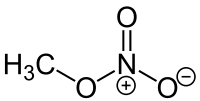
Methyl nitrate
 | |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Methyl nitrate | |||
| Other names
nitric acid, methyl ester | |||
| Identifiers | |||
| 598-58-3 | |||
| ChemSpider | 11231 | ||
| |||
| Jmol-3D images | Image | ||
| PubChem | 11724 | ||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| CH3NO3 | |||
| Molar mass | 77.04 g/mol | ||
| Appearance | Liquid | ||
| Density | 1.203 g/cm3, liquid | ||
| Melting point | −82.3 °C (−116.1 °F; 190.8 K)[1] | ||
| Boiling point | 64.6 °C (148.3 °F; 337.8 K) (explodes)[1] | ||
| Explosive data | |||
| Detonation velocity | 6300 m s−1 [2] | ||
| Hazards | |||
| Main hazards | Toxic, High Explosive | ||
| Except where noted otherwise, data is given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |||
| | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Methyl nitrate is the methyl ester of nitric acid and has the chemical formula CH3NO3. It is a colourless volatile liquid that is explosive.
Synthesis
It can be produced by the condensation of nitric acid and methanol:[3]
- CH3OH + HNO3 → CH3NO3 + H2O
Methyl nitrate can be produced on a laboratory or industrial scale either through the distillation of a mixture of methanol and nitric acid, or by the nitration of methanol by a mixture of sulfuric and nitric acids. The first procedure is not preferred due to the great explosion danger presented by the methyl nitrate vapour. The second procedure is essentially identical to that of making nitroglycerin. However, the process is usually run at a slightly higher temperature and the mixture is stirred mechanically on an industrial scale instead of with compressed air.
Explosive properties
Methyl nitrate is a sensitive explosive. When ignited it burns extremely fiercely with a gray-blue flame. Methyl nitrate has a relatively low brisance in comparison to other explosives, including other nitrate esters. The sensitivity of methyl nitrate to initiation by detonation is among the greatest known, with even a number one blasting cap, the lowest power available, producing a near full detonation of the explosive.
Despite the superior explosive properties of methyl nitrate, it has not received application as an explosive due mostly to its high volatility, which prevents it from being stored or handled safely. It was used as a rocket fuel by Germany in World War II, in a mixture containing 25% methanol, which was named "myrol". This mixture would evaporate at a constant rate and so its composition would not change over time. It presents a slight explosive danger (it is somewhat difficult to detonate) and does not detonate easily via shock.
Safety
As well as being an explosive, methyl nitrate is toxic and causes headaches when inhaled.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 64th ed.". 1983. pp. C–376.
- ↑ Meyer, R.; Köhler, J.; Homberg, A. (2007). Explosives (PDF) (6th ed.). Wiley-VCH. p. 212. ISBN 978-3-527-31656-4.
- ↑ Black, A. P.; Babers, F. H. (1939). "Methyl nitrate". Org. Synth. 19: 64.; Coll. Vol. 2, p. 412
External links
- "Methyl nitrate". Webbook. NIST.