. Retrieved 13 April 2013.
- ↑ "Glyset (miglitol) tablets label - Accessdata FDA". Drugs@FDA. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. August 2012. Retrieved 13 April 2013.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||