Member states of NATO
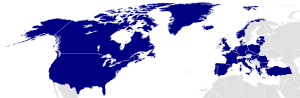
The NATO (North Atlantic Treaty Organization) is an international alliance that consists of 28 member states from North America and Europe. It was established at the signing of the North Atlantic Treaty on 4 April 1949. Article Five of the treaty states that if an armed attack occurs against one of the member states, it should be considered an attack against all members, and other members shall assist the attacked member, with armed forces if necessary.[1]
Of the 28 member countries, two are located in North America (Canada and the United States) and 25 are European countries while Turkey is in Eurasia. All members have militaries, except for Iceland which does not have a typical army (but does, however, have a coast guard and a small unit of soldiers for NATO operations). Three of NATO's members are nuclear weapons states: France, the United Kingdom, and the United States. NATO has 12 original founding member nation states and from 18 February 1952 to 1 April 2009 it added 16 more member nations.
Original and joining members
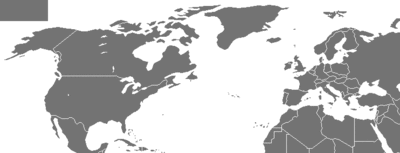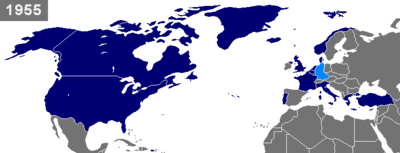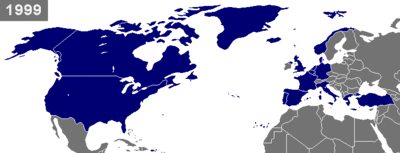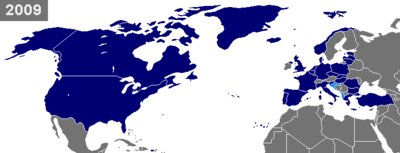
NATO has added new members six times since its founding in 1949, and since 2009 NATO has had 28 members. Twelve countries were part of the founding of NATO: Belgium, Canada, Denmark, France, Iceland, Italy, Luxembourg, the Netherlands, Norway, Portugal, the United Kingdom, and the United States. In 1952, Greece and Turkey became members of the Alliance. In 1990, with the reunification of Germany, NATO grew to include the former country of East Germany. Between 1994 and 1997, wider forums for regional cooperation between NATO and its neighbors were set up, including the Partnership for Peace, the Mediterranean Dialogue initiative and the Euro-Atlantic Partnership Council. In 1997, three former Warsaw Pact countries, Hungary, the Czech Republic, and Poland, were invited to join NATO. After this fourth enlargement in 1999, the Vilnius group of The Baltics and seven East European countries formed in May 2000 to cooperate and lobby for further NATO membership. Seven of these countries joined in the fifth enlargement in 2004. Albania and Croatia joined in the sixth enlargement in 2009.
Member states by date of accession
| Date | Country | Enlargement | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4 April 1949 | | Founders | |
| | |||
| | Denmark's NATO membership includes the Faroe Islands and Greenland. | ||
| | France withdrew from the integrated military command in 1966 to pursue an independent defense system but returned to full participation on 3 April 2009. | ||
| | Iceland, the sole member that does not have its own standing army, joined on the condition that it would not be expected to establish one. However, its strategic geographic position in the Atlantic made it an invaluable member. It has a Coast Guard and has recently contributed a voluntary peacekeeping force, trained in Norway for NATO. | ||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| 18 February 1952 | | First | Greece withdrew its forces from NATO’s military command structure from 1974 to 1980 as a result of Greco-Turkish tensions following the 1974 Turkish invasion of Cyprus. |
| | |||
| 9 May 1955 | | Second | Joined as West Germany; Saarland reunited with it in 1957 and the territories of Berlin and the former German Democratic Republic reunited with it on 3 October 1990. The GDR (East Germany) was a member of the rival Warsaw Pact 1956–1990. |
| 30 May 1982 | | Third | |
| 12 March 1999 | | Fourth | Member of the rival Warsaw Pact 1955–1991 as part of Czechoslovakia. |
| | Member of the rival Warsaw Pact 1955–1991. | ||
| | Member of the rival Warsaw Pact 1955–1990. | ||
| 29 March 2004 | | Fifth | Member of the rival Warsaw Pact 1955–1991. |
| | Member of the rival Warsaw Pact 1955–1991 as part of the Soviet Union. | ||
| | Member of the rival Warsaw Pact 1955–1991 as part of the Soviet Union. | ||
| | Member of the rival Warsaw Pact 1955–1991 as part of the Soviet Union. | ||
| | Member of the rival Warsaw Pact 1955–1991. | ||
| | Member of the rival Warsaw Pact 1955–1991 as part of Czechoslovakia. | ||
| | Previously part of Yugoslavia 1945–1991 (Non-aligned) | ||
| 1 April 2009 | | Sixth | Member of the rival Warsaw Pact 1955–1968. |
| | Previously part of Yugoslavia 1945–1991 (Non-aligned) |
Military personnel
| Country | Active personnel | Reserve personnel | Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| 14,500 | 5,000 | 19,500 | |
| 24,500 | 100,500 | 125,000 | |
| 35,000 | 302,500 | 337,475 | |
| 92,000 | 51,000 | 143,000 | |
| 18,000 | 180,000 | 198,000 | |
| 21,057 | 676 | 21,733 | |
| 26,000 | 63,000 | 89,000 | |
| 3,209 | 60,000 | 63,209 | |
| 222,215 | 100,000 | 322,215 | |
| 148,996 | 14,400 | 163,396 | |
| 109,070 | 280,000 | 389,070 | |
| 19,000 | 19,000 | ||
| 210 | 170 | 380 | |
| 180,000 | 41,867 | 220,867 | |
| 6,000 | 11,000 | 17,000 | |
| 14,995 | 4,260 | 19,255 | |
| 1,057 | 278 | 1,335 | |
| 47,660 | 57,200 | 104,860 | |
| 26,200 | 56,200 | 82,400 | |
| 120,000 | 515,000 | 635,000 | |
| 44,900 | 210,930 | 255,830 | |
| 73,350 | 79,900 | 153,250 | |
| 16,000 | 16,000 | ||
| 7,300 | 1,500 | 8,800 | |
| 123,000 | 16,200 | 139,200 | |
| 612,900 | 429,000 | 1,041,900 | |
| 205,850 | 181,720 | 387,570 | |
| 1,369,532 | 850,880 | 2,220,412 | |
| 3,585,000 | 4,300,000 | 7,885,000 |
Military expenditures
| Country | Population (2011) | GDP (nominal) (2010, US$ millions) | Military expenditures (2011, US$ millions) | Military expenditures (2012, % of GDP) | Defence expenditures, (2011, US$ per capita) | Deployable military (2011) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3,011,405 | 13,292 | 197 | 1.5 | 51 | 10,000 | |
| 10,827,519 | 465,676 | 5,541 | 1.1 | 404 | 35,000 | |
| 7,351,234 | 44,843 | 758 | 1.55 | 64 | 29,000 | |
| 34,447,000 | 1,574,051 | 23,685 | 1.3 | 492 | 60,000 | |
| 4,425,747 | 59,917 | 970 | 1.5 | 161 | 16,009 | |
| 10,515,818 | 192,152 | 2,448 | 1.1 | 162 | 23,000 | |
| 5,560,628 | 310,760 | 4,518 | 1.4 | 636 | 18,000 | |
| 1,311,870 | 19,220 | 389 | 1.7 | 195 | 6,000 | |
| 65,821,885 | 2,582,527 | 53,444 | 2.3 | 666 | 227,000 | |
| 81,802,000 | 3,315,643 | 48,140 | 1.4 | 500 | 205,000 | |
| 11,306,183 | 305,415 | 6,425 | 2.1 | 427 | 124,000 | |
| 9,937,628 | 128,960 | 1,378 | 1.0 | 111 | 29,000 | |
| 318,452 | 12,767 | 12 | 0.09 | 37 | 0a | |
| 60,605,053 | 2,055,114 | 30,228 | 1.4 | 351 | 352,000 | |
| 2,003,900 | 23,385 | 289 | 1.0 | 76 | 5,000 | |
| 2,944,459 | 35,734 | 351 | 0.8 | 75 | 9,000 | |
| 502,100 | 52,433 | 279 | 0.5 | 402 | 900 | |
| 16,667,700 | 783,293 | 11,339 | 1.3 | 553 | 48,000 | |
| 4,937,900 | 483,650 | 7,232 | 1.5 | 1,036 | 21,000 | |
| 38,092,000 | 468,539 | 8,908 | 1.95 | 181 | 100,000 | |
| 10,636,888 | 229,336 | 3,611 | 1.5 | 274 | 39,000 | |
| 21,466,174 | 161,629 | 2,380 | 1.3 | 67 | 66,000 | |
| 5,435,273 | 86,262 | 1,065 | 1.1 | 126 | 16,000 | |
| 2,046,510 | 46,442 | 665 | 1.3 | 255 | 7,000 | |
| 46,148,605 | 1,409,946 | 13,984 | 0.9 | 241 | 127,000 | |
| 73,722,988 | 741,853 | 14,479 | 2.3 | 149 | 495,000 | |
| 63,181,775 | 2,247,455 | 63,567 | 2.5 | 994 | 192,000 | |
| 311,328,000 | 14,657,800 | 731,879 | 4.8 | 2,060 | 1,427,000 | |
| 906,002,051 | 32,223,344 | 1,038,145 | 3.0 | 987 | 3,515,000 | |
| From "Data Relating to NATO Defence", estimates for 2011 and SIPRI estimates for 2012 percentage of GDP[2][3] a Iceland has no armed forces. | ||||||
References
- ↑ "The North Atlantic Treaty". North Atlantic Treaty Organization. 1949-04-04. Retrieved 2008-06-16.
- ↑ "Financial and Economic Data Relating to NATO Defence" (PDF). NATO. 13 April 2012. Retrieved 5 September 2013.
- ↑ http://books.sipri.org/product_info?c_product_id=458#. Missing or empty
|title=(help)
| ||||||||||||||||||||