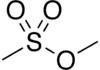
Methyl methanesulfonate
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Methanesulfonic acid methyl ester | |||
| Other names
Methyl mesylate; MMS | |||
| Identifiers | |||
| 66-27-3 | |||
| ChEBI | CHEBI:25255 | ||
| ChemSpider | 4013 | ||
| EC number | 200-625-0 | ||
| |||
| Jmol-3D images | Image | ||
| KEGG | C19181 | ||
| MeSH | D008741 | ||
| PubChem | 4156 | ||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C2H6O3S | |||
| Molar mass | 110.13 g/mol | ||
| Density | 1.3 g/mL at 25 °C | ||
| Boiling point | 202 to 203 °C (396 to 397 °F; 475 to 476 K) | ||
| Related compounds | |||
| Related compounds |
Ethyl methanesulfonate | ||
| Except where noted otherwise, data is given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |||
| | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Methyl methanesulfonate (MMS) is an alkylating agent and a carcinogen. It is also a suspected reproductive toxicant, and may also be a skin/sense organ toxicant.[1] It is used in cancer treatment.[2]
Chemical reactions with DNA
MMS methylates DNA predominantly on N7-deoxyguanosine and N3-deoxyadenosine, and to a much lesser extent also methylates at other oxygen and nitrogen atoms in DNA bases, and also methylates the phosphodiester linkage. Originally, this action was believed to directly cause double-stranded DNA breaks, because homologous recombination-deficient cells are particularly vulnerable to the effects of MMS.[3] However, it is now believed that MMS stalls replication forks, and cells that are homologous recombination-deficient have difficulty repairing the damaged replication forks.[3]
See also
Dimethyl sulfite, a chemical with the same molecular formula but different arrangement
References
- ↑ Scorecard Pollution Information Site: Methyl Methanesulfonate Scorecard.org Accessed 14 Feb 08
- ↑ Medical.Webends.com: Methyl Methanesulfonate Medical.webends.com Accessed 14 Feb 08
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Lundin C, North M, Erixon K, Walters K, Jenssen D, Goldman ASH and Helleday T (2005). "Methyl methanesulfonate (MMS) produces heat-labile DNA damage but no detectable in vivo DNA double-strand breaks". Nucleic Acids Research 33 (12): 3799–3811. doi:10.1093/nar/gki681. PMC 1174933. PMID 16009812.