Marinduque
| Marinduque | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Province | |||
| |||
| Nickname(s): The Heart of the Philippines | |||
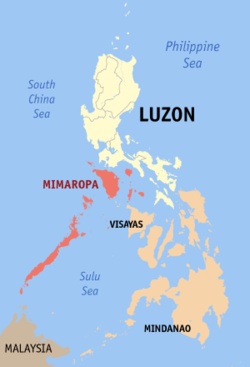
 Map of the Philippines with Marinduque highlighted | |||
| Coordinates: 13°24′N 121°58′E / 13.400°N 121.967°ECoordinates: 13°24′N 121°58′E / 13.400°N 121.967°E | |||
| Country | Philippines | ||
| Region | MIMAROPA (Region IV-B) | ||
| Founded | February 21, 1920 | ||
| Capital | Boac | ||
| Government | |||
| • Governor | Carmencita Reyes (Liberal) | ||
| • Vice Governor | Romulo Baccoro (Liberal) | ||
| • Representative |
Regina Ongsiako Reyes (Liberal) Lone District | ||
| Area[1] | |||
| • Total | 952.58 km2 (367.79 sq mi) | ||
| Area rank | 75th out of 81 | ||
| Highest elevation (Mount Malindig) | 1,157 m (3,796 ft) | ||
| Population (2010)[2] | |||
| • Total | 227,828 | ||
| • Rank | 68th out of 81 | ||
| • Density | 240/km2 (620/sq mi) | ||
| • Density rank | 38th out of 81 | ||
| Divisions | |||
| • Independent cities | 0 | ||
| • Component cities | 0 | ||
| • Municipalities | 6 | ||
| • Barangays | 218 | ||
| • Districts | Lone district of Marinduque | ||
| Time zone | PHT (UTC+8) | ||
| ZIP code | 4900 to 4905 | ||
| Dialing code | 42 | ||
| ISO 3166 code | PH-MAD | ||
| Spoken languages | Tagalog and English | ||
| Website |
www | ||
Marinduque (Tagalog pronunciation: [marinˈduke]) is an island province of the Philippines located in Region IV-B MIMAROPA region. Its capital is the Municipality of Boac. Marinduque lies between Tayabas Bay to the north and Sibuyan Sea to the south. It is west of the Bondoc Peninsula of Quezon province; east of Mindoro Island; and north of the island province of Romblon.
The province of Marinduque resided by its peace-loving people was ranked number 1 by the Philippine National Police and Philippine Security Forces as the 2013 Most Peaceful Province of the country due to its low crime rate statistics conversely ranking with the province of Batanes yearly. Furthermore for almost 200 years, the province is home to one of the oldest religious festivals of the country: the unique and colorful Moriones Festival celebrated annually every holy week.
Physical geography
Marinduque is considered as the geographical center of the Philippine archipelago by the Luzon Datum of 1911, the mother of all Philippine geodetic surveys. The province is a "heart-shaped" island with a total land area of 95,258 hectares (235,390 acres). It is situated between Tayabas Bay in the north and Sibuyan Sea to the south. It is separated from the Bondoc Peninsula in Quezon by the Mompong Pass. West of Marinduque is Tablas Strait, which separates it from Mindoro Island. Some of the smaller islands to the northeast are Polo Island, Maniwaya Island, and Mompong Island. Southwest portion includes the Tres Reyes Islands and Elephant Island.
The highest peak in Marinduque is Mount Malindig (formerly called Mt. Marlanga), a potentially active stratovolcano with an elevation of 1,157 metres (3,796 ft) above sea level, located at the southern tip of the island. Various cave systems occupy the province, which include the grand Bathala Cave; the newly discovered San Isidro Cave with its complex subterranean river; and Talao Caves with its 12 series of caves overlooking the western part of the island.
Climate
Marinduque is categorized on the Type III climate having rainfall more or less evenly distributed throughout the year with no clear boundary between dry and wet seasons. The annual mean, maximum, and minimum temperatures were calculated at 27.0 °C (80.6 °F), 32.9 °C (91.2 °F) and 22.3 °C (72.1 °F) respectively. Humidity average is 78% year-round with an average annual rainfall totaling 2,034.6 millimetres (80.10 in).[3]
Subdivisions
Marinduque is divided into 6 municipalities and 218 barangays.[4]
- Boac - the provincial capital.
- Buenavista - home of the famous Bellaroca Island Resort and Spa.
- Gasan - the Cultural Nerve Center of the Province.
- Mogpog - the original home of the Moriones Festival.
- Santa Cruz - the largest town in the province.
- Torrijos- home of the Poctoy White Beach
History
Legend has it that the island of Marinduque was formed as a consequence of a tragic love affair between two people: Mariin and Gatduke. Mariin's father, a local chieftain, did not approve of this affair and ordered the beheading of Gatduke. Before this could be done, the couple sailed out to sea and drowned themselves, forming the island now called Marinduque.
During the Spanish and early American occupations, Marinduque was part of Balayan Province (now Batangas) in the 16th century, Mindoro in the 17th century, and had a brief period as an independent province in 1901, when the Americans arrived.
During the Philippine-American War, Marinduque was the first island to have American concentration camps.[5] Marinduque is the site of the Battle of Pulang Lupa, where 250 Filipino soldiers under Colonel Maximo Abad, defeated a smaller force of 54 American Infantrymen. Col. Abad surrendered in 1901.[6]:535
| Battle of Marinduque | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of World War II | |||||||
| |||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
|
| |||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||
|
18,700 killed 27,600 wounded |
37,000 killed 43,000 wounded 8,000 captured | ||||||
In 1902, the US-Philippine Commission annexed the islands of Mindoro (now two separate provinces) and Lubang (now part of Occidental Mindoro) to the province.
Four months later, the province became part of the province of Tayabas (now Quezon).
On February 21, 1920, Act 2280 was passed by the Philippine Congress, reestablishing Marinduque as a separate province.
In 1942, the Japanese Imperial forces landed in Marinduque.
In 1945, combined American and Philippine Commonwealth troops attacked from the Japanese Troops liberated to the Battle of Marinduque in the Second World War.
Archaeological finds
Archaeology in the Philippines began in Marinduque. Prior to 1900, only one important archaeological investigation had been carried out in the country: the Antoine-Alfred Marche ’s exploration of Marinduque from April to July 1881. According to anthropologist Henry Otley Beyer, while many other accidental finds have been recorded from time to time and a few burial caves and sites had been casually explored by European or local scientists, no systematic work had been done anywhere else prior to these explorations. After Marche, the next important archaeological work was undertaken by Dr. Carl Gunthe in the Central Visayan Islands in 1922.
An abundant yield of Chinese urns, vases, gold ornaments, skulls and other ornaments of pre-Spanish origin was what Marche finds represented. He brought back to France the Marinduque artifacts he uncovered in 40 crates. Part of it now said to be housed at the Musée de l'Homme in France. The finds also included a wooden image of the Marinduque anito called ‘Pastores’ by the natives.
One of these artifacts also found its way into the National Museum of Natural History of the Smithsonian Institution in Washington, D.C. (Catalogue No. A127996-0, Department of Anthropology, NMNH, Smithsonian Institution). These fragile jarlets traveled from China to the pre-colonial Philippines. Buried in a cave in Marinduque for centuries, excavated in the late 19th century, brought to Paris and eventually one ended up at the Smithsonian Institution museum.
Part of Marinduque's history lies at the Marinduque Museum in Poblacion,Boac, Marinduque and in museums abroad. It will take some time to analyze these artifacts to piece together its pre-colonial past.
Demography
| Population census of Marinduque | ||
|---|---|---|
| Year | Pop. | ±% p.a. |
| 1990 | 185,524 | — |
| 1995 | 199,910 | +1.41% |
| 2000 | 217,392 | +1.81% |
| 2007 | 229,636 | +0.76% |
| 2010 | 227,828 | −0.29% |
| Source: National Statistics Office[7] | ||
Marinduqueños are said to be very hospitable in nature and are very welcoming. One such custom reflecting this is putong or tubong, which is a custom of welcoming and honoring friends and visitors. The honoree (or honorees) are seated and crowned with flowers while local women dance and sing for them. Other well-wishers throw coins and flower petals for long life. Marinduqueños are known to speak a dialect of Tagalog known as the Marinduque Tagalog.
Religion
Marinduque is resided by various religious groups, with Catholics belonging to the Latin Rite predominantly making up the greatest number. Several congregations of Aglipay, The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints, Iglesia ni Cristo, Members Church of God International (popularly called Ang Dating Daan) are also established in the province and various Protestant- Born Again- are also present on the island.
Some Protestant denominations include Assemblies of God, Baptists, JIL, Methodists, and Presbyterian.
Language
The version of Tagalog spoken in Marinduque has been described as "the root from which modern national forms of speech have sprung," where remnants of archaic Tagalog could be found, spoken in a lilting manner by its inhabitants. If this linguistic theory is accurate, Marinduque's Tagalog has contributed significantly to the development of the official Philippine national language.[8]
To this day, Marinduqueños speak an old variation of the Tagalog language that is very close to the way Tagalog was spoken before the Spanish colonization. According to language experts , the Tagalog dialects of Marinduque are the most divergent, especially the Eastern Marinduque dialect, perhaps due to the relative isolation from the Tagalogs of Luzon and also perhaps due to the influence of the Visayan and Bikol migrants.[9]
Linguist Rosa Soberano's 1980 The Dialects of Marinduque Tagalog goes into great depth concerning the dialects spoken there. The following is a verb chart which outlines the conjugation of the Eastern Marinduque dialect of Tagalog:
| Infinitive | Contemplative
(future actions) |
Progressive
(past and present actions) |
Completed
(past actions) |
Imperative | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Actor Focus 1 | -um-
(gumawa) (future actions) |
má-
(mágawâ) |
ná-
(nágawâ) |
-um-
(gumawa) |
0
(gawa) |
| Actor Focus 2 | mag-
(magbigay) |
(ma)ga-
([ma]gabigay) |
naga-
(nagabigay) |
nag-
(nagbigay) |
pag-
(pagbigay) |
| Object Focus 1 | -in
(kainin) |
a-
(akainin) |
ina-
(inakain) |
-in-
(kinain) |
-a
(kaina) |
| Object Focus 2 | i-
(isulat) |
a-
(asulat) |
ina-
(inasulat) |
i- -in-
(isinulat) |
-an
(sulatan) |
| Object Focus 3 | -an
(tawagan) (future actions) |
a-...-an
(atawagan) |
ina- ... -an
(inatawagan) |
-in- ... -an
(tinawagan) |
-i
(tawagi) |
Linguist Christopher Sundita observed that some of the affixes in Marinduque Tagalog, particularly "a-" and "ina-," are affixes used in Asi (Bantoanon), a Visaya language spoken in Romblon, just south of Marinduque. Marinduque Tagalog, like the Tagalog spoken over two centuries ago, had an additional verb category, the imperative, which was used for commands and requests (e.g., Matulog ka na - Go to sleep). Even then, the imperative and the infinitive were used side by side in expressing commands; but in standard Tagalog, apparently the infinitive became used exclusively. And in the Eastern Marinduque dialect, the imperative affixes are very much alive.[10]
Economy
Marinduque is an agricultural province, primarily growing rice and coconuts. Handicrafts from Marinduque are also exported to dıfferent parts of the world, and fishing is another important part of the economy. Mining was once an important player in the economy until a mining accident (the Marcopper Mining Disaster) occurred, bringing the industry to a standstill on the island and causing enormous damage to the people and the island. The provincial government has just recently sued Marcopper's parent company, Placer Dome, for $100 million in damages. Placer Dome was purchased in 2006 by Barrick Gold, who has now been joined in the lawsuit.
A significant role in Marinduque's economy is also played by tourism, especially during the lenten season. While this is not one of the larger parts of the island's economy, it has shown great growth. Recently, some residents are now engaged in butterfly farming. Butterflies are raised for export to countries in both Europe and the Americas. Locally, live butterflies are released in celebration on different occasions, such as birthdays, weddings, and some corporate events.
Culture
- Festivals
- The Moriones Festival also plays a prominent role in Marinduque's culture. Marinduque is famous for this annual festival locally known as "Moryonan". During the month of March or April, parades and celebrations can be seen on the streets. In Santa Cruz, Gasan, Boac, and Mogpog, a parade of people dressed as "Moryons" can be seen on the main road connecting the towns of the island. Boac and Sta. Cruz, the biggest towns in the province, shows a reenactment in the evening of the actual event when Longinus, a blind soldier, punctures Jesus with his spear and blood droplets from the wound restores Longinus'sight.[11]
- Music
- The Marinduque is also home to a musical instrument called the Kalutang. The Kalutang is an instrument made of two pieces of wood that produce different note ranges depending on its size. A band of 10 to 12 can create music with this instrument.
- Putong
- The province welcome ceremony treating the guest like royalty.
Governors
Marinduque has had its own Governor since becoming a sub-province of Tayabas (now Quezon) in 1902 and after gaining its independence from Tayabas in 1920.
| Period | Governor |
|---|---|
| (sub-province under Tayabas) |
|
| (sub-province under Tayabas) |
|
| (sub-province under Tayabas) |
|
| (sub-province under Tayabas) |
|
| (sub-province under Tayabas until 1920) |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
Transport
- By Air
Currently, Marinduque is served by direct daily flights to-and-fro Manila by Zest Airways (formerly Asian Spirit). The Marinduque Airport is located in Barangay Masiga, roughly between Gasan and Boac.
- By Water
Montenegro Lines - plying the sea routes from Dalahican Pier in Barangay Talao-Talao in Lucena City to Marinduque via Balanacan Port in Mogpog (5 trips daily going to Marinduque including the Cawit Pier in Boac or 10 to 14 trips daily back and forth)).(See Schedule of Montenegro Shipping Lines - Source: Google or MSLI Website)
Star Horse Shipping Lines - plying the sea routes from Talao Talao Port in Lucena City to Balanacan, Marinduque - (See Schedule of Star Horse Shipping - Source: Google or SHSLI Website).
JAC Liner Inc. serves a direct bus route from Cubao in Quezon City to Marinduque via roll-on/roll-off ship.
Schools/Educational institutions
Tertiary
- Educational Systems Technological Institute (ESTI) - Murallon, Boac, Marinduque
- Marinduque Midwest College (MMC) - Dili, Gasan, Marinduque
- Marinduque State College (MSC) - Main College Campus in Tanza, Boac, Marinduque
- Marinduque State College (MSC) - College of Fisheries in Banuyo, Gasan, Marinduque
- Marinduque State College (MSC) - Marinduque Community College in Matalaba, Sta. Cruz, Marinduque
- Marinduque State College (MSC) - Santa Cruz Annex, Sta. Cruz, Marinduque
- Marinduque State College (MSC) - College of Agriculture in Poctoy, Torrijos, Marinduque
- Santa Cruz Institute(SCI) - Banahaw,Sta. Cruz, Marinduque
- Malindig Institute (MI) - Lapu-Lapu, Sta. Cruz, Marinduque
- Saint Mary's College of Boac (SMCB) - Isok, Boac, Marinduque
- Marinduque Victorian College (MVC) - Buenavista, Marinduque
- Buyabod School of Arts and Trades (BSAT) - Buyabod, Sta. Cruz, Marinduque
- Torrijos Poblacion School of Arts and Trades (TPSAT)- Poctoy, Torrijos, Marinduque
- Lighthouse Maritime Schools, Inc. (LMSI) - Boac, Marinduque
Secondary
- Private schools
- Marinduque State College - School of Secondary Teacher Education- Laboratory High School (2012)
- Saint Mary's College of Marinduque (formerly Immaculate Concepcion College) (High School Department) (Founded 1953) - Brgy Isok, Boac, Marinduque
- Santa Cruz Institute (Marinduque) Inc. (Founded 1951 as Quezon Memorial School) - Bonifacio St., Santa Cruz, Marinduque. The premier private school offering quality education in the province of Marinduque
- Malindig Institute Foundation Inc.-(Private School) The Pioneer School in the field of Private Education in the province of Marinduque.(Founded 1922) - Osmena St., Barangay Lapu-Lapu Sta. Cruz, Marinduque
- Marcopper High School - Kilo-Kilo, Sta. Cruz Marinduque
- Quezon-Roxas High School(private school)-Dulong Bayan, Mogpog, Marinduque
- Marinduque Academy - Gitnang Bayan, Mogpog, Marinduque
- Saint Joseph the Worker Academy Of Marinduque, Inc. (formerly St. Joseph Academy) - Malabon (Napo), Sta. Cruz, Marinduque
- Our Mother of Perpetual Succor Academy (OMPSA)(Catholic Private School) - Poblacion, Torrijos, Marinduque
- Educational Systems Technological Institute (High School Department) - Murallon, Boac, Marinduque
- Lord of Lords Christian School (Private) - Cawit, Boac, Marinduque
- Marinduque Victorians College (High School Division) - Private = Poblacion, Buenavista, Marinduque
- Marinduque Christian Academy (High School Division)- Private - Dawis, Gasan, Marinduque
- Marinduque Midwest College (High School Division)- Dili, Gasan, Marinduque
- Escuela De Gratia Plena, Inc. Santa Cruz, Marinduque
- Escuela De Gratia Plena, Inc. Torrijos, Marinduque
- Public schools
- Marinduque National High School, Boac, Marinduque - Marinduque National High School is the premier public school in Marinduque province. It is the home of national and international achievers.This institution once was used as a camp for Spaniards, Japanese, American, and Filipino armies during World War II. It offers a Science Class Curriculum wherein students who qualified in the series of examinations prepared by DepEd are expected to maintain an 85% remark on the 3 core subjects.
- Balanacan National High School - Balanacan, Mogpog, Marinduque
- Alobo National High School - Alobo, Santa Cruz Marinduque
- Argao National High School - Argao, Mogpog, Marinduque
- Butansapa National High School - Butansapa, Mogpog, Marinduque
- Mogpog Comprehensive National High School - Ino, Mogpog, Marinduque
- Sayao National High School - Sayao, Mogpog, Marinduque
- Makapuyat National High School - (Public School) Since 1968 - Napo, Sta. Cruz, Marinduque
- Tambangan National High School-Since 1977- Tambagan Santa Cruz Marinduque
- Maranlig National High School (Public School) - Maranlig, Torrijos Marinduque
- Bonliw National High School - Bonliw, Torrijos, Marinduque
- Malibago National High School - Malibago, Torrijos, Marinduque
- Poctoy National High School - Poctoy, Torrijos, Marinduque
- Sibuyao National High School - Sibuyao, Torrijos, Marinduque
- Tigwi National High School - Tigwi, Torrijos, Marinduque
- Landy National High School (Public School) - Landy, Santa Cruz, Marinduque
- Ipil National High School - Ipil, Sta. Cruz, Marinduque
- Dolores National High School - Dolores, Sta. Cruz, Marinduque
- Kasily National High School - Kasily, Sta. Cruz, Marinduque
- Kilo Kilo National High School - Kilo Kilo, Sta. Cruz, Marinduque
- Botilao National High School - Botilao, Sta. Cruz, Marinduque
- Hupi National High School - Hupi, Sta. Cruz, Marinduque
- Tagum National High School - Tagum, Sta. Cruz, Marinduque
- Polo National High School - Polo, Sta. Cruz, Marinduque
- Maniwaya National High School - Maniwaya, Sta. Cruz, Marinduque
- Mompong National High School - Mompong, Sta. Cruz, Marinduque
- Matalaba National High School - Matalaba, Sta. Cruz, Marinduque
- Masaguisi National High School - Masaguisi, Sta. Cruz, Marinduque
- Puting Buhangin National High School - Puting Buhangin, Sta. Cruz, Marinduque
- Punong National High School - Punong, Sta. Cruz, Marinduque
- Matuyatuya National High School. (public School) - Matuyatuya Torrijos Marinduque
- Marinduque State College (High School Division) - Tanza, Boac, Marinduque
- Ilaya National High School - Ilaya, Boac, Marinduque
- Cawit Comprehensive National High School - Cawit, Boac, Marinduque
- Bangbang National High School - Since 1968 - Bangbang, Gasan, Marinduque
- Bognuyan National High School - Bognuyan, Gasan, Marinduque
- Tapuyan National High School - Tapuyan, Gasan, Marinduque
- Tiguion National High School - Tiguion, Gasan, Marinduque
- Paciano A. Sena Memorial High School - Tabionan, Gasan, Marinduque
- Buenavista National High School Main Campus - Poblacion, Buenavista, Marinduque
- Buenavista National High School Bagacay Annex - Bagacay, Buenavista, Marinduque
- Buenavista National High School Daykitin Annex - Daykitin, Buenavista, Marinduque
- Buenavista National High School Lipata-Tungib Annex - Tungib-Lipata, Buenavista, Marinduque
- Buenavista National High School Sihi Annex - Sihi, Buenavista, Marinduque
- Bagtingon National High School - Bagtingon, Buenavista, Marinduque
- Yook National High School - Yook, Buenavista, Marinduque
References
- ↑ "List of Provinces". PSGC Interactive. Makati City, Philippines: National Statistical Coordination Board. Retrieved 20 February 2013.
- ↑ "Total Population by Province, City, Municipality and Barangay: as of May 1, 2010" (PDF). 2010 Census of Population and Housing. National Statistics Office. Retrieved 2012-10-24.
- ↑ Birtle, Andrew J. (April 1997). "The U.S. Army's Pacification of Marinduque, Philippine Islands, April 1900 – April 1901". The Journal of Military History (AT JSTOR) (Society for Military History) 61 (2): 255–282. doi:10.2307/2953967. JSTOR 2953967.
Jessup, Philip Caryl (1938). Elihu Root. Dodd, Mead, & Co./Reprint Services Corp. ISBN 0-7812-4908-2.http://www.namria.gov.ph - ↑ "Province: Marinduque - Municipalities and Cities". Philippine Standard Geographic Code. Retrieved on 2014-09-18.
- ↑ Birtle, p. 272
- ↑ Foreman, J., 1906, The Philippine Islands, A Political, Geographical, Ethnographical, Social and Commercial History of the Philippine Archipelago, New York: Charles Scribner's Sons
- ↑ "Population and Annual Growth Rates for The Philippines and Its Regions, Provinces, and Highly Urbanized Cities" (PDF). 2010 Census and Housing Population. National Statistics Office. Retrieved 13 February 2013.
- ↑ http://www.travelblog.org/Asia/Philippines/Marinduque/blog-462972.html
- ↑ http://salitablog.blogspot.com/2007/03/tagalog-verbs.html
- ↑ http://salitablog.blogspot.com
- ↑ http://fil.wikipilipinas.org/index.php?title=Imahen:Moriones_festival1.jpg
12. ^ http://www.philstar.com/breaking-news/796944/unveiling-other-treasures-marinduque
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Marinduque. |
- Official Provincial Government of Marinduque website
- Total Population by Province, City, Municipality and Barangay as of August 1, 2007
 |
Batangas / Tayabas Bay | Quezon Tayabas Bay |
 | |
| Oriental Mindoro / Sibuyan Sea | |
Sibuyan Sea / Quezon | ||
| ||||
| | ||||
| Sibuyan Sea Romblon |
| ||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||