Mammutidae
| Mammutidae Temporal range: 28.4–0Ma | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Mounted mastodon skeleton, Museum of the Earth | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Infraclass: | Eutheria |
| Superorder: | Afrotheria |
| Order: | Proboscidea |
| Family: | †Mammutidae Hay, 1922 |
| Genera[1] | |
|
†Eozygodon Tassy and Pickford, 1983 | |
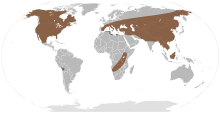 | |
| The inferred range of the Mammutidae | |
The Mammutidae are a family of extinct proboscideans that lived between the Miocene and the Pleistocene to Holocene. The family was first described in 1922, classifying fossil specimens of the type genus Mammut (mastodons), and has since been placed in various arrangements of the order. The name mastodon derives from Greek, μαστός "nipple" and ὀδούς "tooth", as with the genus, to indicate a characteristic that distinguishes them from allied families. The genus Zygolophodon has also been assigned to this family.
Mammutidae classify taxa known by the common name mastodon, a name also used by Georges Cuvier for the genus Mastodon.
Discoveries

In August 2008, miners in Romania unearthed the skeleton of a 2.5-million-year-old mastodon, believed to be one of the best preserved in Europe.[2] Ninety percent of the skeleton's bones were intact, with damage to the skull and tusks.[2] In 2009, a family in Portland, Michigan unearthed mastodon bones while excavating a new pond on their property. It is one of around 250 mastodons found in Michigan over the past century.[3]
As of July 2009, six mastodon fossils were discovered in Elmacık village, in Burdur province, Turkey. Also, the first excavation to discover mastodon fossils in Elmacık village took place in 2006.[4]
In August 2011, a skeleton of a mastodon was found near Tomislavgrad in Bosnia and Herzegovina.[5] In November 2011, a mastodon skeleton was unearthed in Daytona Beach, FL during construction of a retention pond.[6] The find is being studied by the Daytona Beach Museum of Arts and Sciences.
Classification
The family diverged from a common ancestor with the Elephantidae, which includes the extinct genus Mammuthus, the mammoths, and extant species of Elephas and Loxodonta, the modern elephants.
The author of Mammutidae also published Gomphotheriidae, which also includes species previously described as Mastodon. The classification of proboscideans is unstable and frequently revised; relationships within the order are controversial, and it is incompletely summarised as:
- Elephantimorpha
- Elephantida
- Elephantidae (elephants and mammoths)
- Gomphotheriidae (gomphotheres)
- Mammutida
- Mammutidae (mastodons)
- Eozygodon
- Zygolophodon
- Mammut
- Mammutidae (mastodons)
- Elephantida
Some earlier descriptions of specimens as Mastodon have been transferred to the genera of Mammutidae.
References
- ↑ Shoshani, Jeheskel; Pascal Tassy (2005). "Advances in proboscidean taxonomy & classification, anatomy & physiology, and ecology & behavior". Quaternary International. 126-128: 5–20. doi:10.1016/j.quaint.2004.04.011.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.5 million-year-old mastodon unearthed in Romania, USA Today, 2008-08-08, Retrieved on 11 August 2008
- ↑ "Michigan Family Finds Prehistoric Bones - Mastodon Bones To Be Given To University Of Michigan". The Associated Press. July 2, 2009. Retrieved 3 July 2009.
- ↑ "Mastodon Fossils Discovered In Burdur/Turkey". Yerbilimleri. July 17, 2009. Retrieved 17 July 2009.
- ↑ U Tomislavgradu otkriven kostur pretka slona, Večernji list, 2011-08-18. Retrieved 2011-08-26 (Croatian)
- ↑ http://www.news-journalonline.com/breakingnews/2011/11/mastodon-bones-found-at-daytona-beach-work-site.html
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Mammutidae. |
| Wikispecies has information related to: Mammutidae |