Messerschmitt Me 163 Komet
| Me 163 Komet | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Me 163 B-1a at the National Museum of Flight in Scotland | |
| Role | Interceptor |
| Manufacturer | Messerschmitt |
| First flight | Me 163A V4 in 1 September 1941 |
| Introduction | 1944 |
| Primary user | Luftwaffe |
| Number built | ~370[1] |
|
| |
The Messerschmitt Me 163 Komet, designed by Alexander Lippisch, was a German rocket-powered fighter aircraft. It is the only rocket-powered fighter aircraft ever to have been operational. Its design was revolutionary, and the Me 163 was capable of performance unrivaled at the time. German test pilot Heini Dittmar in early July 1944 reached 1,130 km/h (700 mph), a flight airspeed record. Over 300 aircraft were built, but the Komet proved ineffective as a fighter and was responsible for the destruction of only about nine Allied aircraft.[2] (16 air victories for 10 losses, according to other sources.)[3]
Development

Work on the design started under the aegis of the Deutsche Forschungsanstalt für Segelflug (DFS)—the German Institute for the Study of sailplane flight. Their first design was a conversion of the earlier Lippisch Delta IV known as the DFS 39 and used purely as a glider testbed of the airframe. A larger follow-on version with a small propeller engine started as the DFS 194. This version used wingtip-mounted rudders, which Lippisch felt would cause problems at high speed. He later redesigned them to be mounted on a conventional vertical stabilizer at the rear of the aircraft. The design included a number of features from its origins as a glider, notably a skid used for landings, which could be retracted into the aircraft's keel in flight. For takeoff, a pair of wheels, each mounted onto the ends of a specially designed cross-axle, were needed due to the weight of the fuel, but the wheels, forming a takeoff "dolly" under the landing skid, were released shortly after takeoff.
The designers planned to use the forthcoming Walter R-1-203 cold engine of 400 kg (880 lb) thrust, which used a monopropellant consisting of stabilized HTP known by the name T-Stoff. Heinkel had also been working with Hellmuth Walter on his rocket engines, mounting them in the He 112 for testing, and later in the first purpose-designed rocket aircraft, the He 176. Heinkel had also been selected to produce the fuselage for the DFS 194 when it entered production, as it was felt that the highly volatile fuel would be too dangerous in a wooden fuselage, with which it could react. Work continued under the code name Projekt X.[4]
The division of work between DFS and Heinkel led to problems, notably that DFS seemed incapable of building even a prototype fuselage. Lippisch eventually asked to leave DFS and join Messerschmitt instead. On 2 January 1939, he moved with his team and the partly completed DFS 194 to the Messerschmitt works at Augsburg. The delays caused by this move allowed the engine development to "catch up". Once at Messerschmitt, the team decided to abandon the propeller-powered version and move directly to rocket-power. The airframe was completed in Augsburg and in early 1940 was shipped to receive its engine at Peenemünde West, one of the quartet of Erprobungsstelle-designated military aviation test facilities of the Reich. Although the engine proved to be extremely unreliable, the aircraft had excellent performance, reaching a speed of 342 mph (550 km/h) in one test.
Me 163A

Production of a prototype series started in early 1941, known as the Me 163. Secrecy was such that the RLM's "GL/C" airframe number, 8-163, was actually that of the earlier, pre-July 1938 Messerschmitt Bf 163 project to produce a small two-passenger light aircraft, which had unsuccessfully competed against the winning Fieseler Fi 156 Storch for a production contract. It was thought that intelligence services would conclude any reference to the number "163" would be for that earlier design. The Me 163A V4 was shipped to Peenemünde to receive the HWK RII-203 engine on May 1941. By 2 October 1941, the Me 163A V4, bearing the radio call sign letters, or Stammkennzeichen, "KE+SW", set a new world speed record of 1,004.5 km/h (624.2 mph), piloted by Heini Dittmar, with no apparent damage to the aircraft during the attempt.[5][6] Some postwar aviation history publications stated that the Me 163A V3 was thought to have set the record.[7]
The 1,004 km/h record figure would not be officially approached until the postwar period by the new jet fighters of the British and U.S., and was not surpassed (except by the later Me 163B V18 in 1944, but seriously damaged by the attempt) until the American Douglas Skystreak turbojet-powered research aircraft did so on 20 August 1947 with no damage. Five prototype Me 163A experimental V aircraft were built, adding to the original DFS 194 (V1), followed by eight pre-production examples designated as "Me 163 A-0".[8] Some doubt once existed about the Stammkennzeichen code assigned to the Me 163A V4 prototype - at one time it was thought to have used the code CD+IM (also speculated to be the A V3's code), but later re-examination of available Luftwaffe records indicated that the sixth through 13th A-series prototypes were assigned the Stammkennzeichen code block of "CD+IK" through "CD+IR", confirming the "KE+SW" designation for the V4 airframe.[9]

During testing, the jettisonable main landing gear arrangement, of a differing design to that used on the later B-series production aircraft, was a serious problem. The A-series "dolly" landing gear caused many aircraft to be damaged on takeoff when the wheels rebounded and crashed into the aircraft due to the sizable springs and shock absorbers on the A-series "dolly" devices which possessed well-sprung independent suspension systems for each main wheel,[10] not used on the much simpler, crossbeam-axled B-series aircraft dollies. Malfunctioning hydraulic dampers in the skid — or with the pilot simply forgetting to release the hydraulic pressure on the skid before landing, after extending it for touchdown to absorb the force of the landing itself — could cause back injuries to the pilot when landing, as the aircraft lacked steering or braking control during landing, and was unable to avoid obstacles.
Once on the ground, the aircraft had to be retrieved by a Scheuch-Schlepper, a converted small agricultural vehicle towing a special retrieval trailer that rolled on a pair of short, triple-wheeled continuous track setups (one per side), with twin trailing lifting arms, that lifted the stationary aircraft off the ground from under each wing.[11] Another form of trailer, known also to have been trialled with the later B-series examples, was tried during the Komet 's test phase, which used a pair of sausage-shaped air bags in place of the lifting arms and could also be towed by the Scheuch-Schlepper tractor, inflating the air bags to lift the aircraft.[12][13] The three-wheeled Scheuch-Schlepper tractor used for the task was originally meant for farm use, but such a vehicle with a specialized trailer was required as the Komet was unpowered after exhausting its rocket propellants, and lacked main wheels after landing, from the jettisoning of its "dolly" main gear at takeoff.[14]
During flight testing, the superior gliding capability of the Komet proved detrimental to safe landing. As the now un-powered aircraft completed its final descent, it could rise back into the air with the slightest updraft. Since the approach was unpowered, there was no opportunity to make another landing pass. For production models, a set of landing flaps allowed somewhat more controlled landings. This issue remained a problem throughout the program. Nevertheless, the overall performance was tremendous, and plans were made to put Me 163 squadrons all over Germany in 40-kilometre rings (25 mi) around any potential target. Development of an operational version was given the highest priority.
Me 163B

A simplified construction format for the Me 163 fighter's airframe was deemed necessary, as the Me 163A version was not truly optimized for large-scale production, with design work starting in December 1941. The result was the Me 163B subtype, which had the desired, more mass-producible fuselage, wing panel, retractable landing skid and tailwheel designs with the previously mentioned unsprung "dolly" takeoff gear, and a generally one-piece nose for the forward fuselage which could incorporate a pioneering example of a "windmill" generator at the extreme front for supplementary electrical power while in flight, as well as a one-piece, perimeter frame-only hinged canopy for ease of production.[15]
Meanwhile, Walter had started work on the newer HWK 109-509 bipropellant hot engine, which added a true fuel of hydrazine hydrate and methanol, designated C-Stoff, that burned with the oxygen-rich exhaust from the T-Stoff, used as the oxidizer, for added thrust (see: List of Stoffs). The new powerplant and numerous detail design changes meant to simplify production over the general A-series airframe design resulted in the significantly modified Me 163B of late 1941. Due to the Reichsluftfahrtministerium (RLM) requirement that it should be possible to throttle the engine, the original power plant grew complicated and lost reliability.
The fuel system was particularly troublesome, as leaks incurred during hard landings easily caused fires and explosions. Metal fuel lines and fittings, which failed in unpredictable ways, were used as this was the best technology available. Both fuel and oxidizer were toxic and required extreme care when loading in the aircraft, yet there were occasions when Komets exploded on the tarmac from the propellants' hypergolic nature. Both propellants were clear fluids, with different tanker trucks used for delivering each propellant to a particular Komet aircraft, one at a time, with one truck - usually the one delivering the C-Stoff hydrazine/methanol-base fuel - leaving the immediate area of the aircraft following its delivery and capping off of the Komet's fuel tanks from a rear located dorsal fuselage filling point just ahead of the Komet's vertical stabilizer, before the other truck - most often an Opel Blitz tanker truck, of a special Ausführung S model carrying the very reactive T-Stoff hydrogen peroxide oxidizer would come anywhere near to deliver its oxidizer load to the fighter for safety reasons, through a different filling point on the Komet's dorsal fuselage surface, located not far behind the rear edge of the canopy.[16]
The corrosive nature of the liquids, especially for the T-Stoff oxidizer, required special protective gear for the pilots. To help prevent explosions, the Walter rocket engine and the Komet's propellant storage and delivery systems were frequently and thoroughly hosed down and flushed with water run through both the fuel and oxidizer tanks and rocket engine's propellant systems before and after flights, to clean out any remnants of the hypergolic fuel and oxidizer.[17] The relative "closeness" to the pilot of some 120 litres (31.7 US gal) of the chemically active T-Stoff oxidizer, split between two auxiliary oxidizer tanks of equal volume to either side within the lower flanks of the cockpit area — besides the main oxidizer tank of some 1,040 litre (275 US gal) volume just behind the cockpit's rear wall, could present a serious or even fatal hazard to a pilot in a fuel-caused mishap with the Me 163B.[18]
Two prototypes were followed by 30 Me 163 B-0 pre-production aircraft armed with two 20 mm MG 151/20 cannon and some 400 Me 163 B-1 production aircraft armed with two 30 mm (1.18 inch) MK 108 cannons, but which were otherwise similar to the B-0. Occasional references to B-1a or Ba-1 subtypes are found in the literature on the aircraft, but the meanings of these designations are somewhat unclear. Early in the war, when German aircraft firms created versions of their aircraft for export purposes, the a was added to export (ausland) variants (B-1a) or to foreign-built variants (Ba-1) but for the Me 163, there were neither export nor a foreign-built version. Later in the war, the "a" and successive letters were used for aircraft using different engine types: as Me 262 A-1a with Jumo engines, Me 262 A-1b with BMW engines. As the Me 163 was planned with an alternative BMW P3330A rocket engine, it is quite safe to assume the "a" was used for this purpose on early examples. Only one Me 163, the V10, was tested with the BMW engine, so this designation suffix was soon dropped. The Me 163 B-1a did not have any wingtip "washout" built into it, and as a result, it had a much higher critical Mach number than the Me 163 B-1.[19]
The Me 163B had very docile landing characteristics, mostly due to its integrated leading edge slots, located directly forward of the elevon control surfaces, and just behind and at the same angle as the wing's leading edge. It would neither stall nor spin. One could fly the Komet with the stick full back, and have it in a turn and then use the rudder to take it out of the turn, and not fear it snapping into a spin. It would also slip well. Because the Me 163B's airframe design was solidly derived from glider design concepts, it had excellent gliding qualities, and had tendency to continue flying above the ground due to ground effect. On the other hand, making a too close turn from base onto final, the sink rate would increase, and one could quickly lose altitude and come in short. Another main difference from a propeller-driven aircraft is that there was no slipstream over the rudder. On takeoff, one had to attain the speed at which the aerodynamic controls become effective—about 129 km/h (80 mph)—and that was always a critical factor. Pilots used to flying propeller-driven aircraft had to be careful the control stick was not somewhere in the corner when the control surfaces began working. These, like many other specific Me 163 problems, would be resolved by specific training.
The performance of the Me 163 far exceeded that of contemporary piston engine fighters. At a speed of over 320 km/h (200 mph) the aircraft would take off, in a so-called "scharfen start" ("sharp start", with "start" being the German word for "take-off") from the ground, from its two-wheeled dolly. The aircraft would be kept at level flight at low altitude until the best climbing speed of around 676 km/h (420 mph) was reached, at which point it would jettison the dolly, pull up into a 70° angle of climb, heading upwards rapidly to a bomber's altitude. It could go higher if required, reaching 12,000 m (39,000 ft) in an unheard of three minutes. Once there, it would level off and quickly accelerate to speeds around 880 km/h (550 mph) or faster, which no Allied fighter could match. The usable Mach number was similar to that of the Me 262, but because of the high thrust-to-drag ratio, it was much easier for the pilot to lose track of the onset of severe compressibility and loss of control. A Mach warning system was installed as a result. The aircraft was remarkably agile and docile to fly at high speed. According to Rudolf Opitz, chief test pilot of the Me 163, it could "fly circles around any other fighter of its time".
By this point, Messerschmitt was completely overloaded with production of the Messerschmitt Bf 109 and attempts to bring the Me 210 into service. Production in a dispersed network was handed over to Klemm, but quality control problems were such that the work was later given to Junkers, who were, at that time, underworked. As with many German designs of World War II's later years, parts of the airframe (especially the wings) were made of wood by furniture manufacturers. The older Me 163A and first Me 163B prototypes were used for training. It was planned to introduce the Me 163S, which removed the rocket engine and tank capacity and placed a second seat for the instructor above and behind the pilot, with its own canopy. The Me 163S would be used for glider landing training, which as explained above, was essential to operate the Me 163. It appears the 163 Ss were converted from the earlier Me 163B series prototypes.
In service, the Me 163 turned out to be difficult to use against enemy aircraft. Its tremendous speed and climb rate meant a target was reached and passed in a matter of seconds. Although the Me 163 was a stable gun platform, it required excellent marksmanship to bring down an enemy bomber. The Komet was equipped with two 30 mm (1.18 inch) MK 108 cannons which had a relatively low muzzle velocity of 540 meters per second (1,207 mph, 1,944 km/h), with the characteristic ballistic drop of such a weapon. The drop meant they were only accurate at short distance, and that it was almost impossible to hit a slow moving bomber when the Komet was traveling very fast. Four or five hits were typically needed to take down a B-17.
A number of innovative solutions were implemented to ensure kills by less experienced pilots. The most promising was a unique weapon called the Sondergerät 500 Jägerfaust. This consisted of a series of single-shot, short-barreled 50 mm (2 inch) guns pointing upwards. Five were mounted in the wing roots on each side of the aircraft. The trigger was tied to a photocell in the upper surface of the aircraft, and when the Komet flew under the bomber, the resulting change in brightness caused by the underside of the aircraft could cause the rounds to be fired. As each shell shot upwards, the disposable gun barrel that fired it was ejected downwards, thus making the weapon recoilless. It appears that this weapon was used in combat only once, resulting in the destruction of a Halifax bomber, although other sources say it was a Boeing B-17.[20][21][22]
Later versions

The biggest concern about the design was the short flight time, which never met the projections made by Walter. With only seven and a half minutes of powered flight, the fighter truly was a dedicated point defense interceptor. To improve this, the Walter firm began developing two more advanced versions of the 509A rocket engine, the 509B and C, each with two separate combustion chambers of differing sizes, one above the other, with greater efficiency.[23] The B-version possessed a main combustion chamber with an exterior shape much like that on the single chamber 509A version, with the C-version having a forward chamber shape of a more cylindrical nature, designed for a higher top thrust level of some 2,000 kg (4,410 lb) of thrust.[24][25] The 509B and 509C rocket motors' main combustion chambers were supported by the "thrust tube" exactly as the 509A motor's single chamber had been. They were tuned for "high power" for takeoff and climb. The added, smaller volume "lower" chamber on the two later models, nicknamed the Marschofen with approximately 400 kg (880 lb) of thrust at its top performance level, was intended for more efficient, lower power cruise flight. These HWK 109–509B and C motors would improve endurance by as much as 50%. Two 163 Bs, models V6 and V18, were experimentally fitted with the lower-thrust B-version of the new twin-chamber engine, a retractable tailwheel, and tested in spring 1944.[26][23]
The main combustion chamber of the 509B engine used for the B V6 and V18 occupied the same location as the A-series' engine did, with the lower Marschofen "cruise chamber" housed within the retractable tailwheel's appropriately widened ventral tail fairing. On 6 July 1944, the Me 163B V18 (VA+SP), like the B V6 basically a standard production Me 163B airframe outfitted with the new-twin chamber "cruiser" rocket motor with the aforementioned modifications beneath the original rocket motor orifice to accept the extra combustion chamber, set a new unofficial world speed record of 1,130 km/h (702 mph), piloted by Heini Dittmar, and landed with almost all of the vertical rudder surface broken away from flutter.[27][5][28] This record was not broken in terms of absolute speed until 6 November 1947 by Chuck Yeager in a flight that was part of the Bell X-1 test program, with a 1,434 km/h (891 mph), or Mach 1.35 supersonic speed, recorded at an altitude of nearly 14,820 m (48,620 ft).[N 1]
The X-1 never exceeded Dittmar's speed from a normal runway liftoff. Heini Dittmar had reached the 1,130 km/h (702 mph) performance, after a normal "sharp start" ground takeoff, without an air drop from a mother ship. Neville Duke exceeded Heini Dittmar's record mark in 31 August 1953, with the Hawker Hunter F Mk3 at a speed of 1,171 km/h (728 mph), after a normal ground start.[29][N 2] Postwar experimental aircraft of the aerodynamic configuration that the Me 163 used, were found to have serious stability problems when entering transonic flight, like the similarly configured, and turbojet powered, Northrop X-4 Bantam and de Havilland DH 108, which made the V18's record with the Walter 509B "cruiser" rocket motor more remarkable.
Waldemar Voigt of Messerschmitt's Oberammergau project and development offices started a redesign of the 163 to incorporate the new twin-chamber Walter rocket engine, as well as fix other problems. The resulting Me 163C design featured a larger wing through the addition of an insert at the wing root, an extended fuselage with extra tank capacity through the addition of a "plug" insert behind the wing, and a new pressurized cockpit topped with a bubble canopy for improved visibility, on a fuselage that had dispensed with the earlier B-version's dorsal fairing. The additional tank capacity and cockpit pressurization allowed the maximum altitude to increase to 15,850 m (52,000 ft), as well as improving powered time to about 12 minutes, almost doubling combat time (from about five minutes to nine). Three Me 163 C-1a prototypes were planned, but it appears only one was flown, without its intended engine.[30]
By this time the project was moved to Junkers. There, a new design effort under the direction of Heinrich Hertel at Dessau attempted to improve the Komet. The Hertel team had to compete with the Lippisch team and their Me 163C. Hertel investigated the Me 163 and found it was not well suited for mass production and not optimized as a fighter aircraft, with the most glaring deficiency being the lack of retractable landing gear. To accommodate this, what would eventually become the Me 263 V1 prototype would be fitted with the desired tricycle gear, also accommodating the twin-chamber Walter rocket from the start — later it was assigned to the Ju 248 program.[31][32]
The resulting Junkers Ju 248 used a three-section fuselage to ease construction. The V1 prototype was completed for testing in August 1944, and was glider-tested behind a Junkers Ju 188. Some sources state that the Walter 109–509C engine was fitted in September, but it was probably never tested under this power. At this point the RLM reassigned the project to Messerschmitt, where it became the Messerschmitt Me 263. This appears to have been a formality only, with Junkers continuing the work and planning production.[33] By the time the design was ready to go into production, the plant where it was to be built was overrun by Soviet forces. While it did not reach operational status, the work was briefly continued by the Soviet Mikoyan-Gurevich (MiG) design bureau as the Mikoyan-Gurevich I-270.[34]
Operational history
The initial test deployment of the Me 163A, to acquaint prospective pilots with the world's first rocket-powered fighter, occurred with Erprobungskommando 16, led by Luftwaffe Major Wolfgang Späte and first established in late 1942, receiving their eight A-model service test aircraft by July 1943. Their initial base was as the Erprobungsstelle test facility located at the Peenemünde-West field, then departed permanently following an RAF bombing raid on the area on August 17, 1943. The next day the unit moved out, southwards to the base at Anklam, near the Baltic coast. Their stay was brief, as a few weeks later they were placed in northwest Germany, based at the military airfield at Bad Zwischenahn (at 53°12′16.48″N 7°59′37.20″E / 53.2045778°N 7.9936667°E) from August 1943 to August 1944. EK 16 received their first B-series armed Komets in January 1944, and was ready for action by May while at Bad Zwischenahn, first seeing combat flights on the 13th of the month.[35]
As EK 16 commenced small-scale combat operations with the Me 163B in May 1944, the Me 163B's unsurpassed velocity was something that the Allied fighter pilots were at a loss to counter. The Komets attacked singly or in pairs, often even faster than the intercepting fighters could dive. A typical Me 163 tactic was to zoom through the bomber formations at 9,000 m (30,000 ft), rise up to an altitude of 10,700–12,000 m (35,100–39,400 ft), then dive through the formation again. This approach afforded the pilot two brief chances to fire a few rounds from his cannons before gliding back to his airfield. The pilots reported that it was possible to make four passes on a bomber, but only if it was flying alone.[36] As the cockpit was unpressurized, the operational ceiling was limited by what the pilot could endure for several minutes while breathing oxygen from a mask, without losing consciousness. Pilots underwent altitude-chamber training to harden them against the rigors of operating in the thin air of the stratosphere without a pressure suit. Special low fiber diets were prepared for pilots, as gas in the gastrointestinal tract would expand rapidly during ascent.
Following the initial combat trials of the Me 163B with EK 16, during the winter and spring of 1944 Major Wolfgang Späte formed the first dedicated Me 163 fighter wing, (Jagdgeschwader 400 (JG 400) ), in Brandis near Leipzig. JG 400's purpose was to provide additional protection for the Leuna synthetic gasoline works which were raided frequently during almost all of 1944. A further group was stationed at Stargard near Stettin to protect the large synthetic fuel plant at Pölitz (today Police, Poland). Further defensive units of rocket fighters were planned for Berlin, the Ruhr and the German Bight.[37]

The first actions involving the Me 163 occurred on 28 July 1944, from I./JG 400's base at Brandis, when two USAAF B-17 Flying Fortress were attacked without confirmed kills. Combat operations continued from May 1944 to spring 1945. During this time, there were nine confirmed kills with 14 Me 163s lost. Feldwebel Siegfried Schubert was the most successful pilot, with three bombers to his credit.[38] Allied fighter pilots soon noted the short duration of the powered flight. They would wait, and when the engine exhausted its propellant supply, pounce on the unpowered Komet. However, the Komet was extremely manoeuvrable in gliding flight. Another Allied method was to attack the fields the Komets operated from and strafe them after the Me 163s landed. Due to the skid-based landing gear system, the Komet was immobile until the Scheuch-Schlepper tractor, could back the trailer up to the nose of the aircraft, place its two rear arms under the wing panels, and jack up the trailer's arms to hoist the aircraft off the ground or place it back on its take-off dolly to tow it back to its maintenance area.[39]
Establishing a defensive perimeter with anti-aircraft guns ensured that Allied fighters avoided these bases. At the end of 1944, 91 aircraft had been delivered to JG 400 but a continuous lack of fuel had kept most of them grounded. It was clear that the original plan for a huge network of Me 163 bases was never going to be realized. Up to that point, JG 400 had lost only six aircraft due to enemy action. Nine were lost to other causes, remarkably few for such a revolutionary and technically advanced aircraft. In the last days of the Third Reich the Me 163 was given up in favor of the more successful and threatening Me 262. In May 1945, Me 163 operations were stopped, the JG 400 disbanded, and many of its pilots sent to fly Me 262s.[36] In any operational sense, the Komet was a failure. Although it shot down 16 aircraft, mainly expensive four-engined bombers, that did not warrant the effort put into the project. With the projected Me 263, things could have turned out differently, but due to fuel shortages late in the war, few went into combat, and it took an experienced pilot with excellent shooting skills to achieve "kills" with the Me 163. The Komet also spawned later weapons like the Bachem Ba 349 Natter and Convair XF-92. Ultimately, the point defense role that the Me 163 played would be taken over by the surface-to-air missile (SAM), Messerschmitt's own example being the Enzian. The airframe designer, Alexander Martin Lippisch went on to design delta winged supersonic aircraft for the Convair Corporation.
Flying the Me 163
Captain Eric Brown RN, Chief Naval Test Pilot and commanding officer of the Captured Enemy Aircraft Flight, who tested the Me 163 at the Royal Aircraft Establishment (RAE) at Farnborough, said, "The Me 163 was an aeroplane that you could not afford to just step into the aircraft and say 'You know, I'm going to fly it to the limit.' You had very much to familiarise yourself with it because it was state-of-the-art and the technology used."[40] Acting unofficially, after a spate of accidents involving Allied personnel flying captured German aircraft resulted in official disapproval of such flights, Brown was determined to fly a powered Komet, and on around 17 May 1945, he flew an Me 163B at Husum with the help of a cooperative German ground crew, after initial towed flights in an Me 163A to familiarise himself with the handling.
The day before the flight, Brown and his ground crew had performed an engine run on the chosen Me 163B to ensure that everything was running correctly, the German crew being apprehensive should an accident befall Brown, until being given a disclaimer signed by him to the effect that they were acting under his orders. On the takeoff the next day, after dropping the takeoff dolly and retracting the skid, Brown later described the resultant climb as "like being in charge of a runaway train", the aircraft reaching 32,000 ft (9.76 km) altitude in 2 minutes, 45 seconds. During the flight, while practicing attacking passes at an imaginary bomber, he was surprised at how well the Komet accelerated in the dive with the engine shut down. When the flight was over Brown had no problems on the approach to the airfield apart from the rather restricted view from the cockpit due to the flat angle of glide, the aircraft touching down at 125 mph. Once down safely, Brown and his much-relieved ground crew celebrated with a drink.[41]
Apart from Brown's unauthorised flight, the British never tested the Me 163 under power themselves, due to the danger of its hypergolic propellants it was only flown unpowered, Brown himself piloted RAE's Komet VF241 on a number of occasions, the rocket motor being replaced with test instrumentation. When interviewed for a 1990s television programme, Brown said he had flown five tailless aircraft in his career (including the British de Havilland DH 108). Referring to the Komet, he said "this is the only one that had good flight characteristics"; he called the other four "killers".[42]
Surviving aircraft
It has been claimed that at least 29 Komets were shipped out of Germany after the war and that of those at least 10 have been known to survive the war to be put on display in museums around the world.[43] Most of the 10 surviving Me 163s were part of JG 400, and were captured by the British at Husum, the squadron's base at the time of Germany's surrender in 1945. According to the RAF museum, 48 aircraft were captured intact and 24 were shipped to the United Kingdom for evaluation, although only one, VF241, was test flown (unpowered).[44]
Australia

- Me 163B, Werknummer 191907 was part of JG 400, captured at Husum and was shipped to the RAE. It was allocated the RAF Air Ministry number of AM222 and was dispatched from Farnborough to No. 6 MU, RAF Brize Norton, on 8 August 1945. On 21 March 1946, it was recorded in the Census of No. 6 MU, and allocated to No. 76 MU (Wroughton) on 30 April 1946 for shipment to Australia. For many years this aircraft was displayed at RAAF Williams Point Cook, but in 1986, the Me 163 was transferred to The Australian War Memorial for refurbishment. It was stored at the AWM Treloar Technology Annex Mitchell, refurbished and reassembled, and was later put up for display together with a Messerschmitt Me 262A-2a, Werknummer 500200 (AM81).[45]
Canada
.jpg)
- Me 163B, Werknummer 191659 (AM215) or 191914 (AM220), is held at the Canada Aviation and Space Museum, Ottawa. Like two of the British Komets, this aircraft was part of JG 400 and captured at Husum. It was shipped to Canada in 1946.
- Werknummer 19116 (but more probable 191916) and 191095 (AM211) also seem to have been held at one time in this museum.[46][47]
Germany

- A Me 163B, Werknummer 191904, "Yellow 25", belonging to JG 400 was captured by the RAF at Husum in 1945. It was sent to England, arriving first at Farnborough, receiving the RAF Air Ministry number AM219 and then transferred to Brize Norton on 8 August 1945, before finally being placed on display at the Station Museum at Colerne. When the museum closed in 1975 the aircraft went to RAF St Athan, receiving the ground maintenance number 8480M. On 5 May 1988 the aircraft was returned to the Luftwaffe and moved to the Luftwaffe Alpha Jet factory at the air base in Oldenburg (JBG 43), not far from the JG 400 unit's wartime base at Bad Zwischenahn, now a golf course. The airframe was in good condition but the cockpit had been stripped and the rocket engine was missing.
Eventually an elderly German woman came forward with Me 163 instruments that her late husband had collected after the war, and the engine was reproduced by a machine shop owned by Me 163 enthusiast Reinhold Opitz. The factory closed in the early 1990s and the "Yellow 25" was moved to a small museum created on the site. The museum contained aircraft that had once served as gate guards, monuments and other damaged aircraft previously located on the air base. In 1997 "Yellow 25" was moved to the official Luftwaffe Museum located at the former RAF base at Berlin-Gatow, where it is displayed today alongside a restored Walter HWK 109–509 rocket engine. This particular Me 163B is one of the very few World War II–era German military aircraft, restored and preserved in a German aviation museum, to have a swastika national marking of the Third Reich, in a "low visibility" white outline form, currently displayed on the tailfin.
- Me 163B, Werknummer 120370, "Yellow 6" of JG 400, is displayed at the Deutsches Museum, Munich. It was originally sent to Britain, where it had received the RAF Air Ministry number AM210. It was given to the Deutsches Museum by RAF Biggin Hill Station. Some claim this is 191316, but that is still at the London Science Museum.
United Kingdom
Of the 21 aircraft that were captured by the British, at least three have survived. They were assigned the British serial numbers AM200 to AM220.[46]
- Me 163B, Werknummer 191316, "Yellow 6", has been on display at the Science Museum in London, since 1964 with the Walter motor removed for separate display. A second Walter motor and a takeoff dolly are part of the museum's reserve collection and are not generally on display to the public.
- Me 163B, Werknummer 191614, has been at the RAF Museum site at RAF Cosford, since 1975. Before then, it was at the Rocket Propulsion Establishment at Westcott, Buckinghamshire. This aircraft last flew on 22 April 1945, when it shot down an RAF Lancaster.[44]
- Me 163B-1a, Werknummer 191659 and RAF Air Ministry serial number AM215, "Yellow 15", was captured at Husum in 1945 and was sent to the College of Aeronautics at Cranfield, England in 1947. After many years of touring airshows and various outdoor gatherings around the UK it was loaned to the National Museum of Flight at East Fortune Airfield, East Lothian, Scotland in 1976.
United States
- Five Me 163s were originally brought to the United States in 1945, receiving the Foreign Equipment numbers FE-495 and FE-500 to 503.[48] An Me 163 B-1a, Werknummer (serial number) 191301, arrived at Freeman Field, Indiana, during mid-1945, and received the foreign equipment number FE-500. On 12 April 1946, it was flown aboard a cargo aircraft to the U.S. Army Air Forces facility at Muroc dry lake in California for flight testing. Testing began on 3 May 1946 in the presence of Dr. Alexander Lippisch and involved towing the unfueled Komet behind a Boeing B-29 Superfortress to an altitude of 9,000–10,500 m (29,500–34,400 ft) before it was released for a glide back to earth under the control of test pilot Major Gus Lundquist. Powered tests were planned, but not carried out after delamination of the aircraft's wooden wings was discovered. It was then stored at Norton AFB, California until 1954, when it was transferred to the Smithsonian Institution. The aircraft remained on display in an unrestored condition at the museum's Paul E. Garber Preservation, Restoration, and Storage Facility in Suitland, Maryland, until 1996, when it was lent to the Mighty Eighth Air Force Museum in Pooler, Georgia for restoration and display but has since been returned to the Smithsonian and as of 2011 is on display unrestored at the National Air and Space Museum's Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center near Washington D.C..
- Me 163B, Werknummer 191095, is on display at the National Museum of the United States Air Force near Dayton, Ohio. It was acquired from the Canadian National Aviation Museum (now the Canada Aviation and Space Museum), where it had been restored, and was placed on display 10 December 1999. Komet test pilot Rudolf "Rudi" Opitz was on hand for the dedication of the aircraft and discussed his experiences of flying the rocket-propelled fighter to a standing room only crowd. During the aircraft's restoration in Canada it was discovered that the aircraft had been assembled by French forced laborers who had deliberately sabotaged it by placing stones between the rocket's fuel tanks and its supporting straps. There are also indications that the wing was assembled with contaminated glue. Patriotic French writing was found inside the fuselage. The aircraft is displayed without any unit identification or Werknummer.
- Me 163B, Werknummer 191660, "Yellow 3", is owned by Paul Allen's Flying Heritage Collection. Between 1961 and 1976, this aircraft was displayed at the Imperial War Museum in London. In 1976, it was moved to the Imperial War Museum Duxford. It underwent a lengthy restoration, beginning in 1997, that was frequently halted as the restorers were diverted to more pressing projects. In May 2005, it was sold, reportedly for £800,000, to raise money for the purchase of a de Havilland/Airco DH.9 as the Duxford museum had no examples of a World War I bomber in its collection. Permission for export was granted by the British government's Department for Culture, Media and Sport as three other Komets were held in British museums.
Japanese versions
As part of their alliance, Germany provided the Japanese Empire with plans and an example of the Me 163.[49] One of the two submarines carrying Me 163 parts did not arrive in Japan, so at the time, the Japanese lacked a few important parts, including the turbopump which they could not make themselves. The Japanese Me 163 crashed on its first flight and was completely destroyed.[50] The Japanese versions were designed as trainers, fighters, and interceptors. Differences between the versions were fairly minor. The Mitsubishi Ki-200 Shusui ("Shu" means "autumn", "sui" means "water" in Japanese) was the equivalent of the 163 B, armed with two 30 mm (1.18 in) Ho 155-II cannon.
The Navy version, the Mitsubishi J8M1 Shusui, replaced the Ho 155 cannon with the Navy's 30 mm (1.18 in) Type 5. Mitsubishi also planned on producing a version of the 163 C for the Navy, known as the J8M2 Shusui Model 21. A version of the 163 D/263 was known as the J8M3 Shusui for the Navy with the Type 5 cannon, and a Ki-202 Shusui-kai ("kai" means "modified" in Japanese) with the Ho 155-II for the Army. Trainers were planned, roughly the equivalent of the Me 163 A-0/S. These were known as the Yokoi Ku-13 Akigusa ("Aki" means also "autumn" and "gusa (kusa)" means "grass" in Japanese) or Ki-200 Shusui Rocket Interceptor practice glider.
Other trainer variants included:
- Yokoi Experimental Ki-13 Shusui Heavy Glider. This glider was created as the Ki-200 Syusui Rocket Interceptor practice glider. The project was cancelled due to high costs.
- Kugisho/Yokosuka MXY-8 Akigusa Rocket Interceptor practice glider (Experimental Shusui Light Glider). Created as the J8M1 Syusui Rocket Interceptor practice glider.
- Kugisho/Yokosuka MXY-9 Experimental Shusui Heavy Glider. This glider was created as the J8M1 Shusui Rocket Interceptor practice glider, but was cancelled due to high costs.
- Kugisho/Yokosuka MXY-9 Shuka Rocket Interceptor Operative training glider. This aircraft would have used the Hitachi "Hatsukaze-11" fan jet engine on the MXY-8 "Akigusa" airframe.
One complete example of the Japanese aircraft survives at the Planes of Fame Air Museum in California. The fuselage of a second aircraft is displayed at the Mitsubishi company's Komaki Plant Museum, at Komaki, Aichi in Japan.[51]
Replicas

A flying replica Me 163 was constructed between 1994 and 1996 by Joseph Kurtz, a former Luftwaffe pilot who trained to fly Me 163s, but who never flew in combat. He subsequently sold the aircraft to EADS. The replica is an unpowered glider whose shape matches that of an Me 163, although its construction completely differs - the glider is built of wood with an empty weight of 285 kilograms (628 lb), a fraction of the weight of a wartime aircraft. Reportedly, it has excellent flying characteristics.[52] The glider is painted red to represent the Me 163 flown by Wolfgang Späte. As of 2011, it was still flying with the civil registration D-1636.[53]
In the early 2000s, a rocket-powered airworthy replica, the Komet II, was proposed by XCOR Aerospace, an aerospace company that had previously built the XCOR EZ-Rocket rocket-plane. Although outwardly the same as a wartime aircraft, the Komet II's design would have differed considerably for safety reasons. It would have been partially constructed with composite materials, powered by one of XCOR's own simpler and safer, pressure fed, liquid oxygen/alcohol engines, and retractable undercarriage would have been used instead of a takeoff dolly and landing skid.[54] The project is no longer discussed on the company's website, and it appears work has ceased on this project.
Several static replica Me 163's are exhibited in museums.
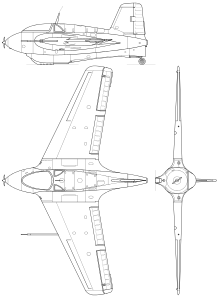
Specifications: Me 163 B-1
General characteristics
- Crew: 1
- Length: 5.98 m (19 ft 7 in)
- Wingspan: 9.33 m (30 ft 7 in)
- Height: 2.75 m (9 ft 0 in)
- Wing area: 18.5 m² (200 ft²)
- Empty weight: 1,905 kg (4,200 lb)
- Loaded weight: 3,950 kg (8,710 lb)
- Max. takeoff weight: 4,310 kg (9,500 lb)
- Powerplant: 1 × Walter HWK 109-509A-2 liquid-fuel rocket, 17 kN (3,800 lbf)
Performance
- Maximum speed: 959 km/h (596 mph)
- Range: 40 km (25 mi)
- Service ceiling: 12,100 m (39,700 ft)
- Rate of climb: 50 metres per second (9,800 ft/min) at 1000 meters; 160 metres per second (31,000 ft/min) at 12000m.[55] ()
- Wing loading: 213 kg/m² (43 lb/ft²)
- Thrust/weight: 0.42
Armament
- Guns: 2 × 30 mm (1.18 in) Rheinmetall Borsig MK 108 cannons (60 rpg)
See also
- Hanna Reitsch
- Eric "Winkle" Brown
- Hellmuth Walter
- Related development
- Aircraft of comparable role, configuration and era
- Related lists
- List of aircraft of World War II
- List of military aircraft of Germany
- List of fighter aircraft
- World War II Luftwaffe
- List of rocket planes
- Wunderwaffe
References
Notes
- ↑ List of X-1 flights
- ↑ Test Pilot Neville Duke set a world record on 7 September 1953.
Citations
- ↑ Wilson 1998, p. 121.
- ↑ Boyne 1997, p. 349.
- ↑ Thompson with Smith 2008, p. 233.
- ↑ "Messerschmitt Me 163 Komet." World War 2 Planes. Retrieved: 22 March 2009.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Käsemann 1999, pp. 17, 122.
- ↑ Stüwe 1999, pp. 207, 211, 212, 213.
- ↑ Spate and Bateson 1975, p. 55.
- ↑ Stüwe 1999, p. 207.
- ↑ "The LEMB Stammkennzeichen Database Project - C?+??." Luftwaffe Experten Message Board. Retrieved: 26 October 2012.
- ↑ "Lippisch Nürflugels-The Me 163A Komet." nurflugel.com. Retrieved: 7 October 2012.
- ↑ de Bie, Rob."Me 163 ground equipment: Scheuch-Schlepper." Me 163 Komet Website. Retrieved: 7 October 2012.
- ↑ United States Army Air Forces, Wright Field Air Materiel Command, Film WF 69-28 (1944). WW2: Flight test of German Aeronautical equipment -- Me 163 (1944) (YOUTUBE) (in no sound). USAAF. Event occurs at 0:33 seconds in.
- ↑ de Bie, Rob."Me 163B "White 05" of Erprobungskommando 16." Me 163 Komet Website. Retrieved: 7 October 2012.
- ↑ de Bie, Rob."Me 163 ground equipment: Scheuch-Schlepper." Me 163 Komet Website. Retrieved: 5 December 2012.
- ↑ de Bie, Rob. "Me 163B Komet - Me 163 Production." xs4all.nl. Retrieved: 5 December 2012.
- ↑ de Bie, Rob. "Me 163 ground equipment: Opel Blitz T-Stoff tanker". http://robdebie.home.xs4all.nl/me163.htm''. Retrieved October 4, 2013.
- ↑ "Messerschmitt Me 163 Komet". Wings of the Luftwaffe (in English). 30:25 minutes in. Discovery Military Channel.
- ↑ Gunston and Wood 1977, p. 228.
- ↑ Stüwe 1999, p. 254.
- ↑ Komet weapons: SG500 Jägerfaust
- ↑ Ethell and Price 1979, pp. 133–135.
- ↑ Ethell 1978, p. 140.
- ↑ 23.0 23.1 Wiedmer, Erwin. "Me 163 B V18 control panel." cockpitinstrumente.de. Retrieved: 31 August 2011.
- ↑ "Me.163B - The Walter RII-211, HWK 109-509.B." The Hellmuth Walter Website. Retrieved: 28 July 2013.
- ↑ "Junkers Ju.248 (aka Me.263) The Walter RII-211, HWK 109-509.C." The Hellmuth Walter Website. Retrieved: 28 July 2013.
- ↑ "Me.163B V6 and V18 - The Walter RII-211, HWK 109-509.B." The Hellmuth Walter Website. Retrieved: 28 July 2013.
- ↑ de Bie, Rob. "Me 163B Komet - Me 163 Production - Me 163B: Werknummern list." robdebie.home. Retrieved: 28 July 2013.
- ↑ "Me 163." walterwerke.co.uk. Retrieved: 28 August 2010.
- ↑ Käsemann 1999, pp. 47, 128
- ↑ Green 1970, p. 604.
- ↑ German site about the Me 163. Retrieved: 5 August 2011
- ↑ Dressel, Griehl. Die deutschen Raketenflugzeuge 1935-1945 (in German). Augsburg, Germany: Weltbild Verlag, 1995.
- ↑ Green 1971, pp. 112–114.
- ↑ Green 1971, pp. 150–151.
- ↑ de Bie, Rob. "Me 163B Komet - Me 163 units - Erprobungskommando 16 (EK 16)". http://robdebie.home.xs4all.nl/me163.htm''. Rob de Bie. Retrieved September 28, 2013.
- ↑ 36.0 36.1 Späte 1989, p. 252.
- ↑ Galland 1957, p. 251.
- ↑ Späte 1989, p. XII.
- ↑ Ethell 1978, pp. 94–144.
- ↑ Thompson with Smith 2008, pp. 231–232.
- ↑ Brown 2006, pp. 105–106.
- ↑ "Messerschmitt Me 163 Komet". Wings of the Luftwaffe (in English). 25:00 minutes in. Discovery Military Channel.
- ↑ Ethell 1978, pp. 157–158.
- ↑ 44.0 44.1 Simpson, Andrew. "Individual History Messerschmitt ME163B-1a W/NR.191614/8481M." Royal Air Force Museum, 2007. Retrieved: 2 November 2009.
- ↑ Butler 1994, p. 107.
- ↑ 46.0 46.1 Pejčoch 2007, p. 69.
- ↑ Ethell 1978, p. 158.
- ↑ Andrade 1979, p. 251.
- ↑ Ethell 1978, pp. 155–157.
- ↑ Späte 1989, p. 243.
- ↑ "List of surviving Japanese aircraft." j-aircraft.com. Retrieved; 27 October 2010.
- ↑ de Bie, Rob. "Mr Kurz' flying glider replica." Me 163 Komet Website, 10 July 2012. Retrieved: 27 May 2013.
- ↑ "The Messerschmitt Me 163 Komet Takes to the Air Again". Tails Through Time. Retrieved 14 November 2014.
- ↑ "Me 163 Flying Replica." Internet Archive, 1 October 2003. Retrieved: 26 December 2008.
- ↑ Wolfgang Späte Der Streng geheime Vogel Me 163; Erprobung an der Schallgrenze page 228 Verlag für Wehrwissenschaften München.
Bibliography
- Andrade, John M. U.S. Military Aircraft Designations and Serials since 1909. Earl Shilton, Leicester, UK: Midland Counties Publications, 1979. ISBN 0-904597-22-9.
- Boyne, Walter J. Clash of Wings. New York: Simon & Schuster, 1994. ISBN 0-684-83915-6.
- Brown, Eric. Wings On My Sleeve. London: Orion Books, 2006. ISBN 0-297-84565-9.
- Butler, Phil. War Prizes. Leicester, UK: Midland Counties Publications, 1994. ISBN 0-904597-86-5.
- Ethell, Jeffrey L. Komet, the Messerschmitt 163. Shepperton, Surrey, UK: Ian Allan Ltd., 1978. ISBN 0-7110-0827-2.
- Ethell, Jeffrey L. and Alfred Price. The German Jets in Combat. London: Jane's Publishing Company, 1979. ISBN 978-0-35401-252-2.
- Galland, Adolf. The First and the Last. New York: Ballantine Books, 1957. No ISBN.
- Green, William. Warplanes of the Third Reich. London: Macdonald and Jane's (Publishers) Ltd., 1970 (fourth Impression 1979). ISBN 0-356-02382-6.
- Green, William. Rocket Fighter (Ballantine's Illustrated History of World War II, Weapons Book No.20). New York: Ballantine Books, 1971. ISBN 0-345-25893-2.
- Gunston, Bill and Tony Wood. Hitler's Luftwaffe. London: Salamander Books Ltd., 1977. ISBN 0-86101-005-1.
- Käsmann, Ferdinand C.W. Die schnellsten Jets der Welt (in German). Berlin: Aviatic-Verlag GmbH, 1999. ISBN 3-925505-26-1.
- Maloney, Edward T., Uwe Feist and Ronald Ferndock. Messerschmitt 163 "Komet". Fallbrook, California: Aero Publishers, Inc., 1968. ISBN 0-8168-0564-4.
- Pejčoch, Ivo. Bojové Legendy: Messerschmitt Me 163 Komet (in Czech). Prague, Chech Republic: Jan Vašut s.r.o., 2007. ISBN 978-8-07236-305-6.
- Späte, Wolfgang. Der streng geheime Vogel Me 163 (in German), "The Top Secret Bird Me 163". Eggolsheim, Germany: Dörfler im Nebel Verlag GmbH, 2003. ISBN 978-3-89555-142-0.
- Späte, Wolfgang. Top Secret Bird: Luftwaffe's Me-163 Komet. Missoula, Montana: Pictorial Histories Publishing Co., 1989. ISBN 1-872836-10-0.
- Späte, Wolfgang and Richard P. Bateson. Messerschmitt Me 163 Komet (Aircraft in Profile number 225). Windsor, Berkshire, UK: Profile Publications Ltd., 1971.
- Stüwe, Botho. Peenemünde West (in German). Augsburg, Germany: Bechtermünz Verlag, 1999. ISBN 3-8289-0294-4.
- Thompson, J. Steve with Peter C. Smith. Air Combat Manoeuvres: The Technique and History of Air Fighting for Flight Simulation. Hersham, Surrey, UK: Ian Allan Publishing, 2008. ISBN 978-1-903223-98-7.
- Wilson, Stewart. Aircraft of WWII. Fyshwick, ACT, Australia: Aerospace Publications Pty Ltd, 1998. ISBN 1-875671-35-8.
- Ziegler, Mano. Rocket Fighter: The Story of the Messerschmitt Me 163. London: Arms and Armour Press, 1976. ISBN 0-85368-161-9.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Messerschmitt Me 163. |
- The Hellmuth Walter Website — reference site for the Me 163's rocket motors
- "Fastest Controlled Flight", October 1944, Popular Science earliest drawing released by USAAF to public about Me 163
- "Secrets of the German Jet Planes" June 1945, Popular Science page 124—the first detailed drawing in a general public magazine
- Photos of Me 163B
- Luftwaffepics
- A large source of information on Me 163B
- Me 163B Test Flight
- Flight Journal
- A list of bases where Komet operated.
- French archive site
| ||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||