Marian Rejewski
| Marian Rejewski | |
|---|---|
|
Rejewski, c. 1932 | |
| Born |
Marian Adam Rejewski 16 August 1905 Bromberg, German Empire |
| Died |
13 February 1980 (aged 74) Warsaw, People's Republic of Poland |
| Occupation | Mathematician, cryptologist |
| Known for | Solving the Enigma-machine cipher |
| Awards |
Order of Polonia Restituta, Grand Cross[1] War Medal 1939–1945[2] Knowlton Award[3] IEEE Milestone award.[4][5] |
Marian Adam Rejewski [ˈmarjan reˈjefski] (16 August 1905 – 13 February 1980) was a Polish mathematician and cryptologist who in December 1932 solved the plugboard-equipped Enigma machine, the main cipher device used by Nazi Germany. The cryptologic successes of Rejewski and his colleagues Jerzy Różycki and Henryk Zygalski, over six and a half years later, jump-started British reading of Enigma in the Second World War; the intelligence so gained, code-named Ultra, contributed, perhaps decisively, to the defeat of Germany.[Note 1]
While studying mathematics at Poznań University, Rejewski had attended a secret cryptology course conducted by the Polish General Staff's Biuro Szyfrów (Cipher Bureau), which he joined full-time in 1932. The Bureau had achieved little success reading Enigma and in late 1932 set Rejewski to work on the problem. After only a few weeks, he deduced the secret internal wiring of the Enigma. Rejewski and his two mathematician colleagues then developed an assortment of techniques for the regular decryption of Enigma messages. Rejewski's contributions included devising the cryptologic card catalog, derived using his cyclometer, and the cryptologic bomb.
Five weeks before the German invasion of Poland, on 25 July 1939, Rejewski and his colleagues presented their results on Enigma decryption to French and British intelligence representatives summoned to Warsaw. Shortly after the outbreak of war, the Polish cryptologists were evacuated to France, where they continued their work in collaboration with the British and French. They were again compelled to evacuate after the fall of France in June 1940, but within months resumed work undercover, in southern, Vichy France. After that French "Free Zone" was occupied by Germany in November 1942, Rejewski and fellow mathematician Henryk Zygalski fled, via Spain, Portugal and Gibraltar, to Britain. There they enlisted in the Polish Army, initially as privates (later promoted to lieutenant), and were put to work solving low-level German ciphers.
After the war, in 1946, Rejewski reunited with his family in Poland and worked as an accountant, prudently remaining silent about his cryptologic work until 1967.
Education and early work

Marian Rejewski was born 16 August 1905 in Bromberg, now Bydgoszcz,[7][Note 2] to Józef and Matylda, née Thoms.[8] After completing secondary school, he studied mathematics at Poznań University.[9]
In early 1929, shortly before he graduated from university, Rejewski began attending a secret cryptology course organized for selected German-speaking mathematics students by the Polish General Staff's Cipher Bureau (Biuro Szyfrów).[Note 3] The course was conducted off-campus at a military facility[10] and, as Rejewski would discover in France in 1939 during World War II, "was entirely and literally based" on French General Marcel Givièrge's 1925 book, Cours de cryptographie (Course of Cryptography).[11] Rejewski and fellow students Henryk Zygalski and Jerzy Różycki were among the few who could keep up with the course while balancing the demands of their normal studies.[12]
Rejewski graduated with a Master of Philosophy degree in mathematics on 1 March 1929. His thesis was titled "Theory of double periodic functions of the second and third kind and its applications."[13] A few weeks later, without having completed the cryptology course, Rejewski began the first year of a two-year actuarial statistics course at Göttingen, Germany. He would not complete the actuarial-statistics course, for, while home for the summer in 1930, he accepted the offer of a mathematics teaching assistantship at Poznań University.[14] He also began working part-time for the Biuro Szyfrów (Cipher Bureau), which by then had concluded the cryptology course and set up an outpost at Poznań to decrypt intercepted German radio messages.[14] Rejewski worked some twelve hours a week near the Mathematics Institute in an underground vault referred to puckishly as the "Black Chamber".[15]
In the summer of 1932, the Poznań branch of the Cipher Bureau was disbanded. On 1 September 1932, as a civilian employee, Rejewski joined the Cipher Bureau at the General Staff building (the Saxon Palace) in Warsaw, as did Zygalski and Różycki.[16] Their first assignment was to solve a four-letter code used by the Kriegsmarine (German navy). Progress was initially slow, but sped up considerably after a test exchange was intercepted—a six-group signal, followed by a four-group response. The cryptologists guessed correctly that the first signal was the question, "When was Frederick the Great born?" followed by the response, "1712."[17]
Enigma machine

In late October or early November 1932, while work on the German naval code was still underway, Rejewski was set to work, alone and in secret, on the output of the new standard German cipher machine, the Enigma I, which was coming into widespread use.[18] While the Cipher Bureau had succeeded in solving an earlier, plugboard-less Enigma,[Note 4] it had had no success with the Enigma I.[19]
The Enigma machine was an electromechanical device, equipped with a 26-letter keyboard and a set of 26 lamps, corresponding to the letters of the alphabet. Inside was a set of wired drums ("rotors" and a "reflector") that scrambled the input. The machine also featured a plugboard to swap pairs of letters. To encipher a letter, the operator pushed the relevant key and noted down which of the lamps lit. Each key press caused one or more rotors to advance, and thus the encipherment varied from one key press to the next.[20] For two operators to communicate, both Enigma machines had to be set up in the same way. The large number of possibilities for setting the rotors and the plugboard combined to form an astronomical number of configurations, each of which would produce a different cipher. The settings were changed daily,[Note 5] and consequently the machine had to be "broken" anew each day if the messages were to be read continually.[21]
To decrypt Enigma messages, three pieces of information were needed:
- A general understanding of how Enigma functioned
- The wiring of the rotors
- The daily settings: the sequence and orientations of the rotors (of which there were three initially), and the plug connections on the plugboard
Rejewski had only the first at his disposal, based on information already acquired by the Cipher Bureau.[21]
Solving Enigma's wiring
Rejewski has published several articles describing the technical details of how he and his colleagues broke the German Enigma.[22][23][24] Some of the salient points are discussed below with a minimum of mathematics.

First Rejewski tackled the problem of finding the wiring of the rotors. To do this, he pioneered the use of pure mathematics in cryptanalysis. Previous methods had largely exploited linguistic patterns and the statistics of natural-language texts—letter-frequency analysis. Rejewski, however, applied techniques from group theory—theorems about permutations—in his attack on Enigma. These mathematical techniques, combined with material supplied by Captain Gustave Bertrand,[Note 6] chief of French radio intelligence,[Note 7] enabled him to reconstruct the internal wirings of the machine's rotors and nonrotating reflector. "The solution", writes historian David Kahn, "was Rejewski's own stunning achievement, one that elevates him to the pantheon of the greatest cryptanalysts of all time."[25] Rejewski used a mathematical theorem—that two permutations are conjugate if and only if they have the same cycle structure—that mathematics professor and Cryptologia co-editor Cipher A. Deavours describes as "the theorem that won World War II."[Note 8][26]
Before receiving the French intelligence material, Rejewski had made a careful study of Enigma messages, particularly of the first six letters of messages intercepted on a single day.[18] For security, each message was encrypted using different starting positions of the rotors, as selected by the operator. This message setting was three letters long. To convey it to the receiving operator, the sending operator began the message by sending the message setting in a disguised form — a six-letter indicator. The indicator was formed using the Enigma with its rotors set to a common global setting for that day, termed the ground setting, which was shared by all operators.[27] The particular way that the indicator was constructed introduced a weakness into the cipher.[28]
For example, suppose the operator chose the message setting KYG for a message. The operator would first set the Enigma's rotors to the ground setting, which might be GBL on that particular day, and then encrypt the message setting on the Enigma twice; that is, the operator would enter KYGKYG (which might come out to something like QZKBLX). The operator would then reposition the rotors at KYG, and encrypt the actual message. A receiving operator could reverse the process to recover first the message setting, then the message itself. The repetition of the message setting was apparently meant as an error check to detect garbles, but it had the unforeseen effect of greatly weakening the cipher. Due to the indicator's repetition of the message setting, Rejewski knew that, in the plaintext of the indicator, the first and fourth letters were the same, the second and fifth were the same, and the third and sixth were the same. These relations could be exploited to break into the cipher.[27]
Rejewski studied these related pairs of letters. For example, if there were four messages that had the following indicators on the same day: BJGTDN, LIFBAB, ETULZR, TFREII, then by looking at the first and fourth letters of each set, he knew that certain pairs of letters were related. B was related to T, L was related to B, E was related to L, and T was related to E: (B,T), (L,B), (E,L), and (T,E). If he had enough different messages to work with, he could build entire sequences of relationships: the letter B was related to T, which was related to E, which was related to L, which was related to B (see diagram). This was a "cycle of 4", since it took four jumps until it got back to the start letter. Another cycle on the same day might be A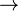 F
F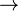 W
W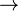 A, or a "cycle of 3". If there were enough messages on a given day, all the letters of the alphabet might be covered by a number of different cycles of various sizes. The cycles would be consistent for one day, and then would change to a different set of cycles the next day. Similar analysis could be done on the 2nd and 5th letters, and the 3rd and 6th, identifying the cycles in each case and the number of steps in each cycle.[29]
A, or a "cycle of 3". If there were enough messages on a given day, all the letters of the alphabet might be covered by a number of different cycles of various sizes. The cycles would be consistent for one day, and then would change to a different set of cycles the next day. Similar analysis could be done on the 2nd and 5th letters, and the 3rd and 6th, identifying the cycles in each case and the number of steps in each cycle.[29]
Using the data thus gained, combined with Enigma operators' tendency to choose predictable letter combinations as indicators (such as girlfriends' initials or a pattern of keys that they saw on the Enigma keyboard), Rejewski was able to deduce six permutations corresponding to the encipherment at six consecutive positions of the Enigma machine. These permutations could be described by six equations with various unknowns, representing the wiring within the entry drum, rotors, reflector, and plugboard.[30]
Help from France
At this point, Rejewski ran into difficulties due to the large number of unknowns in the set of equations that he had developed. He would later comment in 1980 that it was still not known whether such a set of six equations was soluble without further data.[31] But he was assisted by cryptographic documents that Section D of French military intelligence (the Deuxième Bureau), under future General Gustave Bertrand, had obtained and passed on to the Polish Cipher Bureau. The documents, procured from a spy in the German Cryptographic Service, Hans-Thilo Schmidt, included the Enigma settings for the months of September and October 1932. About 9 or 10 December 1932,[32][Note 9] the documents were given to Rejewski. They enabled him to reduce the number of unknowns and solve the wirings of the rotors and reflector.[33]
There was another obstacle to overcome, however. The military Enigma had been modified from the commercial Enigma, of which Rejewski had had an actual example to study. In the commercial machine, the keys were connected to the entry drum in German keyboard order ("QWERTZU..."). However, in the military Enigma, the connections had instead been wired in alphabetical order: "ABCDEF..." This new wiring sequence foiled British cryptologists working on Enigma, who dismissed the "ABCDEF..." wiring as too obvious. Rejewski, perhaps guided by an intuition about a German fondness for order, simply guessed that the wiring was the normal alphabetic ordering. He later recalled that, after he had made this assumption, "from my pencil, as by magic, began to issue numbers designating the connections in rotor N. Thus the connections in one rotor, the right-hand rotor, were finally known."[31]
The settings provided by French Intelligence covered two months which straddled a changeover period for the rotor ordering. A different rotor happened to be in the right-hand position for the second month, and so the wirings of two rotors could be recovered by the same method.[Note 10] Rejewski later recalled: "Finding the [wiring] in the third [rotor], and especially... in the [reflector], now presented no great difficulties. Likewise there were no difficulties with determining the correct torsion of the [rotors'] side walls with respect to each other, or the moments when the left and middle drums turned." By year's end 1932, the wirings of all three rotors and the reflector had been recovered. A sample message in an Enigma instruction manual, providing a plaintext and its corresponding ciphertext produced using a stated daily key and message key, helped clarify some remaining details.[31]
There has been speculation as to whether the rotor wirings could have been solved without the documents supplied by French Intelligence. Rejewski recalled in 1980 that another way had been found that could have been used to solve the wirings, but that the method was "imperfect and tedious" and relied on chance. Rejewski wrote that "the conclusion is that the intelligence material furnished to us should be regarded as having been decisive to solution of the machine."[31] In 2005, mathematician John Lawrence published a paper arguing that it would have taken four years for this method to have had a reasonable likelihood of success.[34]
Solving daily settings
After Rejewski had determined the wiring in the remaining rotors, he was joined in early 1933 by Różycki and Zygalski in devising methods and equipment to break Enigma ciphers routinely.[Note 11] Rejewski later recalled:
Now we had the machine, but we didn't have the keys and we couldn't very well require Bertrand to keep on supplying us with the keys every month ... The situation had reversed itself: before, we'd had the keys but we hadn't had the machine — we solved the machine; now we had the machine but we didn't have the keys. We had to work out methods to find the daily keys.[35]
Early methods
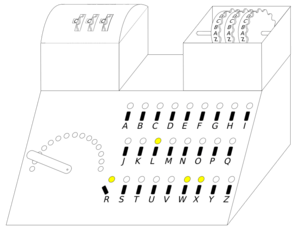
A number of methods and devices had to be invented in response to continual improvements in German operating procedure and to the Enigma machine itself. The earliest method for reconstructing daily keys was the "grill", based on the fact that the plugboard's connections exchanged only six pairs of letters, leaving fourteen letters unchanged.[36] Next was Różycki's "clock" method, which sometimes made it possible to determine which rotor was at the right-hand side of the Enigma machine on a given day.[37]
After 1 October 1936, German procedure changed, and the number of plugboard connections became variable, ranging between five and eight. As a result, the grill method became considerably less effective.[36] However, a method using a card catalog had been devised around 1934 or 1935, and was independent of the number of plug connections. The catalog was constructed using Rejewski's "cyclometer", a special-purpose device for creating a catalog of permutations. Once the catalog was complete, the permutation could be looked up in the catalog, yielding the Enigma rotor settings for that day.[36]
The cyclometer comprised two sets of Enigma rotors, and was used to determine the length and number of cycles of the permutations that could be generated by the Enigma machine. Even with the cyclometer, preparing the catalog was a long and difficult task. Each position of the Enigma machine (there were 17,576 positions) had to be examined for each possible sequence of rotors (there were 6 possible sequences); therefore, the catalog comprised 105,456 entries. Preparation of the catalog took over a year, but when it was ready about 1935, it made obtaining daily keys a matter of 12–20 minutes.[36][38] However, on 1 or 2 November 1937, the Germans replaced the reflector in their Enigma machines, which meant that the entire catalog had to be recalculated from scratch.[36] Nonetheless, by January 1938 the Cipher Bureau's German section was reading a remarkable 75% of Enigma intercepts, and according to Rejewski, with a minimal increase in personnel this could have been increased to 90%.[39]
Rejewski's bomba and Zygalski's sheets
In 1937 Rejewski, along with the German section of the Cipher Bureau, transferred to a secret facility near Pyry in the Kabaty Woods south of Warsaw. On 15 September 1938, the Germans introduced new rules for enciphering message keys (a new "indicator procedure"), making the Poles' earlier techniques obsolete.[Note 12] The Polish cryptanalysts rapidly responded with new techniques. One was Rejewski's bomba, an electrically powered aggregate of six Enigmas, which solved the daily keys within about two hours. Six bombas were built and were ready for use by mid-November 1938.[40] The bomba exploited the fact that the plugboard connections did not affect all the letters; therefore, when another change to German operating procedure occurred on 1 January 1939, increasing the number of plugboard connections, the usefulness of the bombas was greatly reduced. The British bombe, the main tool that would be used to break Enigma messages during World War II, would be named after, and likely inspired by, the Polish bomba, though the cryptologiic methods embodied by the two machines were different.[41]
Around the same time as Rejewski's bomba, a manual method was invented by Henryk Zygalski, that of "perforated sheets" ("Zygalski sheets"), which was independent of the number of plugboard connections. Rejewski describes the construction of the Zygalski mechanism and its manipulation:
Fairly thick paper sheets, lettered "a" through "z", were prepared for all twenty-six possible positions of rotor L [the left-hand Enigma rotor] and a square was drawn on each sheet, divided into 51 by 51 smaller squares. The sides, top, and bottom of each large square (it could as well be a rectangle) were lettered "a" through "z" and then again "a" through "y". This was, as it were, a system of coordinates in which the abscissas and ordinates marked successive possible positions of rotors M [the middle Enigma rotor] and N [the right-hand Enigma rotor], and each little square marked permutations, with or without constant points, corresponding to those positions. Cases with constant points were perforated.[42][E]ach constant point had to be perforated as many as four times. [...] When the sheets were superposed and moved in the proper sequence and the proper manner with respect to each other, in accordance with a [precisely] defined program, the number of visible apertures gradually decreased. And, if a sufficient quantity of data was available, there finally remained a single aperture, probably corresponding to the right case, that is, to the solution. From the position of the aperture one could calculate the order of the rotors, the setting of their rings, and, by comparing the letters of the cipher keys with the letters in the machine, likewise permutation S; in other words, the entire cipher key.[43]
However, application of both the bomba and Zygalski sheets was complicated by yet another change to the Enigma machine on 15 December 1938. The Germans had supplied Enigma operators with an additional two rotors to supplement the original three, and this increased the complexity of decryption tenfold. Building ten times as many bombas (60 would now be needed) was beyond the Cipher Bureau's ability—that many bombas would have cost fifteen times its entire annual equipment budget.[44] The following month, things became even worse when the number of plugboard cables increased from six to ten. Instead of twelve letters being swapped before entering the rotor scrambler, there were now twenty swapped letters, reducing the effectiveness of the bomba and increasing the number of possible plugboard settings by more than a thousandfold.[45] The Poles had two sets of Zygalski sheets; they would have needed to produce 58 more, for a total of 60.[46]
Allies informed
As it became clear that war was imminent and that Polish financial resources were insufficient to keep pace with the evolution of Enigma encryption (e.g., due to the prohibitive expense of an additional 54 bombas and due to the Poles' difficulty in producing in timely fashion the full 60 series of 26 "Zygalski sheets" each[47]), the Polish General Staff and government decided to initiate their Western allies into the secrets of Enigma decryption.[48] The Polish methods were revealed to French and British intelligence representatives in a meeting at Pyry, south of Warsaw, on 25 July 1939. France was represented by Gustave Bertrand and Henri Braquenié; Britain, by Alastair Denniston, Alfred Dillwyn Knox, and Royal Navy electronics expert Humphrey Sandwith. The Polish hosts included Stefan Mayer, Gwido Langer, Maksymilian Ciężki, and the three cryptologists.[48][49][50]
The Poles' gift of Enigma decryption to their Western allies, five weeks before the outbreak of World War II, came not a moment too soon. Knowledge that the cipher was crackable was a morale boost to Allied cryptologists. The British were able to manufacture at least two complete sets of perforated sheets—they sent one to PC Bruno, outside Paris,[51] in mid-December 1939—and began reading Enigma within months of the outbreak of war.[Note 13]
Without the Polish assistance, British cryptologists would, at the very least, have been considerably delayed in reading Enigma. Author Hugh Sebag-Montefiore concludes that substantial breaks into German Army and Air Force Enigma ciphers by the British would have occurred only after November 1941 at the earliest, after an Enigma machine and key lists had been captured, and similarly into Naval Enigma only after late 1942.[53] Former Bletchley Park cryptologist Gordon Welchman goes further, writing that the Army and Air Force Enigma section, Hut 6, "would never have gotten off the ground if we had not learned from the Poles, in the nick of time, the details both of the German military... Enigma machine, and of the operating procedures that were in use."[54]
Intelligence gained from solving high-level German ciphers—intelligence codenamed "Ultra" by the British and Americans—came chiefly from Enigma decrypts. While the exact contribution of Ultra intelligence to Allied victory is disputed, Kozaczuk and Straszak note that "it is widely believed that Ultra saved the world at least two years of war and possibly prevented Hitler from winning."[55] The English historian Sir Harry Hinsley, who worked at Bletchley Park, similarly assessed it as having "shortened the war by not less than two years and probably by four years".[56] The availability of Ultra was, at the least, due largely to the earlier Polish breaking of Enigma.
In France and Britain
PC Bruno

In September 1939, after the outbreak of World War II, Rejewski and his fellow Cipher Bureau workers were evacuated from Poland, crossing the border into Romania on 17 September (the day that the Soviet Union invaded eastern Poland).[57] Rejewski, Zygalski and Różycki managed to avoid being interned in a refugee camp and made their way to Bucharest, where they contacted the British embassy. Having been told by the British to "come back in a few days," they next tried the French embassy, introducing themselves as "friends of Bolek" (Bertrand's Polish code name) and asking to speak with a French military officer. A French Army colonel telephoned Paris and immediately issued instructions for the three Poles to be assisted in evacuating to Paris.[58]
On 20 October 1939 the three Polish cryptologists resumed work on German ciphers at a joint French-Polish-Spanish radio-intelligence unit stationed at Gretz-Armainvillers, forty kilometers northeast of Paris, and housed in the Château de Vignolles (code-named PC Bruno).[59] On 17 January 1940, the Poles found the first Enigma key to be solved in France, one for 28 October 1939.[60] The PC Bruno staff collaborated by teleprinter with their opposite numbers at Bletchley Park in England. Paradoxically, for their mutual communications security, the Polish, French and British cryptologic agencies used the Enigma machine itself. Bruno closed its Enigma-encrypted messages to Britain with an ironic "Heil Hitler!"[61]
On 24 June 1940, after Germany's victory in the Battle of France, Gustave Bertrand flew Bruno's international personnel—fifteen Poles, and seven Spaniards who worked on Italian ciphers[62]—in three planes to Algeria.[63]
Cadix

Some three months later, in September 1940, they returned to work covertly in unoccupied southern, Vichy France. Rejewski's cover was as Pierre Ranaud, a lycée professor from Nantes. A radio-intelligence station was set up at the Château des Fouzes, code-named Cadix, near Uzès. Cadix began operations on 1 October. Rejewski and his colleagues solved German telegraph ciphers, and also the Swiss version of the Enigma machine (which had no plugboard).[64] Rejewski may have had little or no involvement in working on German Enigma at Cadix.[Note 14]

In early July 1941, Rejewski and Zygalski were asked to try solving messages enciphered on the secret Polish Lacida cipher machine, which was used for secure communications between Cadix and the Polish General Staff in London. Lacida was a rotor machine based on the same cryptographic principle as Enigma, yet had never been subjected to rigorous security analysis. The two cryptologists created consternation by breaking the first message within a couple of hours; further messages were solved in a similar way.[65]
On 9 January 1942, Różycki, the youngest of the three mathematicians, died in the sinking of a French passenger ship as he was returning from a stint in Algeria to Cadix in southern France.[66][Note 15]
By summer 1942 work at Cadix was becoming dangerous, and plans for evacuation were drawn up. Vichy France was liable to be occupied by German troops, and Cadix's radio transmissions were increasingly at risk of detection by the German Funkabwehr, a unit tasked with locating enemy radio transmitters. Indeed, on 6 November a pickup truck equipped with a circular antenna arrived at the gate of the Château des Fouzes where the cryptologists were operating. The visitors, however, did not enter, and merely investigated — and terrorized — nearby farms. Nonetheless, at Bertrand's suggestion French intelligence ordered the evacuation of Cadix. The order was carried out on 9 November, the day after the Allied "Operation Torch" landings in North Africa. Three days later, on 12 November, the Germans occupied the chateau.[67]
Escaping France
The Poles were split into groups of two and three. On 11 November 1942 Rejewski and Zygalski were sent to Nice, in the Italian-occupied zone. After coming under suspicion there, they had to flee again, moving or hiding constantly. Their trek took them to Cannes, Antibes, back to Nice, then on to Marseilles, Toulouse, Narbonne, Perpignan, and Ax-les-Thermes, near the Spanish border.[68] On 29 January 1943, accompanied by a local guide, Rejewski and Zygalski, bound for Spain, began a climb over the Pyrenees, avoiding German and Vichy patrols. Near midnight, close to the Spanish border, the guide pulled out a pistol and demanded that they hand over their remaining money.[69]
After being robbed, Rejewski and Zygalski succeeded in reaching the Spanish side of the border, only to be arrested within hours by security police.[70] They were sent first to a prison in La Seu d'Urgell, then on 24 March transferred to a prison at Lerida. On 4 May 1943, after having spent over three months in Spanish prisons, on intervention by the Polish Red Cross the pair were released and sent to Madrid.[71] Leaving there on 21 July,[72] they made it to Portugal; from there, aboard HMS Scottish, to Gibraltar; and thence, aboard an old Dakota, to RAF Hendon in north London, arriving on 3 August 1943.[73]

Britain
Rejewski and Zygalski were inducted as privates into the Polish Army on 16 August 1943 and were posted to a Polish Army facility in Boxmoor, cracking German SS and SD hand ciphers. The ciphers were usually based on the Doppelkassettenverfahren ("double Playfair") system, which the two cryptologists had already worked on in France.[74] On 10 October 1943, Rejewski and Zygalski were commissioned second lieutenants;[75] on 1 January 1945 Rejewski, and presumably also Zygalski, were promoted to lieutenant.[76] When Gustave Bertrand fled to England in June 1944, he and his wife were provided with a house in Boxmoor, a short walk from the Polish radio station and cryptology office, where it seems likely that his collaboration with Rejewski and Zygalski continued.[67]
Enigma decryption, however, had become an exclusively British and American domain; the two mathematicians who, with their late colleague, had laid the foundations for Allied Enigma decryption were now excluded from making further contributions to their métier.[77] British cryptologist Alan Stripp suggests that by that time, at Bletchley Park, "very few even knew about the Polish contribution" because of the strict secrecy and the "need-to-know" principle. Stripp comments further that "Setting them to work on the Doppelkassetten system was like using racehorses to pull wagons."[78]
Back in Poland
On 15 November 1946 Marian Rejewski was discharged from the Polish Army in Britain. Six days later, on 21 November, he returned to Poland to reunite with his wife and family. He had married Irena Maria Lewandowska five years before the war, on 20 June 1934, and they had two children: a son, Andrzej (Andrew), born in 1936; and a daughter, Janina (Joan), born in 1939. Janina would later become a mathematician like her father.[79]
On his return to Poland, Rejewski was urged by his old Poznań University professor, Zdzisław Krygowski, to take a university mathematics post at Poznań or Szczecin, in western Poland. He could have looked forward to rapid advance due to shortages in personnel, decimated in the war. But Rejewski was still recovering from the strains and health effects of the war; among other things, he had contracted rheumatism in the dank Spanish prisons. Then, soon after his return to Poland, in the summer of 1947, after only five days' illness, his 11-year-old son Andrzej died of polio. After that, Rejewski did not want to part, even briefly, with his wife and daughter. They lived in Bydgoszcz with his in-laws (his wife's father was a prosperous dentist).[79] Rejewski took a position in Bydgoszcz as director of the sales department at a cable-manufacturing company, Kabel Polski (Polish Cable).[79]

Between 1949 and 1958 Rejewski, who was suspect to the postwar Polish authorities as an ex-member of the Polish Armed Forces in the West, was repeatedly investigated by the Office of Public Security.[80] He retired in 1967, and in 1969 he moved with his family back to Warsaw, to the apartment that he had acquired in May 1939 with financial help from his father-in-law. (After the Germans had suppressed the 1944 Warsaw Uprising, they had sent Mrs. Rejewska and her children west, along with other Warsaw survivors; the family had eventually found refuge with her parents in Bydgoszcz.)[79]
Rejewski had in 1942, at Uzès, in Vichy France, written a "Report of Cryptologic Work on the German Enigma Machine Cipher."[81] Before his retirement in 1967 a quarter-century later, he began writing his "Memoirs of My Work in the Cipher Bureau of Section II of the [Polish] General Staff," which were purchased by the Military Historical Institute, in Warsaw.[79] Rejewski often wondered, after the 1940 French debacle, what use Alan Turing (who in early 1940 had visited the Polish cryptologists outside Paris[82]) and Bletchley Park had ultimately made of the Polish discoveries and inventions. For nearly three decades after the war, little was publicly known due to a ban that had been imposed on 25 May 1945 by British Prime Minister Winston Churchill.[83]
Until 1974, what little was published concerning Enigma decryption attracted little attention. Ladislas Farago's 1971 best-seller The Game of the Foxes presented a garbled account of Ultra's origins: "Commander Denniston went clandestinely to a secluded Polish castle [sic!] on the eve of the war [to pick up an Enigma, "the Wehrmacht's top system" during World War II]. Dilly Knox later solved its keying [sic!]..."[84] Still, this was marginally closer to the truth than many British and American best-seller accounts that would follow after 1974. Their authors were at a disadvantage: they did not know that the founder of Enigma decryption, Marian Rejewski, was still alive and alert, and that it was therefore hazardous to fabricate stories about the history of Enigma decryption.[Note 16]
With Gustave Bertrand's 1973 publication of his Enigma, substantial information about the origins of Ultra began to seep out to the broader world public. With F.W. Winterbotham's 1974 best-seller The Ultra Secret, the dam began to burst. Still, many authors aspiring to best-sellerdom were not averse to filling gaps in their information with whole-cloth fabrications. Rejewski fought a gallant (if, into the 21st century, still not entirely successful) fight to get the truth before the public. He published a number of papers on his cryptologic work and contributed generously to articles, books, and television programs. He was interviewed by scholars, journalists, and television crews from Poland, East Germany, the United States, Britain, Sweden, Belgium, the Soviet Union, Yugoslavia and Brazil.[85]
Rejewski maintained a lively correspondence with his wartime French host, General Gustave Bertrand, and at the General's bidding he began translating Bertrand's Enigma into Polish.[85] In 1976, at the request of the Józef Piłsudski Institute of America, Rejewski broke enciphered correspondence of Józef Piłsudski and his fellow Polish Socialist conspirators from 1904.[86] On 12 August 1978 he received from a grateful Polish people the Officer's Cross of the Order of Polonia Restituta.[85]
Rejewski, who had been suffering from heart disease, died of a heart attack on 13 February 1980, aged 74, after returning home from a shopping trip. He was buried with military honors at Warsaw's Powązki Military Cemetery.[79]
Recognition
In 1979 Rejewski and his colleagues became heroes of Sekret Enigmy ("The Enigma Secret"), a Polish-cryptologists-and-German-spies movie thriller about the Poles' solution of the German Enigma cipher. Late 1980 also saw a Polish TV series with a similar theme, Tajemnice Enigmy ("The Secrets of Enigma").[87]
On 21 July 2000, Poland's President Aleksander Kwaśniewski posthumously awarded Poland's highest civilian decoration, the Grand Cross of the Order of Polonia Restituta, to Marian Rejewski and Henryk Zygalski.[1]
On 4 July 2005, Rejewski's daughter Janina Sylwestrzak received on his behalf, from the British Chief of the Defence Staff, the War Medal 1939–1945.[2]
In 2007 a three-sided bronze monument was dedicated before Poznań Castle. Each side bears the name of one of the three mathematics students who had attended the 1929 cryptology course and subsequently collaborated on breaking the Enigma cipher.[88]
On 1 August 2012, Marian Rejewski posthumously received the Knowlton Award of the U.S. Military Intelligence Corps Association.[89] Rejewski's mathematician daughter Janina accepted the award on behalf of her late father at his home town, Bydgoszcz, on 4 September 2012. Rejewski had been nominated for the award by NATO Allied Command Counterintelligence. The Knowlton Award, named for an American War of Independence military intelligence chief, was established in 1995.[3]
On 5 August 2014, the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) honored Rejewski, Różycki and Zygalski with its prestigious Milestone award, which recognizes achievements that have changed the world. Only some 120 persons have been so honored.[4][5]
 Plaque at Bletchley Park, unveiled 2002. English side reads: "This plaque commemorates the work of Marian Rejewski, Jerzy Różycki and Henryk Zygalski, mathematicians of the Polish intelligence service, in first breaking the Enigma code [sic: it was a cipher]. Their work greatly assisted the Bletchley Park code breakers and contributed to the Allied victory in World War II." |
 Polish prepaid postcard (2005) commemorating centennial of Rejewski's birth |
Military ceremony (2005) at Rejewski's grave on centennial of his birth |
See also
| Methods and technology |
|---|
| Locations |
| Personnel |
|
Chief
Gwido Langer German Section cryptologists Wiktor Michałowski
Chief of Russian Section
Jan Graliński Russian Section cryptologist
Piotr Smoleński |
- Cryptanalysis of the Enigma
- List of cryptographers
- List of Poles
- Tadeusz Pełczyński
- Polish contribution to World War II
- Polish School of Mathematics
Citations
Notes
- ↑ The exact extent of the contribution of Ultra to Allied victory is debated. The typical view is that Ultra shortened the war; Supreme Allied Commander Dwight D. Eisenhower called Ultra "decisive" to Allied victory. (Brzezinski 2005, p. 18) For a fuller discussion, see "Ultra".
- ↑ Bydgoszcz (called "Bromberg" in German) was then part of the Prussian Province of Posen. Bydgoszcz—which had been seized by Prussia in the 1772 First Partition of Poland—returned to Poland in 1919 after the Greater Poland Uprising.
- ↑ The course began on 15 January 1929. A letter dated "Warsaw, 29 January 1929, To Professor Z. Krygowski, in Poznań, ul. Głogowska 74/75," and signed by the "Chief of the General Staff, Piskor [i.e., Tadeusz Piskor], Generał Dywizji," reads: "I hereby thank Pan Profesor for his efforts and assistance given to the General Staff in organizing the cipher [i.e., cryptology] course opened in Poznań on 15 January 1929." The letter is reproduced in Jakóbczyk & Stokłosa (2007, p. 44)
- ↑ An early Naval Enigma model (the "O Bar" machine) had been solved before 1931 by the Polish Cipher Bureau, but it did not have the plugboard of the later standard Enigma. (Mahon 1945, p. 12) Mahon cites, as his source for "most of the information I have collected about prewar days", Alan Turing, who had received it from the "Polish cryptographers", who Mahon says had done "nearly all the early work on German Naval Enigma [and] handed over the details of their very considerable achievements just before the outbreak of war."
- ↑ One element of the key, the sequence of rotors in the machine, at first was changed quarterly; but from 1 January 1936 it was changed monthly; from 1 October 1936, daily; and later, during World War II, as often as every eight hours. (Rejewski 1984c, p. 242)
- ↑ Bertrand had obtained the material from a German Chiffrierdienst (Cryptographic Service) employee, Hans-Thilo Schmidt. (Kozaczuk 1984, pp. 16–17)
- ↑ In the 1920s, French radio intelligence had been decentralized. Decryption of foreign, chiefly German and Italian, ciphers and codes had been the responsibility of a General Staff cryptology department, while radio monitoring had been conducted by the intelligence service, Service de Renseignement or S.R. At the end of 1930, decryption was turned over to the S.R., which created a Section D (for Decryptement), of which Bertrand became chief. He later took over all of French radio intelligence. (Kozaczuk 1984, p. 22)
- ↑ Cipher A. Deavours writes: "No doubt practitioners of group theory should introduce this property of permutations [that they do not change the cyclic structure] to students as 'the theorem that won World War II.'" Cipher A. Deavours, in an afterword to Rejewski (1981, pp. 229, 232).
- ↑ Some writers, after Bloch & Deavours (1987), argue that Rejewski is more likely to have received these documents in mid-November, rather than on 9 or 10 December 1932. Rejewski, however, recalls: "I later... learned that... it was on December 8 [1932, that] Bertrand had come to Warsaw and delivered this material. [H]e describes it in his book [Enigma. T]here is a mistake [in the book] and he gives the year [as] 1931. But later I corresponded with him, and it turned out that it had been... the eighth of December, 1932." Marian Rejewski, in Woytak (1984b, p. 233).
- ↑ Lawrence (2004) shows how Rejewski could have adapted his method to solve for the second rotor, even if the settings lists had not straddled the quarterly changeover period.
- ↑ More Enigma settings were provided to the Polish Cipher Bureau by French Intelligence, but these were never passed on to Rejewski and his colleagues. A possible explanation for this is that the Poles wished to remain independent of French assistance for reading Enigma, and without outside help the cryptologists were forced to develop their own self-sufficient techniques.
- ↑ The Navy had already changed its Enigma indicator procedure on 1 May 1937. For most other branches, the message key procedure changed on 15 September 1938. (Rejewski 1981, pp. 225–226) The SD net, which lagged behind the other services, changed procedure only on 1 July 1939. (Rejewski 1981, p. 227)
- ↑ F.H. Hinsley writes: "[D]ecrypts from the German Enigma were obtained regularly [by the British] from the spring of 1940 [though] they were confined for the next twelve months to an Enigma key used only in the Norwegian campaign and to two keys used by the German Air Force."[52]
- ↑ Rejewski later wrote that at Cadix they did not work on Enigma. (Rejewski 1984d, p. 270) Other sources indicate that they had, and Rejewski conceded that this was likely the case. Rejewski's correspondent concluded that "Rejewski either had forgotten or had not known that, e.g., Zygalski and Różycki had read Enigma after the fall of France". (Kozaczuk 1984, p. 117)
- ↑ Kozaczuk writes:"For security and personal safety, the Poles seldom participated in courier missions or the like. An exception was departures [from Cadix] for two- to three-month stints at the Château Couba [on the outskirts of Algiers]. One such expedition across the Mediterranean ended tragically. In circumstances that remain unclear to this day, the French ship Lamoricière, on which four Poles were returning from Algiers, suffered [disaster] on 9 January 1942, near the Balearic Islands. It is not clear whether, amid a raging storm, the ship struck a reef or one of the thousands of mines that the belligerents were laying. Killed in the Lamoricière [disaster] were Capt. Jan Graliński, Jerzy Różycki, and Piotr Smoleński.[...] Also lost was a French officer accompanying the Poles, Capt. François Lane." (Kozaczuk 1984, p. 128) Nearly 38 years later, in a letter of 25 November 1979, Rejewski recalled Różycki: "As a person, he was a very good friend, cheerful, sociable. [...] He had married shortly before the war in Poland, and when he left Poland [in September 1939] he left behind his wife and a child of several months. His son is presently living in England...." (Kozaczuk 1984, pp. 238–239)
- ↑ In 1982, Polish-American historian Richard Woytak critiqued the absurd stories about the origins of Poland's mastery of decryption of German Enigma ciphers via theft or pure espionage, and about how the British had learned of the Polish achievements, that had been published in British and American best-seller books: in F. W. Winterbotham's The Ultra Secret (1974); in Anthony Cave Brown's Bodyguard of Lies (1975); in William Stevenson's A Man Called Intrepid (1976); and in Appendix 1 of the official history of British Intelligence in the Second World War, by F.H. Hinsley et al., vol. 1, 1979. (After Woytak published Rejewski's "Remarks on Appendix 1 to British Intelligence in the Second World War, by F.H. Hinsley" in Cryptologia, vol. 6, no. 1, January 1982, the spurious story about "a Pole who was working in an Enigma factory in Germany" was finally retracted in a subsequent volume of British Intelligence in the Second World War.) Richard Woytak, prefatory note (pp. 75–76) to Rejewski & Kasparek (1982).
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "Postanowienie Prezydenta Rzeczypospolitej Polskiej z dnia 14 lutego 2000 r. o nadaniu orderów." [Polish Order of the President of the Republic on 14 February 2000. On awarding orders.], Monitor Polski (in Polish) 13 (273), 14 February 2000
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Untold Story of Enigma Code-Breaker, 5 July 2005, archived from the original on 18 November 2005, retrieved 9 January 2006
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 "Najwyższe odznaczenie amerykańskiego wywiadu za złamanie kodów Enigmy" [Highest American Intelligence Award for Breaking Enigma Ciphers], Gwiazda Polarna (in Polish) 103 (20), 22 September 2012: 6
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Guz, Rafał (2015-01-11), Wyróżnienie Milestone dla polskich matematyków za złamanie Enigmy [Milestone Award for Polish mathematicians for breaking the Enigma] (in Polish), Polska Agencja Prasowa
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Mazierska, Janina (December 2014), "IEEE Milestone Dedication on the First Breaking of Enigma Code (Poland Section)" (PDF), The IEEE Region 10 Newsletter: 2–4, retrieved 1 February 2015
- ↑ Kozaczuk 1984, p. 7, note 6
- ↑ Kasparek & Woytak 1982, p. 19
- ↑ Information on Marian Rejewski's military service record, reproduced in Kozaczuk (1979, opposite p. 257).
- ↑ Kasparek & Woytak 1982, p. 20
- ↑ Woytak 1984b, p. 230
- ↑ Woytak 1984b, p. 238
- ↑ Kozaczuk 1984, p. 4
- ↑ Information on Marian Rejewski's Master of Philosophy diploma, 1 March 1929, reproduced in Kozaczuk (1979, opposite p. 128).
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 Woytak 1984b, pp. 230–231
- ↑ Kozaczuk 1984, pp. 5–6
- ↑ Woytak 1984b, p. 231
- ↑ Kozaczuk 1984, pp. 10–11
- ↑ 18.0 18.1 Woytak 1984b, p. 232
- ↑ Kozaczuk 1984, p. 12
- ↑ Rejewski 1984d, pp. 247–251
- ↑ 21.0 21.1 Kozaczuk 1984, pp. 12, 19–21
- ↑ Rejewski (1984c)
- ↑ Rejewski 1984d
- ↑ Rejewski 1984e
- ↑ Kahn 1996, p. 974
- ↑ Bauer 2007, pp. 384, 418
- ↑ 27.0 27.1 Rejewski 1984e, p. 274
- ↑ Rejewski 1984d, p. 254
- ↑ Rejewski 1984d, pp. 251–254
- ↑ Rejewski 1984d, pp. 254–255
- ↑ 31.0 31.1 31.2 31.3 Rejewski 1984d, p. 258
- ↑ Woytak 1984b, p. 233
- ↑ Rejewski 1984d, pp. 258–259
- ↑ Lawrence 2005a; Lawrence 2005b
- ↑ Woytak 1984b, pp. 234–235
- ↑ 36.0 36.1 36.2 36.3 36.4 Rejewski 1984c, p. 242
- ↑ Rejewski 1984d, p. 262
- ↑ Rejewski 1984e, pp. 284–287
- ↑ Rejewski 1984d, p. 265
- ↑ Kozaczuk 1984, pp. 242, 290
- ↑ Welchman 1986
- ↑ Rejewski 1984e, p. 288
- ↑ Rejewski 1984e, p. 289
- ↑ Kozaczuk, 1984, p. 63, note 6.
- ↑ Miller 2001
- ↑ Marian Rejewski, 1984d, p. 269.
- ↑ Rejewski & Kasparek 1982, p. 80. Cited in Kozaczuk (1984, p. 63, note 7).
- ↑ 48.0 48.1 Erskine 2006
- ↑ Kozaczuk 1984, p. 59
- ↑ Woytak 1984b, p. 236
- ↑ Kozaczuk 1984, p. 84
- ↑ F.H. Hinsley, "Introduction: The influence of Ultra in the Second World War", in F.H. Hinsley and Alan Stripp, eds., Codebreakers: The Inside Story of Bletchley Park, Oxford, Oxford University Press, 1993, p. 2.
- ↑ Sebag-Montefiore 2000
- ↑ Welchman 1982, p. 289
- ↑ Kozaczuk & Straszak 2004, p. 74
- ↑ Hinsley 1993
- ↑ Kozaczuk 1984, p. 71
- ↑ Kozaczuk 1984, pp. 71–73, 79
- ↑ Kozaczuk 1984, pp. 81–82
- ↑ Kozaczuk 1984, pp. 84; 94, note 8
- ↑ Kozaczuk 1984, p. 87
- ↑ Kozaczuk 1984, p. 82
- ↑ Kozaczuk 1984, p. 109
- ↑ Kozaczuk 1984, pp. 113–114, 118–130
- ↑ Kozaczuk 1984, pp. 134–135
- ↑ Kozaczuk 1984, p. 128
- ↑ 67.0 67.1 Bertrand 1973, pp. 137–141
- ↑ Kozaczuk 1984, pp. 148–150
- ↑ Kozaczuk 1984, pp. 150
- ↑ Kozaczuk 1984, pp. 150–151
- ↑ Kozaczuk 1984, pp. 151–154
- ↑ Kozaczuk 1984, p. 155
- ↑ Kozaczuk 1984, pp. 205–206
- ↑ Kozaczuk 1984, pp. 207–209
- ↑ Kozaczuk 1984, p. 209
- ↑ Kozaczuk 1984, p. 220
- ↑ Kozaczuk 1984, pp. 207–208
- ↑ Stripp 2004, p. 124
- ↑ 79.0 79.1 79.2 79.3 79.4 79.5 Kozaczuk 1984, p. 226
- ↑ Polak 2005, p. 78
- ↑ Kozaczuk 1984, p. 326
- ↑ Kozaczuk 1984, p. 96–98
- ↑ Winterbotham 1974, p. 15
- ↑ Farago 1971, p. 674
- ↑ 85.0 85.1 85.2 Kozaczuk 1984, p. 225
- ↑ Kozaczuk 1990
- ↑ Kasparek & Woytak 1982, p. 24
- ↑ Jakóbczyk & Stokłosa 2007
- ↑ "Awards". MICAStore.com. Military Intelligence Corps Association. Retrieved 5 February 2015.
Bibliography
| The Enigma cipher machine |
|---|
|
- The main source used for this article was Kozaczuk (1984).
- Bauer, Friedrich L. (2007), "14. Rotor Machines and Bombes", in de Leeuw, Karl Maria Michael; Bergstra, Jan, The History of Information Security: A Comprehensive Handbook, Elsevier, pp. 381–446, doi:10.1016/B978-044451608-4/50015-8, ISBN 9780444516084
- Bertrand, Gustave (1973), Enigma ou la plus grande énigme de la guerre 1939–1945 [Enigma: the Greatest Enigma of the War of 1939–1945] (in French), Paris: Librairie Plon
- Bloch, Gilbert; Deavours, C. A. (July 1987), "Enigma before Ultra: Polish Work and the French Contribution", Cryptologia 11 (3): 142–155, doi:10.1080/0161-118791861947
- Brzezinski, Zbigniew (2005), "The Unknown Victors", in Ciechanowski, Jan Stanislaw, Marian Rejewski 1905–1980, Living with the Enigma secret (1st ed.), Bydgoszcz: Bydgoszcz City Council, pp. 15–18, ISBN 83-7208-117-4
- Erskine, Ralph (December 2006), "The Poles Reveal their Secrets: Alastair Denniston's Account of the July 1939 Meeting at Pyry", Cryptologia 30 (4): 294–305, doi:10.1080/01611190600920944
- Farago, Ladislas (1971), The Game of the Foxes: The Untold Story of German Espionage in the United States and Great Britain during World War II, New York: Bantam Books, OCLC 2371136
- F.H. Hinsley and Alan Stripp, eds., Codebreakers: The Inside Story of Bletchley Park, Oxford, Oxford University Press, 1993, ISBN 0-19-820327-6.
- Hinsley, Harry (19 October 1993), "The Influence of Ultra in the Second World War", University of Cambridge History Research Group, archived from the original on 22 June 2011, retrieved 5 February 2015
- Jakóbczyk, Stanisław; Stokłosa, Janusz, eds. (2007), Złamanie szyfru Enigma. Poznański pomnik polskich kryptologów [The Breaking of the Enigma Cipher: the Poznań Monument to the Polish Cryptologists] (in Polish), Poznań: Wydawnictwo Poznańskiego Towarzystwa Przyjaciół Nauk, ISBN 978-83-7063-527-5
- Kahn, David (1996), The Codebreakers: The Comprehensive History of Secret Communication from Ancient Times to the Internet (2nd ed.), New York: Scribner, ISBN 0-684-83130-9
- Kasparek, Christopher; Woytak, Richard (January 1982), "In Memoriam Marian Rejewski", Cryptologia 6 (1): 19–25, doi:10.1080/0161-118291856740
- Kozaczuk, Władysław (1979), W kręgu Enigmy [In the Circle of Enigma] (in Polish), Warsaw: Książka i Wiedza (Kozaczuk's Polish-language book that was later elaborated into the English-language Kozaczuk (1984).)
- Kozaczuk, Władysław (1984), Kasparek, Christopher, ed., Enigma: How the German Machine Cipher Was Broken, and How It Was Read by the Allies in World War Two, Frederick, MD: University Publications of America, ISBN 0-89093-547-5. (The standard reference on the Polish part in the Enigma-decryption epic. This English-language book is substantially revised from the Polish language Kozaczuk (1979) with additional documentation, including many additional substantive chapter notes and papers by, and interviews with, Marian Rejewski.)
- Kozaczuk, Władysław (July 1990), "A New Challenge for an Old Enigma-Buster", Cryptologia 14 (3): 204–216, doi:10.1080/0161-119091864913
- Kozaczuk, Władysław; Straszak, Jerzy (2004), Enigma: How the Poles Broke the Nazi Code, New York: Hippocrene Books, ISBN 0-7818-0941-X
- Lawrence, John (April 2004), "The Versatility of Rejewski's Method: Solving for the Wiring of the Second Rotor", Cryptologia 28 (2): 149–152, doi:10.1080/0161-110491892836
- Lawrence, John (July 2005a), "A Study of Rejewski's Equations", Cryptologia 29 (3): 233–247, doi:10.1080/01611190508951300
- Lawrence, John (October 2005b), "Factoring for the Plugboard — Was Rejewski's Proposed Solution for Breaking the Enigma Feasible?", Cryptologia 29 (4): 343–366, doi:10.1080/0161-110591893924
- Mahon, A. P. (June 1945), The History of Hut Eight: 1939–1945, 117 pp., PRO HW 25/2
- Miller, A. Ray (2001), The Cryptographic Mathematics of Enigma (PDF), OCLC 50900409, archived from the original (PDF) on 2009-01-17
- Polak, Wojciech (2005), "Marian Rejewski in the Sights of the Security Services", in Ciechanowski, Jan Stanisław, Marian Rejewski, 1905–1980: Living with the Enigma Secret, Bydgoszcz: Bydgoszcz City Council, pp. 75–88, ISBN 83-7208-117-4
- Rejewski, Marian (1980), "An Application of the Theory of Permutations in Breaking the Enigma Cipher" (PDF), Applicationes Mathematicae 16 (4): 543–559
- Rejewski, Marian (July 1981), "How Polish Mathematicians Deciphered the Enigma" (PDF), Annals of the History of Computing 3 (3): 213–234, doi:10.1109/MAHC.1981.10033; has afterwords by I. J. Good and Cipher A. Deavours; also appears as Rejewski (1984d)
- Rejewski, Marian; Kasparek, Christopher (January 1982), "Remarks on Appendix 1 to British Intelligence in the Second World War by F. H. Hinsley", Cryptologia 6 (1): 75–83, doi:10.1080/0161-118291856867
- Rejewski, Marian (1984c), "Summary of Our Methods for Reconstructing Enigma and Reconstructing Daily Keys, and of German Efforts to Frustrate Those Methods", in Kozaczuk, Władysław, Enigma, pp. 241–245, ISBN 0-89093-547-5, Appendix C
- Rejewski, Marian (1984d), "How the Polish Mathematicians Broke Enigma", in Kozaczuk, Władysław, Enigma, pp. 246–271, ISBN 0-89093-547-5, Appendix D
- Rejewski, Marian (1984e), "The Mathematical Solution of the Enigma Cipher", in Kozaczuk, Władysław, Enigma, pp. 272–291, ISBN 0-89093-547-5, Appendix E. Covers much the same ground as Rejewski (1980).
- Marian Rejewski, interview (transcribed by Christopher Kasparek) in: Richard Woytak, Werble historii (History's Drumroll), edited by and with introduction by Stanisław Krasucki, illustrated with 36 photographs, Bydgoszcz, Poland, Związek Powstańców Warszawskich w Bydgoszczy (Association of Warsaw Insurgents in Bydgoszcz), 1999, ISBN 83-902357-8-1, pp. 123–143. A more complete transcript of the interview, highlights of which earlier appeared in Richard A. Woytak, "A Conversation with Marian Rejewski", Cryptologia, vol. 6, no. 1 (January 1982), pp. 50–60, DOI 10.1080/0161-118291856830, and as Appendix B to Władysław Kozaczuk, Enigma, 1984, pp. 229–240.
- Sebag-Montefiore, Hugh (2000), Enigma: the Battle for the Code, London: Weidenfeld and Nicolson, ISBN 9780297842514
- Stripp, Alan (2004), "A British Cryptanalyst Salutes the Polish Cryptanalysts", in Kozaczuk, Władysław; Straszak, Jerzy, Enigma: How the Poles Broke the Nazi Code, New York: Hippocrene Books, pp. 123–125, ISBN 0-7818-0941-X, Appendix E
- Welchman, Gordon (1982), The Hut Six Story: Breaking the Enigma Codes, New York: McGraw-Hill, ISBN 9780070691803
- Welchman, Gordon (January 1986), "From Polish Bomba to British Bombe: the Birth of Ultra", Intelligence and National Security 1 (1): 71–110, doi:10.1080/02684528608431842
- Winterbotham, F. W. (1974), The Ultra Secret, New York: Dell
- Woytak, Richard (1984b), "A Conversation with Marian Rejewski", in Kozaczuk, Władysław, Enigma, pp. 229–240, ISBN 0-89093-547-5, Appendix B
Further reading
- Kubiatowski, Jerzy (1988). "Rejewski, Marian Adam". Polski słownik biograficzny [Polish Biographical Dictionary] (in Polish). XXXI/1. Warsaw: Wydawnictwo Polskiej Akademii Nauk (Polish Academy of Sciences). pp. 54–56.
External links
- The Enigma Code Breach by Jan Bury: an account of the Polish role
- The Breaking of Enigma by the Polish Mathematicians by Tony Sale
- How Mathematicians Helped Win WWII — National Security Agency
- Enigma documents
- Marian Rejewski and the First Break into Enigma
|


