Methylmalonyl CoA epimerase
Methylmalonyl CoA epimerase (EC 5.1.99.1, methylmalonyl-CoA racemase, methylmalonyl coenzyme A racemase, DL-methylmalonyl-CoA racemase, 2-methyl-3-oxopropanoyl-CoA 2-epimerase [incorrect]) is an enzyme that converts (S)-methylmalonyl-CoA to the (R) form.[1][2] This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
- (R)-methylmalonyl-CoA
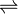 (S)-methylmalonyl-CoA
(S)-methylmalonyl-CoA
Role in Fatty Acid Catabolism
Methylmalonyl CoA epimerase plays an important role in the catabolism of fatty acids with odd-length carbon chains. In the catabolism of even-chain saturated fatty acids, the β-oxidation pathway breaks down fatty acyl-CoA molecules in repeated sequences of four reactions to yield one acetyl CoA per repeated sequence. This means that, for each round of β-oxidation, the fatty acyl-Co-A is shortened by two carbons. If the fatty acid began with an even number of carbons, this process could break down an entire saturated fatty acid into acetyl-CoA units. If the fatty acid began with an odd number of carbons, however, β-oxidation would break the fatty acyl-CoA down until the three carbon propionyl-CoA is formed. In order to convert this to the metabolically useful succinyl-CoA, three reactions are needed. The propionyl-CoA is first carboxylated to (R)-methylmalonyl-CoA by the enzyme Propionyl-CoA carboxylase. Methylmalonyl CoA epimerase then catalyzes the rearrangement of (R)-methylmalonyl-CoA to the (S) form in a reaction that uses a vitamin B12 cofactor and a resonance-stabilized carbanion intermediate. The (S)-methylmalonyl-CoA is then converted to succinyl-CoA in a reaction catalyzed by methylmalonyl-CoA mutase.
Reaction Mechanism
Acting as a general base, the enzyme abstracts a proton from the β-carbon of (R)-methylmalonyl-CoA. This results in the formation of a carbanion intermediate in which the α-carbon is stabilized by resonance. The enzyme then acts as a general acid to protonate the β-carbon, resulting in the formation of (S)-methylmalonyl-CoA.
References
- ↑ Mazumder, R., Sasakawa, T., Kaziro, Y. and Ochoa, S. (1962). "Metabolism of propionic acid in animal tissues. IX. Methylmalonyl coenzyme A racemase". J. Biol. Chem. 237: 3065–3068. PMID 13934211.
- ↑ Overath, P., Kellerman, G.M., Lynen, F., Fritz, H.P. and Keller, H.J. (1962). "Zum Mechanismus der Umlagerung von Methylmalonyl-CoA in Succinyl-CoA. II. Versuche zur Wirkungsweise von Methylmalonyl-CoA-Isomerase and Methylmalonyl-CoA-Racemase". Biochem. Z. 335: 500–518. PMID 14482843.
External links
|
|---|
| | | | K→acetyl-CoA | |
|---|
| | G | |
|---|
| |
|---|
| | Description |
- Metabolism
- Enzymes and pathways: citric acid cycle
- pentose phosphate
- glycoproteins
- glycosaminoglycans
- phospholipid
- cholesterol and steroid
- sphingolipids
- eicosanoids
- amino acid
- urea cycle
- nucleotide
|
|---|
| | Disorders |
- Citric acid cycle and electron transport chain
- Glycoprotein
- Proteoglycan
- Fatty-acid
- Phospholipid
- Cholesterol and steroid
- Eicosanoid
- Amino acid
- Purine-pyrimidine
- Heme metabolism
- Symptoms and signs
|
|---|
| | Treatment | |
|---|
|
|

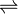 (S)-methylmalonyl-CoA
(S)-methylmalonyl-CoA