Marguerite Gardiner, Countess of Blessington
| Marguerite, Lady Blessington | |
|---|---|
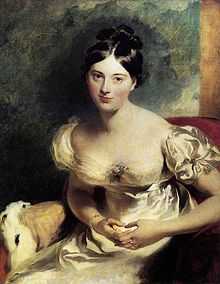 Painted by Sir Thomas Lawrence in 1822 | |
| Born |
Margaret Power 1 September 1789 Clonmel, Ireland |
| Died |
4 June 1849 (aged 59) Paris, France |
| Occupation | Novelist, miscellaneous writer |
| Notable works | Conversations with Lord Byron (1834) |
Marguerite Gardiner, Countess of Blessington (1 September 1789 – 4 June 1849) was an Irish novelist.
Born Margaret Power near Clonmel in County Tipperary, Ireland, she was a daughter of Edmund Power, a small landowner. Her childhood was made unhappy by her father's character and poverty, and her early womanhood wretched by her compulsory marriage at the age of fifteen to a Captain Maurice St. Leger Farmer, an English officer whose drunken habits finally brought him as a debtor to the King's Bench Prison, where he died in October 1817.
Marguerite had left him some time before, moving to Hampshire to live with the family of Thomas Jenkins, a sympathetic and literary sea captain.[1] Jenkins introduced her to the Irish earl Charles John Gardiner, 1st Earl of Blessington, a widower with four children (two legitimate), seven years her senior. They married at St Mary's, Bryanston Square, Marylebone on 16 February 1818 (only four months after her first husband's death). Of rare beauty, charm and wit, she was no less distinguished for her generosity and for the extravagant tastes she shared with her husband, which resulted in encumbering his estates with a load of debt. On 25 August 1822 they set out for a continental tour with Marguerite's youngest sister, the 21-year-old Mary Anne, and servants. They met Count D'Orsay (who had first become an intimate of Lady Blessington in London in 1821) in Avignon on 20 November 1822, before settling at Genoa for four months from 31 March 1823. There they met Byron on several occasions, giving Lady Blessington material for her Conversations with Lord Byron.
After that they settled for the most part in Naples, where she met the Irish writer Richard Robert Madden, who was to become her biographer. They also spent time in Florence with their friend Walter Savage Landor, author of the Imaginary Conversations which she greatly admired. It was in Italy, on 1 December 1827, that Count D'Orsay married Harriet Gardiner, Lord Blessington's only daughter by his former wife. The Blessingtons and the newlywed couple moved to Paris towards the end of 1828, taking up residence in the Hôtel Maréchal Ney, where the Earl suddenly died at 46 of an apopleptic stroke in 1829. D'Orsay and Harriet then accompanied Lady Blessington to England, but the couple separated soon afterwards amidst much acrimony. D'Orsay continued to live with Marguerite until her death. Their home, first at Seymour Place, and afterwards Gore House, Kensington, now the site of the Royal Albert Hall, became a center of attraction for all that was distinguished in literature, learning, art, science and fashion. Benjamin Disraeli wrote Venetia whilst staying there.
After her husband's death she supplemented her diminished income by contributing to various periodicals as well as by writing novels. She was for some years editor of The Book of Beauty and The Keepsake, popular annuals of the day. In 1834 she published her Conversations with Lord Byron. Her Idler in Italy (1839–1840), and Idler in France (1841) were popular for their personal gossip and anecdotes, descriptions of nature and sentiment.
Early in 1849, Count D'Orsay left Gore House to escape his creditors; subsequently the furniture and decorations were sold in a public sale successfully discharging Lady Blessington's debts. Lady Blessington joined the count in Paris, where she died on 4 June 1849 of a burst heart. On examination it was found that her heart was three times normal size.
Her Literary Life and Correspondence (3 vols.), edited by Richard Robert Madden, appeared in 1855. Her portrait was painted in 1808 by Sir Thomas Lawrence and can be seen in The Wallace Collection, London.
References
- ↑ "bio of Blessington". Extra.shu.ac.uk. Retrieved 29 September 2013.
 This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Cousin, John William (1910). A Short Biographical Dictionary of English Literature. London: J. M. Dent & Sons. Wikisource
This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Cousin, John William (1910). A Short Biographical Dictionary of English Literature. London: J. M. Dent & Sons. Wikisource This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). "Blessington, Marguerite". Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press.
This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). "Blessington, Marguerite". Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Marguerite Gardiner, Countess of Blessington. |
- Works by Marguerite, Countess of Blessington at Project Gutenberg
- Works by the Author at the Internet Archive
- Works by or about Marguerite Gardiner, Countess of Blessington in libraries (WorldCat catalog)
- Archival material relating to Marguerite Gardiner, Countess of Blessington listed at the UK National Archives
- Lady Blessington manuscript material, 1820-1849, held by the Carl H. Pforzheimer Collection of Shelley and His Circle, The New York Public Library, New York Public Library
|