Maryland Route 261
| ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
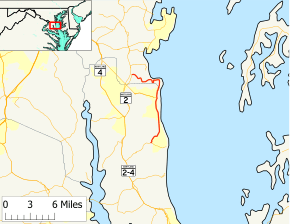
Maryland Route 261 highlighted in red | ||||
| Route information | ||||
| Maintained by MDSHA and Town of North Beach | ||||
| Length: | 12.86 mi[1] (20.70 km) | |||
| Existed: | 1930 – present | |||
| Major junctions | ||||
| South end: |
| |||
|
| ||||
| North end: |
| |||
| Location | ||||
| Counties: | Calvert, Anne Arundel | |||
| Highway system | ||||
| ||||
Maryland Route 261 (MD 261) is a state highway in the U.S. state of Maryland. The highway runs 12.86 miles (20.70 km) from MD 263 near Parran north to MD 778 at Friendship. MD 261 connects Prince Frederick with and serves as the main street through the Chesapeake Bay beach communities of Chesapeake Beach and North Beach in northeastern Calvert County and Rose Haven in southeastern Anne Arundel County. The highway was constructed from north of its present terminus through Chesapeake Beach in the early 1930s. The road was built as MD 613 east from Friendship in the mid-1930s and extended east to Rose Haven in the late 1940s. MD 261 was extended south to its present terminus near Parran and north through North Beach to Rose Haven in the mid-1950s. MD 261 took over MD 613 west to Friendship in the early 1960s.
Route description
MD 261 begins at MD 263 (Plum Point Road) between Prince Frederick and Plum Point and northeast of the hamlet of Parran. The highway heads northeast as two-lane Willows Road and meets the western end of Breezy Point Road, which for several hundred feet east of the intersection is MD 764. At its intersection with county-maintained Willows Road, which heads east toward the shore, MD 261 continues north as Bayside Road. The highway begins to parallel the shoreline of the Chesapeake Bay as it passes through the Chesapeake Beach facility of the U.S. Naval Research Laboratory in the bayside community of Randle Cliff. MD 261 enters the town of Chesapeake Beach and passes through forested Bayfront Park before entering the street grid in the southern part of the town. The highway passes the Chesapeake Beach Railway Station, which is preserved as a museum, immediately before crossing Fishing Creek. MD 261 gains a center turn lane from the creek crossing to its intersection with MD 260 (Chesapeake Beach Road) in the center of town.[1][2]
MD 261 continues through the street grid of the northern part of the town before leaving Chesapeake Beach and entering the town of North Beach at 1st Street. Here, the state highway becomes municipally maintained. The highway heads north along Chesapeake Avenue, which runs one block west of the beach. In the center of town, MD 261 turns east onto 7th Street for one block, then turns north onto Bay Avenue. The highway becomes state-maintained again as it crosses an unnamed creek at the north town limit, which also forms the Calvert–Anne Arundel county line. MD 261 continues along Walnut Avenue, which curves west at Holland Point and follows the southern shore of Herring Bay to Rose Haven. The highway turns south onto Lakeshore Drive, which forms a U-shape as it passes along the edge of Rose Haven Harbor. West of the harbor, MD 261 passes the Old Colony Cove Site, an archaeological site, and heads west away from Herring Bay along Friendship Road. The highway passes the historic home Holly Hill near its intersection with Boyds Turn Road before reaching its northern terminus at MD 778 (Old Solomons Island Road) in the village of Friendship. Friendship Road continues west as a county highway to MD 2 (Solomons Island Road).[1][2]
History
MD 261 was originally constructed as two state highways: MD 261 in Calvert County and MD 613 in Anne Arundel County.[3] MD 261 was built as a gravel road from the Chesapeake Beach–North Beach town line south to Fishing Creek within Chesapeake Beach in 1930.[4] The highway was constructed as a gravel road from south of Fishing Creek to Willows Road along a new alignment parallel to Christiana Parran Road, Dalrymple Road, and Old Bayside Road in 1933.[5][6] The gap in Chesapeake Beach was filled in 1940 when the highway's modern bridge over Fishing Creek and its approaches were completed, replacing a timber bridge that was closer to the shore.[7][8] MD 261 was widened from 16 to 22 feet (4.9 to 6.7 m) and resurfaced with bituminous stabilized gravel from south of Fishing Creek to the Naval Research Lab in 1950.[9] The first portion of MD 613 was built from MD 2 (now MD 778) at Friendship east to Boyds Turn Road in 1934.[6][10] The highway was extended east to Rose Haven, including its U-shape around Rose Haven Harbor, in 1948 and 1949.[9][11] In 1956, MD 261 was extended south along Willows Road to its present terminus at MD 263 and north through North Beach into Anne Arundel County, where the North Beach–Rose Haven road was paved.[12] In 1962, MD 261 was extended west along the route of MD 613 to MD 2, which followed what is now MD 778 until it was relocated to the west in 1965.[13][14]
Junction list
| County | Location | mi [1] | km | Destinations | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calvert | Parran | 0.00 | 0.00 | Southern terminus | |
| Chesapeake Beach | 6.04 | 9.72 | |||
| Anne Arundel | Friendship | 12.86 | 20.70 | Northern terminus | |
| 1.000 mi = 1.609 km; 1.000 km = 0.621 mi | |||||
See also
- Maryland Roads portal
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Highway Information Services Division (December 31, 2013). Highway Location Reference. Maryland State Highway Administration. Retrieved 2012-11-24.
- Calvert County (PDF)
- Anne Arundel County (PDF)
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Google (2013-01-12). "Maryland Route 261" (Map). Google Maps. Google. Retrieved 2013-01-12.
- ↑ Maryland State Roads Commission (1939). General Highway Map: State of Maryland (Map). Baltimore: Maryland State Roads Commission.
- ↑ Maryland Geological Survey (1930). Map of Maryland Showing State Road System: State Aid Roads and Improved County Road Connections (Map). Baltimore: Maryland Geological Survey.
- ↑ Maryland Geological Survey (1933). Map of Maryland Showing State Road System: State Aid Roads and Improved County Road Connections (Map). Baltimore: Maryland Geological Survey.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Byron, William D.; Lacy, Robert (December 28, 1934). "Report of the State Roads Commission of Maryland" (1931–1934 ed.). Baltimore: Maryland State Roads Commission. pp. 319, 322. Retrieved 2013-01-12.
- ↑ Whitman, Ezra B.; Webb, P. Watson; Thomas, W. Frank (March 15, 1941). "Report of the State Roads Commission of Maryland" (1939–1940 ed.). Baltimore: Maryland State Roads Commission. pp. 58, 109. Retrieved 2013-01-12.
- ↑ Prince Frederick, MD quadrangle (Map) (1938 ed.). 1:48,000. 15 Minute Series (Topographic). United States Geological Survey. Retrieved 2013-01-12.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 Reindollar, Robert M.; George, Joseph M.; McCain, Russell H. (December 20, 1950). "Report of the State Roads Commission of Maryland" (1949–1950 ed.). Baltimore: Maryland State Roads Commission. pp. 130, 151. Retrieved 2013-01-12.
- ↑ Maryland State Roads Commission (1934). Map of Maryland Showing State Road System (Map). Baltimore: Maryland State Roads Commission.
- ↑ Maryland State Roads Commission (1949). Maryland: Official Highway Map (Map). Baltimore: Maryland State Roads Commission.
- ↑ Maryland State Roads Commission (1956). Maryland: Official Highway Map (Map). Baltimore: Maryland State Roads Commission.
- ↑ Maryland State Roads Commission (1962). Maryland: Official Highway Map (Map). Baltimore: Maryland State Roads Commission.
- ↑ Maryland State Roads Commission (1965). Maryland: Official Highway Map (Map). Baltimore: Maryland State Roads Commission.
External links
Route map: Bing