Mariana Islands
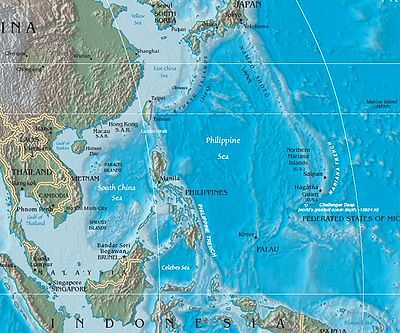
The Mariana Islands (also the Marianas) are an arc-shaped archipelago made up by the summits of fifteen volcanic mountains in the north-western Pacific Ocean between the 12th and 21st parallels north and along the 145th meridian east. They are south of Japan and north of New Guinea, and form the eastern limit of the Philippine Sea. The islands were named after Spanish Queen Mariana of Austria in the 17th century, when Spain started the colonization of the archipelago. They form the northern part of the western Pacific subregion of Micronesia, and are composed of two U.S. jurisdictions: the Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands and, at the southern end of the chain of islands, the territory of Guam.
The islands are part of a geologic structure known as the Izu-Bonin-Mariana Arc system, and range in age from 5 million years old in the north to 30 million years old in the south (Guam). The island chain arises as a result of the western edge of the Pacific Plate moving westward and plunging downward below the Mariana plate, a region which is the most volcanically active convergent plate boundary on Earth. This subduction region, just east of the island chain, forms the noted Mariana Trench, the deepest part of the Earth's oceans and lowest part of the surface of the Earth's crust. In this region, according to geologic theory, water trapped in the extensive faulting of the Pacific Plate as serpentinite, is heated by the higher temperatures of depth during its subduction, and the pressure from the expanding steam results in the hydrothermal activity in the area, and the volcanic activity which formed the Mariana Islands.[1]
Description

The Mariana Islands are the southern part of a submerged mountain range that extends 1,565 miles (2,519 km) from Guam to near Japan. Geographically, the Marianas are the northernmost islands of a larger island group called Micronesia, situated between 13° and 21°N latitude and 144° and 146°E longitude.
The Mariana Islands have a total land area of 1,005 km2 (388 sq mi).[2] They are composed of two administrative units, Guam, a US territory, and the Northern Mariana Islands (including the islands of Saipan, Tinian and Rota) which make up a Commonwealth of the United States.
The island chain geographically consists of two subgroups, a northern group of ten volcanic main islands, all are currently uninhabited; and a southern group of five coralline limestone islands (Rota, Guam, Aguijan, Tinian and Saipan), all inhabited except Aguijan. In the northern volcanic group a maximum elevation of about 2,700 feet (820 m) is reached; there are craters showing signs of activity, and earthquakes are not uncommon. Coral reefs fringe the coasts of the southern isles, which are of slight elevation.
Near the islands can be found the lowest point on the surface of the Earth's crust, the Mariana Trench.
All the islands except Farallon de Medinilla and Uracas or Farallon de Pajaros (in the northern group) are more or less densely wooded, and the vegetation is dense, much resembling that of the Carolines, and also of the Philippines, from where species of plants have been introduced. Owing to the moistness of the soil cryptogams are numerous, as are also most kinds of grasses. On most of the islands there is a plentiful supply of water.
The fauna of the Marianas, though inferior in number and variety, is similar in character to that of the Carolines, and certain species are indigenous to both island groups. The climate though damp is healthy, while the heat, being tempered by the trade winds, is milder than that of the Philippines; the variations of temperature are not great.
History


Prehistory
The islands are part of a geologic structure known as the Izu-Bonin-Mariana Arc system, and range in age from 5 million years old in the north to 30 million years old in the south (Guam). The islands are formed as the highly dense and very old western edge of the Pacific plate plunges downward to form the floor of the Mariana Trench, and carries trapped water under the Mariana plate as it does so. This water is heated and boiled as the plate is carried further downward, and results in the volcanic activity which has formed the arc of Mariana Islands above this subduction region.
Archeological studies of human activity on the islands has revealed potteries with red-slipped, circle- and punctate-stamped designs found in Mariana islands dating between 1500 and 1400 BC show similar aesthetic with the potteries found in Northern and Central Philippines, the Nagsabaran (Cagayan valley) pottery, which flourished during the period between 2000 and 1300 BC.[3]
Spanish exploration and control
The first European to see the island group was the Portuguese explorer Ferdinand Magellan who on March 6, 1521, observed a string of islands and sailed between two of them during a Spanish expedition of world circumnavigation. Historically, the southern village of Umatac, Guam has been credited as the site of Magellan's landing, however, scholarly study of the navigator's diary, now kept in preservation in the Philippines, revealed a drawing of the islands with a tiny island to the south of a much larger island above it. The described placement of the islands made it much more likely that Magellan had actually sailed between Guam and Cocos Island, and not Guam and Rota, as originally thought. This discovery meant Magellan could not have landed in Umatac, but more likely in a northern location like Tanguissan or Tumon Bay. Regardless of where he landed, Magellan's ships arrived in Guam and was unable to get fresh food as the inhabitants, Chamorros, "entered the ships and stole whatever they could lay their hands on", including "the small boat that was fastened to the poop of the flagship."[4]:129 The Spanish crew, however, considered this theft and in retaliation attacked the Chamorros and dubbed the islands Islas de los Ladrones (Islands of the Thieves). "Those people are poor, but ingenious and very thievish, on account of which we called those three islands the islands of Ladroni."[4]:131 Pigafetta writes,
And the captain-general wished to approach the largest of these three islands to replenish his provisions. But it was not possible, for the people of those islands entered the ships and robbed us so that we could not protect ourselves from them. And when we wished to strike and take in the sails so as to land, they stole very quickly the small boat called a skiff which was fastened to the poop of the captain's ship. At which he, being very angry, went ashore with forty armed men. And burning some forty or fifty houses with several boats and killing seven men of the said island, they recovered their skiff.
The islands are still occasionally called the Ladrones. Pigafetta also described the boats the inhabitants used, the sail shaped like a "lateen sail", hence the name Islas de las Velas Latinas (Islands of the Lateen Sails).[4]:131 San Lazarus archipelago, Jardines and Prazeres are among the names applied to them by later navigators.
In 1667 Spain formally claimed them, established a regular colony there, and gave the islands the official title of Las Marianas in honor of Spanish Queen Mariana of Austria, widow of Philip IV of Spain. They then had a population of more than 50,000 inhabitants. With the arrival of passengers and settlers aboard the Manila Galleons from the Americas, new diseases were introduced in the islands, which caused many deaths in the native Chamorro population.[5] The native population, who referred to themselves as Tao Tao Tano (people of the land)[6] but were known to the early Spanish colonists as Hachamori has died out as a distinct people, though their descendants intermarried. At the Spanish occupation in 1668, the Chamorros were estimated at 50,000, but a century later only 1,800 natives remained, as the majority of the population was of mixed Spanish-Chamorro blood or mestizo. They were characteristic Micronesians, with a considerable civilization. In the island of Tinian are some remarkable remains attributed to them, consisting of two rows of massive square stone columns, about 5 feet 4 inches (1.63 m) broad and 14 feet (4.3 m) high, with heavy-round capitals called latte stones. According to early Spanish accounts cinerary urns were found embedded in the capitals.
Research in the archipelago was carried out by Commodore Anson, who in August 1742 landed upon the island of Tinian.[7] The Ladrones were visited by Byron in 1765, Wallis in 1767 and Crozet in 1772.
The Marianas and specifically the island of Guam were a stopover for Spanish galleons en route from Acapulco, Mexico to Manila, Philippines in a convoy known as the Galeon de Manila. Following the 1872 Cavite mutiny, several Filipinos were exiled to Guam, including the father of Pedro Paterno, Maximo Paterno, Dr. Antonio M. Regidor y Jurado and Jose Maria Basa.[8]:107–108
Loss from Spain, and split in governance

The Marianas remained a Spanish colony under the general government of the Philippines until 1898, when, as a result of the Spanish–American War, Spain ceded Guam to the United States. Guam has retained a different political character from the remaining islands since this time. Following the Philippine–American War, Apolinario Mabini and other Filipino leaders were exiled on Guam in 1901.[9]:vi
In the Treaty of February 12, 1899, the remaining Spanish-held islands of the Mariana archipelago were sold by Spain to Germany for 837,500 German gold marks (about $4,100,000 at the time). Along with 6000 islands in other island groups, such as the Carolines and Pelew Islands, all formerly under Spanish control but now indefensible by Spain, these islands were now incorporated as a small part of the larger German Protectorate of New Guinea. The total population in the Northern Marianas portion of these islands around this time was only 2,646 inhabitants; the ten most northerly islands being actively volcanic, and almost uninhabited.
Japan, a member of the Triple Entente, began to occupy the Northern Marianas in 1914. After Germany and the rest of the Central Powers lost World War I, many formerly German-controlled islands in the Pacific were entrusted by the League of Nations to Japanese control as the South Pacific Mandate. These islands included the Northern Mariana Islands. Japan used some of the islands during this time for sugarcane production, increasing the population of a few of them modestly.
World War II
The island chain saw significant fighting during World War II. Guam, a U.S. possession since 1898, was captured by Japan in an attack based from the Northern Mariana Islands that began on the day of the attack on Pearl Harbor (December 8, 1941, the same time as the Pearl Harbor attack across the international dateline). In 1944 the United States captured the Mariana Islands chain from Japan: the Northern Mariana Islands were desired by the U.S. as bombing bases to reach the Japanese mainland, with the invasion of Saipan being launched for that reason in June before the U.S. even moved to recapture Guam; a month later the U.S. recaptured Guam and captured Tinian. Once captured, the islands of Saipan and Tinian were used extensively by the United States military as they finally put mainland Japan within round-trip range of American bombers. In response, Japanese forces attacked the bases on Saipan and Tinian from November 1944 to January 1945. At the same time and afterwards, the United States Army Air Forces based out of these islands conducted an intense strategic bombing campaign against the Japanese cities of military and industrial importance, including Tokyo, Nagoya, Osaka, Kobe, and others. Both the Enola Gay and the Bockscar (which dropped atomic bombs on Hiroshima and Nagasaki, respectively) flew their missions from Tinian's North Field.
According to Werner Gruhl: "Mariana Island historians estimate that 10 percent of Guam's some 20,000 population were killed by violence, most by the Imperial Army and Navy."[10]
The direct result of this conflict was that after the war, the Northern Mariana Islands came under U.S. control in the same way they had earlier come under the control of Japan after World War I, this time as part of the U.S.-administered Trust Territory of the Pacific Islands (TTPI). The Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands became a U.S. territory following its exit from the TTPI. Under U.S. control the Northern Mariana Islands have not united with the territory of Guam, in part due to residual post-war tensions resulting from the very different histories of Guam (occupied by Japan for only 31 months, in wartime) and the Northern Mariana Islands (more peacefully occupied by Japan, for about 30 years). See the main articles above for discussion of present-day politics in these territorial areas.
Tourism
In July 2007 JTB Corporation stated that in the summer of 2007, Guam and Saipan would receive a total of about 170,000 Japanese tourists. This is a decline by 2,000, or 1.2 percent, from the figure in 2006. JTB estimated that a total of 2.52 million Japanese people would travel overseas for that northern hemisphere summer period, and the combined figure for Guam and Saipan made up 6.7% of the total. JTB did not provide separate figures for Guam and Saipan.[11]
Tourism in the Northern Marianas is split mainly between Korean, Chinese, and Russian tourists, with some Japanese still coming to scuba dive. There are several large tour operators in Saipan that cater to Asian tourists coming into the island. By far, the majority of tourism in the Northern Marianas is in Saipan. Several flights a day land in Saipan, mostly in the early hours between 1:00 AM and 3:30 AM. With the close of the garment industries in the Northern Marianas, tourism has grown slowly and is now a major part of the economy of the CNMI.[12]
National cuisine
Here the common dishes are: red rice, meat or poultry on the grill or in coconut milk, chicken kelaguen, apigigi (young coconut with a starch flour wrapped in banana leaf), tropical fruits and many other dishes. They are sometimes sold at Thursday Market in Garapan.

List of islands
| Island name | Population | Municipality or territory |
|---|---|---|
| Farallon de Pajaros | 0 | Northern Islands |
| Maug Islands | 0 | Northern Islands |
| Asuncion | 0 | Northern Islands |
| Agrigan | 0 | Northern Islands |
| Pagan | 0 | Northern Islands |
| Alamagan | 0 | Northern Islands |
| Guguan | 0 | Northern Islands |
| Papaungan | 0 | Northern Islands |
| Sarigan | 0 | Northern Islands |
| Anatahan | 0 | Northern Islands |
| Farallon de Medinilla | 0 | Northern Islands |
| Saipan | 48,220 | Saipan |
| Tinian | 3,136 | Tinian |
| Aguigan | 0 | Tinian |
| Rota | 2,477 | Rota |
| Guam | 159,358 | Guam |
See also
Sources and references

- ↑ Geology of Mariana Islands. Accessed June 28, 2009
- ↑ The CIA World Factbook (2006).
- ↑ Nath. "Epic voyage and potteries: an ancient connection between the Philippines and the Marianas | Imprints of Philippine Science". Imphscience.wordpress.com. Retrieved 2013-03-26.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Nowell, C.E., 1962, Magellan's Voyage Around the World, Antonio Pigafetta's account, Evanston: NorthwesternUniversity Press
- ↑ Tucker, Spencer (2009). The encyclopedia of the Spanish-American and Philippine-American wars: a political, social, and military history. ABC-CLIO. p. 379. ISBN 1-85109-951-4.
- ↑ Warheit, Vanessa "The Insular Empire: America in the Mariana Islands." PBS (documentary). Accessed June 2012.
- ↑ George, Lord Anion (1748). Voyage round the World, book iii.
- ↑ Foreman, J., 1906, The Philippine Islands, A Political, Geographical, Ethnographical, Social, and Commercial History of the Philippine Archipelago, New York: Charles Scribner's Sons
- ↑ Mabini, A., 1969, The Philippine Revolution, Republic of the Philippines, Dept. of Education, National Historical Commission
- ↑ Werner Gruhl, Imperial Japan's World War Two, 1931–1945, Transaction Publishers, 2007 ISBN 978-0-7658-0352-8
- ↑ Donato, Agnes E. "‘Marianas to get 170K Japanese tourists in summer’." (Archive, Archive #2) Saipan Tribune. Thursday July 12, 2013. Retrieved on August 20, 2013.
- ↑ eye-witness
-
 This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). "Marianas, an archipelago in the north-western Pacific Ocean". Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press.
This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). "Marianas, an archipelago in the north-western Pacific Ocean". Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. -
 This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Thomas Kennedy (1913). "Prefecture Apostolic of Mariana Islands". In Herbermann, Charles. Catholic Encyclopedia. Robert Appleton Company.
This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Thomas Kennedy (1913). "Prefecture Apostolic of Mariana Islands". In Herbermann, Charles. Catholic Encyclopedia. Robert Appleton Company.
Additional sources
- Pascal Horst Lehne and Christoph Gäbler: Über die Marianen. Lehne-Verlag, Wohldorf in Germany 1972.
- L. de Freycinet, Voyage autour du monde (Paris, 1826–1844)
- The Marianas Islands in Nautical Magazsile, xxxiv., xxxv. (London, 1865–1866)
- 0. Finsch, Karolinen und Marianen (Hamburg, 1900); Costenoble, Die Marianen in Globus, lxxxviii. (1905).
External links
| Wikisource has original text related to this article: |
-
 Media related to Mariana Islands at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Mariana Islands at Wikimedia Commons - Guam & Northern Marianas – from WorldStatesmen.org
| ||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||