Malaysian Expressway System


The Malaysian Expressway System (Malay: Sistem Lebuhraya Malaysia), which begins with the North-South Expressway (NSE), is currently in the process of being substantially developed. It was built by private companies under the supervision of the government highway authority, Malaysian Highway Authority (abbreviated as MHA; also referred to as Lembaga Lebuhraya Malaysia (LLM) in Malay).
Overview
The expressway network of Malaysia is considered the best expressway network in Southeast Asia and also in Asia after China and Japan and also the fifth in the world. They were 30 expressways in the country and the total length is 1,798 kilometres (1,117 mi).[1] [2] and another 219.3 kilometres (136.3 mi) is still under construction. The closed toll expressway system is similar to the Japanese Expressway System and Chinese Expressway System. All Malaysian toll expressways are managed in the Build-Operate-Transfer (BOT) system.
Malaysian expressways exist in both West Malaysia and East Malaysia, however, the former are better-connected. The North-South Expressway passes through all the major cities and conurbations in West Malaysia, such as Penang, Ipoh, the Klang Valley and Johor Bahru. The Pan Borneo Highway connects the Malaysian states of Sabah and Sarawak with Brunei.
Malaysian expressways as a part of Asian Highway Network
.jpg)

A few major expressways in Malaysia are part of the larger Asian Highway Network. The Asian Highway Network is an international project between Asian nations to develop their highway systems, which will form main routes in the network. There are currently seven Asian Highway routes passing through Malaysia:[3][4]-
- Asian Highway Route 2
 - along the North-South Expressway
- along the North-South Expressway  and
and  [5]
[5] - Asian Highway Route 18
 - along the Federal Route 3
- along the Federal Route 3  [5]
[5] - Asian Highway Route 140
 - along the Federal Route 4
- along the Federal Route 4  and Butterworth-Kulim Expressway
and Butterworth-Kulim Expressway  [4]
[4] - Asian Highway Route 141
 - consists of New Klang Valley Expressway
- consists of New Klang Valley Expressway  (Bukit Lanjan-Jalan Duta), Duta-Ulu Klang Expressway
(Bukit Lanjan-Jalan Duta), Duta-Ulu Klang Expressway  (Jalan Duta-Sentul Pasar and Sentul Pasar-Greenwood), Kuala Lumpur Middle Ring Road 2
(Jalan Duta-Sentul Pasar and Sentul Pasar-Greenwood), Kuala Lumpur Middle Ring Road 2  (Greenwood-Gombak North Interchange), Kuala Lumpur-Karak Expressway
(Greenwood-Gombak North Interchange), Kuala Lumpur-Karak Expressway  , East Coast Expressway
, East Coast Expressway  and Gebeng Bypass
and Gebeng Bypass  [4]
[4] - Asian Highway Route 142
 - along the MEC Highway
- along the MEC Highway  , Tun Razak Highway
, Tun Razak Highway  and Federal Route 1 (Segamat-Yong Peng South Interchange)[4]
and Federal Route 1 (Segamat-Yong Peng South Interchange)[4] - Asian Highway Route 143
 - along the Second Link Expressway
- along the Second Link Expressway  [4]
[4] - Asian Highway Route 150
 - along the Pan Borneo Highway.[5]
- along the Pan Borneo Highway.[5]
AH2 border crossing dispute
The status of the route alignment of the Asian Highway ![]() crossing the Malaysia-Singapore border is currently being disputed. Malaysia had commissioned the Second Link Expressway
crossing the Malaysia-Singapore border is currently being disputed. Malaysia had commissioned the Second Link Expressway ![]() as part of
as part of ![]() to maintain the primary access-controlled highway status of the route.[3] Meanwhile, Singapore had commissioned the Johor-Singapore Causeway and the Bukit Timah Expressway as part of
to maintain the primary access-controlled highway status of the route.[3] Meanwhile, Singapore had commissioned the Johor-Singapore Causeway and the Bukit Timah Expressway as part of ![]() , as the Johor-Singapore Causeway is the main gateway to Singapore from Malaysia,[6] which could mean that the Skudai Highway would be included in the route alignment instead of the Second Link Expressway.
, as the Johor-Singapore Causeway is the main gateway to Singapore from Malaysia,[6] which could mean that the Skudai Highway would be included in the route alignment instead of the Second Link Expressway.
Later, the Second Link Expressway, the Ayer Rajah Expressway, Marina Coastal Expressway and Kallang-Paya Lebar Expressway were later gazetted as Asian Highway ![]() .[4]
.[4]
History
Interstate

Before tolled expressways were introduced in the mid 1970s, most Malaysians traveled around Peninsula Malaysia on federal roads.
The major reasons for building new expressways in Malaysia are the increasing number of vehicles along federal routes, the opening of major ports and airports in Malaysia, and the increasing population in major cities and towns of Malaysia.
In the year 1966, the Highway Planning Unit was established under the Ministry of Works and Communications.
The first tolled highway in Malaysia was the 20 km (10 miles) Tanjung Malim-Slim River tolled road (Federal Route ![]() ) which was opened to traffic on 16 March 1966. It saved journey time by half an hour, and cars were charged 50 sen, buses and lorries RM1 and motorcycles 20 sen. However, in 1994, with the completion of the North-South Expressway, the toll plaza was removed and it became a toll-free highway.
) which was opened to traffic on 16 March 1966. It saved journey time by half an hour, and cars were charged 50 sen, buses and lorries RM1 and motorcycles 20 sen. However, in 1994, with the completion of the North-South Expressway, the toll plaza was removed and it became a toll-free highway.
In the year 1970, the first comprehensive five-year road development programme was formulated by the Highway Planning Unit, which included expanding rural roads and plans to construct three new highways linking the east and west coasts.
On 27 March 1974, the Kuala Lumpur-Seremban Expressway was constructed. Funded by a loan by the World Bank, the 63.4 km (39.3 mile) expressway was constructed in three phases; the first phase was from Kuala Lumpur to Nilai, while the second phase was from Nilai to Seremban. The third phase was the rehabilitation of the old Federal Route 1 from Kuala Lumpur to Seremban as a toll-free alternative to motorists. The completion of the Kuala Lumpur-Seremban Expressway on June 1977 marking the first step towards the construction of the new interstate expressway known as North-South Expressway (NSE).
The Kuala Lumpur-Karak Highway (Federal Route ![]() ) was built between 1976 and 1979. Meanwhile, the 900 m (-- ft) Genting Sempah Tunnel was the first highway tunnel in Malaysia, constructed between 1977 and 1979. The tunnel was officially opened in 1979 by the then Minister of Works and Communications, Dato' Abdul Ghani Gilong.[7]
) was built between 1976 and 1979. Meanwhile, the 900 m (-- ft) Genting Sempah Tunnel was the first highway tunnel in Malaysia, constructed between 1977 and 1979. The tunnel was officially opened in 1979 by the then Minister of Works and Communications, Dato' Abdul Ghani Gilong.[7]
The first sections of the North-South Expressway were the toll sections of the Kuala Lumpur-Seremban Expressway from Sungai Besi to Labu toll plazas, which was opened on 16 June 1982. The next sections were Bukit Kayu Hitam-Jitra and Senai-Johor Bahru stretches opened in 1985. Then the Ipoh-Changkat Jering and Seremban-Ayer Keroh stretches, which were opened to traffic in 1986. However, on 1 October 1987 the closed-toll system came into force along the Kuala Lumpur-Ayer Keroh and Ipoh-Changkat Jering stretches. The Ayer Keroh-Pagoh stretch on the North-South Expressway was opened to traffic in 1988. All sections of the North-South Expressway were completed and officially opened on 8 September 1994 by the former Prime Minister of Malaysia, Tun Dr Mahathir Mohammad.
Other interstate expressway projects in Malaysia are North-South Expressway Central Link (opened 1996), East Coast Expressway (opened 2004) and Kajang-Seremban Highway (opened 2008).
Because of a (permanent) massive traffic jam on the North-South Expressway Southern Route between Seremban and Nilai in Negeri Sembilan, a new bypass expressway named Paroi-Senawang-KLIA Expressway was proposed on 2013 to help reduce the traffic jams at the area.[8]
The Phase 2 of the East Coast Expressway (Terengganu) linking Jabur and Kuala Terengganu was completed on 31 January 2015, thus completing the alignment of the East Coast Expressway from Kuala Lumpur to Kuala Terengganu.
The new project in the west coast of Peninsula Malaysia, West Coast Expressway (WCE) has now unveiled by the government. Construction of the 233.0 km (144.8 mile) expressway linking Banting, Selangor and Taiping, Perak will start on the year 2015.
Greater Kuala Lumpur/Klang Valley
The history of the highways in the Klang Valley started after the separation of Singapore from Malaysia on 9 August 1965, when the Malaysian government decided to make Port Swettenham (now Port Klang) Malaysia's new national port as a replacement for Singapore. As a result, the government planned to build a first highway in Klang Valley known as Federal Highway connecting Port Swettenham (now Port Klang) to Kuala Lumpur in the 1960s.
In 1967, the 45 km (28 mile) Federal Highway (Federal Highway Route 2, the first dual-carriageway highway in Malaysia) was opened to traffic.
In the early 1990s the federal government decided to build more expressways and highways in Klang Valley because of the increasing size and population of the Klang Valley conurbation, development of new townships and industrial estates, and the massive traffic jams along Federal Highway.
The New Klang Valley Expressway (NKVE), which was opened in 1990, is the second link to Kuala Lumpur from Klang after Federal Highway. In 1997, North-South Expressway Central Link (NSECL), which is the main link to Kuala Lumpur International Airport (KLIA) was opened to traffic.
Other expressway projects in Klang Valley are Shah Alam Expressway (SAE/KESAS) (opened 1997), Damansara-Puchong Expressway (LDP) (opened 1999), Sprint Expressway (opened 2001), New Pantai Expressway (NPE) (opened 2004), SMART Tunnel (opened 2007), KL-KLIA Dedicated Expressway or Kuala Lumpur-Putrajaya Expressway (KLPE) (now Maju Expressway (MEX)) (opened 2007) and Duta-Ulu Klang Expressway (DUKE) (opened 2009).
In addition to Kuala Lumpur Inner Ring Road (KLIRR) as the inner ring road in Kuala Lumpur, Kuala Lumpur Middle Ring Road 1 (KLMRR1), Kuala Lumpur Western/Northern Dispersal Link Scheme (Sprint Expressway and Duta-Ulu Klang Expressway (DUKE)) and Kuala Lumpur Middle Ring Road 2 (KLMRR2) also act as middle ring roads of the city. Kuala Lumpur-Kuala Selangor Expressway (KLS) (formerly Assam Jawa-Templer Park Highway (LATAR)), Kajang Dispersal Link Expressway (SILK), South Klang Valley Expressway (SKVE) and the planning Kuala Lumpur Outer Ring Road (KLORR) may form the outer ring roads of Kuala Lumpur.
Following the formation of the Greater Kuala Lumpur in the early 2010s, many expressways and highways will be built in the Greater Kuala Lumpur under the Economic Transformation Programme (ETP). These are the Besraya Extension Expressway (now part of the Besraya Expressway) (opened 2012), Damansara-Shah Alam Elevated Expressway (DASH), Sungai Besi-Ulu Klang Elevated Expressway (SUKE), East Klang Valley Expressway (EKVE) which will be part of the Kuala Lumpur Outer Ring Road (KLORR) system, Sri Damansara Link and Tun Razak Link of the Duta-Ulu Klang Expressway (DUKE), Kinrara-Damansara Expressway (KIDEX Skyway) and Serdang-Kinrara-Putrajaya Expressway (SKIP). However, the proposed Kinrara-Damansara Expressway (KIDEX Skyway) project was officially scrapped by the Selangor State Government due to the several protests by the local Petaling Jaya citizens.
Iskandar Malaysia/Johor Bahru


The history of highways in Johor Bahru started in the 1980s when the city of Johor Bahru became a main southern international gateway to Malaysia from Singapore after the separation of Singapore from Malaysia on 9 August 1965.
The main reasons for building expressways in Johor Bahru are the increasing size of the Johor Bahru metropolitan area since it achieved city status on 1 January 1994, and the formation of the South Johor Economic Region (SJER) or Iskandar Development Region (IDR) (now Iskandar Malaysia) on 30 July 2006. Many townships have been constructed around Johor Bahru and industrial estates have been developed in areas such as Senai, Skudai, Tebrau, Pasir Gudang and Tampoi.
The first highway in Johor Bahru was Skudai Highway linking Senai to Johor Causeway, which was completed in 1985 and it was the first toll highway in Johor Bahru. However the toll plaza near Senai was abolished in 2004. Kempas Highway, the only state road in Malaysia constructed as a 2-lane highway was completed in 1994. The Malaysia-Singapore Second Crossing, which is the second link to Singapore after Johor Causeway, was opened to traffic on 18 April 1998.
Other expressway projects in Johor Bahru are Senai-Desaru Expressway (SDE) linking Senai in the west to Desaru in east coast of Johor, the Johor Bahru Eastern Dispersal Link Expressway (EDL) which linking Pandan interchange of the North-South Expressway to the new Sultan Iskandar CIQ Building in city centre, the Iskandar Coastal Highway linking Nusajaya in the west to the city centre in the east and the Johor Bahru East Coast Highway linking Kampung Bakar Batu passing through Permas Jaya, Taman Rinting and finally towards Pasir Gudang.
In addition to Johor Bahru Inner Ring Road (JBIRR) as the inner ring road in Johor Bahru, Pasir Gudang Highway, Second Link Expressway and Johor Bahru Parkway also act as middle ring roads of the city. Second Link Expressway and the Senai-Desaru Expressway may form the outer ring roads of Johor Bahru.
Penang

The history of highways in Penang started in the 1970s when the federal government decided to build the Penang Bridge, connecting Seberang Perai to Penang Island. The construction of Penang Bridge began in 1982 and was completed in 1985. This bridge was officially opened on 14 September 1985 by then Malaysian Prime Minister Tun Dr Mahathir Mohammad.
The main reasons for constructing new expressways in Penang are the increasing population of George Town and Butterworth since the Penang Bridge was opened. Many townships have been built in Penang and new industrial estates have sprung up in areas such as Perai and Bayan Lepas.
Other expressway projects in Penang are Butterworth-Kulim Expressway (BKE), Butterworth Outer Ring Road (BORR), Penang Outer Ring Road (PORR), Jelutong Expressway (JEWAY) (now Tun Dr Lim Chong Eu Expressway), Sungai Juru Expressway and Penang Second Bridge.
A proposal for a second bridge, the Penang Second Bridge, has been approved by the government and included as one of the Ninth Malaysia Plan national projects. According to official news, construction work of the new Penang Second Bridge started on Nov 2007, and was targeted for completion before the end of the year 2010. The Penang Second Bridge in which now official named as Sultan Abdul Halim Muadzam Shah Bridge was officially opened on 1 March 2014 by the Malaysian Prime Minister Najib Tun Razak.
East Malaysia

The history of highways in East Malaysia started in the 1960s when the federal government decided to build the Pan Borneo Highway, linking Sarawak and Sabah state.
The Pan Borneo Highway project is a joint project between the governments of Brunei and Malaysia. The project started as soon as Sarawak and Sabah joined the federation of Malaysia in 1963. The lack of a road network system in Sarawak was the main factor of the construction.
There are one toll expressway, one toll federal highway and one toll state highway in Sarawak - the Tun Salahuddin Bridge in Kuching city, the Miri-Baram Highway in Miri Division, and the Lanang Bridge in Sibu. The Tun Salahuddin Bridge is the first and currently the only toll expressway in East Malaysia.
Expressway standards
The construction, standards, management and usage of expressways in Malaysia are subject to Federal Roads Act (Private Management) 1984. In Malaysia, expressways are defined as high-speed routes with at least four lanes (two in each direction) and should have full access control or partial access control. Most expressways in Malaysia are controlled-access expressways.
Expressways are defined as high-speed highways built under the JKR R6 rural highway standard, as dual-carriageways of at least 4 lanes (2 lanes per carriageway) with full access control, grade-separated interchanges and high design speed limit of 120 km/h, allowing the maximum speed limit of 110 km/h.[9] However, the section between Cahaya Baru and Penawar of the Senai-Desaru Expressway ![]() is built as a two-lane single carriageway with the similar features as the Swiss autostrasse, making it as the first true two-lane controlled-access expressway in Malaysia followed by the section of Teluk Panglima Garang and Pulau Indah of the South Klang Valley Expressway (SKVE)
is built as a two-lane single carriageway with the similar features as the Swiss autostrasse, making it as the first true two-lane controlled-access expressway in Malaysia followed by the section of Teluk Panglima Garang and Pulau Indah of the South Klang Valley Expressway (SKVE) ![]() [10] All expressways are considered federal highways, but administered by Malaysian Highway Authority (MHA) and the respective concessionaire companies.
[10] All expressways are considered federal highways, but administered by Malaysian Highway Authority (MHA) and the respective concessionaire companies.
Highways, on the other hand, complement the national network of expressways and federal roads and built under the JKR R5 rural highway standard, with relatively high design speed limit (although not as high as the expressway speed limit) of 100 km/h, allowing the maximum speed limit of 90 km/h.[9] The highways are built with partial access control, and grade-spearated interchanges and at-grade crossings are both permitted. However, it is possible for a federal or state highway to be built with almost equivalent standard of an expressway with the exception of lower speed limit, for example the Federal Highway. Highways can be built either as dual-carriageway or 2-lane single carriageway.
Before the mid-1990s, there were no specific coding system for the expressways. When more and more expressways were built, a system of expressway numbering was applied to all expressways. Expressways are labelled with the letter E followed by assigned numbers, for example the code for North-South Expressway southern route is ![]() . The expressways have green signs and the text colour is white.
. The expressways have green signs and the text colour is white.
However, there are some exceptions in some highways. Some highways like Federal Highway (Federal Route ![]() ) and Skudai Highway (Federal Route
) and Skudai Highway (Federal Route ![]() ) retain their federal route codes. In addition, there are some highways in Malaysia which are classified as municipal roads such as Kuala Lumpur Middle Ring Road 1.
) retain their federal route codes. In addition, there are some highways in Malaysia which are classified as municipal roads such as Kuala Lumpur Middle Ring Road 1.
The syntax for highway exits in Malaysia is in the format EXIT xxnn or EXIT xxnn, where xx is the expressway code number (which can be one or two digits) and nn is the two-digit assigned number for each highway exit. For example, Johor Bahru exit at the end of North-South Expressway is labelled EXIT 257, where the last two digits (57) are the assigned exit number and the first digit (2) is the expressway route number (E2). Meanwhile, Jalan Templer exit at the Federal Highway is labelled EXIT 224, where the two digits (24) are the assigned exit number and the first digit (2) is the federal route number (2), . Expressways have distance markers in green colour (blue for federal expressways and highways) placed every 100 m.
Expressways/Highways route number categories
Expressway route numbers
| Examples | Information | Number digits |
|---|---|---|
| Expressway route numbers | E01 - E99 | |
| EXIT 253 EXIT 0123 | Expressway exit numbers | EXIT 201 - EXIT 299 EXIT 0100 - 0199 |
Federal route numbers
| Examples | Information | Number digits |
|---|---|---|
| Main federal route numbers | 1001 - 1999 | |
| EXIT 1 EXIT 201 | Federal road exit numbers | 201 - 299 |
- For more information, please refer to Road signs in Malaysia
Most expressways are paved with typical tarmac, which is a mixture of fine stone chips and tar; however, some expressways are paved with concrete such as North-South Expressway Northern Route (from Bukit Lanjan Interchange, Selangor to Tapah interchange, Perak), New Klang Valley Expressway, North-South Expressway Southern Route (from Ayer Keroh interchange, Melaka to Tangkak interchange, Johor), SMART Tunnel and Skudai-Pontian Highway (from Universiti Teknologi Malaysia interchange to Taman Sri Pulai junction). Meanwhile at Federal Highway linking Klang to Kuala Lumpur, the section of the expressway from Subang Jaya to Kota Darul Ehsan near Petaling Jaya is paved with asphalt.

Expressway monitoring and maintenance
Monitoring
Since 1986, Malaysian expressways have been built by private companies under the supervision of the government highway authority, Lembaga Lebuhraya Malaysia (Malaysian Highway Authority). Every private concession company, such as PLUS Expressways, ANIH Berhad (formerly MTD Prime) and the others have monitored and maintained their expressways.
Maintenance
Projek Penyelenggaraan Lebuhraya Berhad or PROPEL has undertaken repair and maintenance works on highway facilities, such as road works and repair works, road line painting, cleaning works on laybys and rest and service areas, trimming grass and landscaping along expressway areas, installing road furniture, and others. Meanwhile the PROPEL Response Team Unit is a special response team unit.
The Karak Expressway and East Coast Expressway are maintained by Alloy Consolidated Sdn Bhd.
Traffic management
Since late 2006, every expressway in Malaysia has been monitored by the Malaysian Highway Authority (LLM) Traffic Management Centre (LLM TMC). However, in some parts of Klang Valley, the expressways are monitored by the Integrated Transport Information System (ITIS); expressways in Johor Bahru are monitored by Johor Bahru City Council (Majlis Bandaraya Johor Bahru) (MBJB) and those in George Town, Penang are monitored by Penang Municipal Council (Majlis Perbandaran Pulau Pinang) (MPPP).
Toll system
Types of toll systems
Every expressway and highway in Malaysia has a toll system, which is either a closed toll system or open toll system. All transactions are in Malaysian Ringgit (RM)
Open system
Users only have to pay at certain toll plazas within the open system range for a fixed amount.
Closed system
Users collect toll tickets (North South Expressway issues the PLUSTransit cards and other closed toll expressways such as East Coast Expressway, Kajang-Seremban Highway and South Klang Valley Expressway issues the transit card) before entering the expressway at respective toll plazas and pay an amount of toll at the exit toll plaza plus the distance from the plaza to the Limit of Maintenance Responsibility (LMR). The toll rate in this system is based on the distance traveled.
Starting 18 June 2013, the PLUSTransit reusable transit cards has been implemented at all PLUS expressways network to replace the transit ticket.
Electronic Toll Collection (ETC)
There are two types of the electronic toll collection systems, Touch 'n Go card unit and Smart TAG on board unit. Touch 'n Go and Smart TAG, have been made compulsory in all expressways since 1 July 2004, following the instruction of the Works Minister, Datuk Seri S. Samy Vellu. Other electronic payment systems that were previously used by other highway operators such as PLUS TAG for all PLUS expressways network, Express TAG for Shah Alam Expressway, FasTrak for Damansara-Puchong Expressway and Sprint Expressway and SagaTag in Cheras - Kajang Expressway, were abolished in a move to standardise the electronic payment method.
Multi Lane Free Flow (MLFF)
The Multi Lane Free Flow (MLFF) is an electronic toll collection system that allows free flow high speed tolli system highway for all its users. With MLFF, the current toll lanes at toll plazas will be replaced with readers at gantry across the highway to detect vehicle and deduct toll using the existing Electronic Toll Collection (ETC) when fully implemented. The Malaysian Highway Authority (MHA) is planning to implement MLFF system at all highways in stages starting 2010.
Toll rebate
Beginning 1 September 2009, the 20 per cent rebate given to motorists who pay toll charges more than 80 times a month, can be saved for up to six months. The rebate can be redeemed at 126 locations which would be announced in due time.
Malaysian expressway toll rate classes
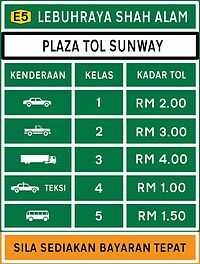
There are fixed toll rate classes for every Malaysian expressway except for the Penang Bridge and the SMART Tunnel where toll rates are not the same.
Toll rate classes for every expressway in Malaysia (including Johor-Singapore Causeway, Malaysia-Singapore Second Link and Sultan Abdul Halim Muadzam Shah Bridge)
| Class | Type of vehicles | Payment | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Motorcycles (Vehicles with two axles and two wheels) | Free | Except: Tanjung Kupang Toll Plaza (Malaysia-Singapore Second Link) TnG Bandar Cassia-JKSB Toll Plaza (Sultan Abdul Halim Muadzam Shah Bridge) RM (Cash) TnG |
| 1 | Private Cars (Vehicles with two axles and three or four wheels (excluding taxi and bus)) | RM (Cash) TnG TAG | |
| 2 | Vans and other small good vehicles (Vehicles with two axles and six wheels (excluding bus)) | RM (Cash) TnG TAG | |
| 3 | Large Trucks (Vehicles with three or more axles (excluding bus)) | RM (Cash) | Cash only Except: TnG for: Sultan Iskandar Building (Johor-Singapore Causeway) Kempas Toll Plaza (North-South Expressway Southern Route) Lima Kedai, Tanjung Kupang and Perling toll plazas (Second Link Expressway) Batu Tiga and Sungai Rasau toll plazas (Federal Highway Route 2) |
| 4 | Taxis | RM (Cash) | Cash only, paid by passengers only. Except: TnG for: Sultan Iskandar Building (Johor-Singapore Causeway) Kempas Toll Plaza (North-South Expressway Southern Route) Lima Kedai, Tanjung Kupang and Perling toll plazas (Second Link Expressway) Batu Tiga and Sungai Rasau toll plazas (Federal Highway Route 2) |
| 5 | Buses | RM (Cash) | Cash only Except: TnG for: Sultan Iskandar Building (Johor-Singapore Causeway) Kempas Toll Plaza (North-South Expressway Southern Route) Lima Kedai, Tanjung Kupang and Perling toll plazas (Second Link Expressway) Batu Tiga and Sungai Rasau toll plazas (Federal Highway Route 2) Note: RapidKL buses using TnG and TAG for Bus Expressway Transit (BET) at all toll plazas in the Klang Valley. |



Toll rate classes for Penang Bridge
| Class | Type of vehicles | Payment | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Motorcycles, bicycles or vehicles with 2 or less wheels | RM (Cash) TnG | |
| 2 | Motorcycle with sidecars, cars including station wagon and commercial vehicles on three wheels | RM (Cash) TnG TAG | For taxis, toll charges are paid by passengers only. |
| 3 | Lorries, vans and buses with two axles and four wheels | RM (Cash) TnG TAG | |
| 4 | Lorries, vans and buses with two axles and five and six wheels | RM (Cash) | Cash only |
| 5 | Vehicles with three axles | RM (Cash) | Cash only |
| 6 | Vehicles with four axles | RM (Cash) | Cash only |
| 7 | Vehicles with five or more axles | RM (Cash) | Cash only |
Toll rate classes for SMART Tunnel
| Class | Type of vehicles | Payment | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Private Cars (Vehicles with two axles and three or four wheels (excluding taxis)) | RM (Cash) TnG TAG | |
| 4 | Taxis | RM (Cash) | Cash only, paid by passengers only. |

Facilities on Malaysian expressways
There are several facilities provided along Malaysian expressway as follows:-
- Rest and Service Area (R&R) – Rest and service areas (RSA) are located roughly about every 60 km along interstate expressways such as the North-South Expressway and the East Coast Expressway. However, some urban expressways may also provide RSA, such as the Shah Alam Expressway, the Damansara-Puchong Expressway and the Guthrie Corridor Expressway. A typical RSA may have a food court, fruit stall, craft shop, public toilets and baths, public telephones, huts (wakaf), petrol stations and prayer rooms (surau) for Muslims. Some RSAs may have ATMs, motels like "Highway Inn", convenience shops such as Highway Mart and 7-Eleven, fast food restaurants and a food court. The wireless broadband internet facility is now available in RSAs; the Tapah RSA in Perak was the first RSA on a Malaysian expressway to provide wireless broadband internet facilities.
- Layby (P) – Laybys are basic parking lots beside the expressways that may also have public toilets and baths, fruit stall, huts (wakaf) and public telephones. However, some laybys may have a few food stalls and petrol stations. Usually, there are about two laybys in between every two RSAs.
- Overhead restaurants (R&R) – Overhead restaurants are special RSAs with restaurants above the expressway. Unlike typical laybys and RSAs which are only accessible in one-way direction only, an overhead restaurant is accessible from both directions of the expressway. Currently, there are 3 overhead bridges in Malaysia - Sungai Buloh (North-South Expressway Northern Route), Ayer Keroh (North-South Expressway Southern Route) and USJ (North-South Expressway Central Link). The PLUS Art Gallery is located in Ayer Keroh Overhead Bridge Restaurant.
- Customer Service Centre (CSC) – Every toll plaza in Malaysia has a customer service centre. This centre includes highway maps, toll fare lists, information counters, Touch 'n Go card reload counters, Touch 'n Go and Smart TAG sales counters and many more.
- Touch 'n Go Hub (TnG TAG Hub) – The hub for the Touch 'n Go and Smart TAG sales.
- Touch 'n Go Spot (TnG TAG Spot) – The spot for the Touch 'n Go and Smart TAG sales counter. Usually can be found at all petrol stations.
- Touch ‘n Go Drive-Through Purchase and Refill card lane (POS) (TnG POS) – Touch 'n Go card users can refill existing or purchase new Touch 'n Go cards directly from the lane without the hassle of going to customer service centres. This Touch 'n Go POS lane are available at all expressways on the PLUS Expressway network.
- Vista point (V) – Vista points are special parking areas that allow motorists to see scenic views of the expressway; available only at Senawang (both directions) and Ipoh (northbound only).
- Motorcycle shelter – Motorcycle shelters provide protection and shelter for motorcyclists from heavy rain. Usually, most motorcycle shelters are located below overhead bridges, but some may be special booths.
- Motorcycle lane – In some parts of the whole expressway, there is an additional lane designated for motorcycles. These lanes are usually about half the width of a normal lane on the North-South expressway and are positioned on the extreme left side of the main carriageway in each direction of travel. These special lanes are found in Shah Alam Expressway, Butterworth-Kulim Expressway, Federal Highway and Guthrie Corridor Expressway
- Emergency phones – Emergency phones are located every 2 km along interstate expressways; useful if there are breakdowns on the expressway. Attendants from the nearest toll plaza will tow the broken cars to the nearest workshops.
- Tunnel emergency exits (Ventilation/ escape shafts) – Tunnel emergency exits are located every 1 km along expressway tunnels, such as SMART Tunnel, Penchala Tunnel on Sprint Expressway, Menora Tunnel on North-South Expressway and Genting Sempah Tunnel on Kuala Lumpur-Karak Expressway.
- Highway hotline service – Every expressway has a hotline service.
- Highway patrol unit – Every expressway has a highway patrol unit.
- Highway helicopter patrol unit – This unit is available at all PLUS Expressway networks only.
- Traffic Control and Surveillance System (TCCS) – The Traffic Control and Surveillance System (TCSS) comprises a number of traffic monitoring systems such as Traffic Closed-Circuit Television (CCTV), Traffic Monitoring Centre (TMC), Variable Message Systems (VMS) and Vehicles Breakdown Sensors.
- Integrated Transport Information System (ITIS) – This system is normally found in the Klang Valley, Penang and Iskandar Malaysia/Johor Bahru.
- Road Transport Department (JPJ) Enforcement Stations – These stations can be found at Karak Expressway and East Coast Expressway. These JPJ enforcement stations have weighing bridges to detect heavy vehicles.
- Police Watch Tower – These towers can be found at all interstate expressways in Malaysia to monitor traffic situations during festive seasons.
- Warning lights – These yellow lights can be found in hazardous and accident areas.
- Automated Enforcement System (AES) – These systems can be found at accident-prone areas and the red-light camera at traffic light junctions.
- Speed Indicator Display (SID) – These systems can be found at the Kerinchi Link of the Sprint Expressway to remind drivers in the event they are exceeding the permitted speed limit not to do so.
- Runaway truck ramp – A traffic device that enables vehicles having braking problems to stop safely. These systems are found at mountainous areas such as at nearby Ipoh North Toll Plaza Interchange along the North–South Expressway Northern Route
Types of expressway interchanges in Malaysia
These are the different types of expressway interchanges in Malaysia:
- Trumpet interchange – It is usually found in every closed toll system expressway like the North-South Expressway and East Coast Expressway. The trumpet design is popular as a highway exit with toll booths for the closed toll system because of the minimum construction cost of its toll booths.
- Cloverleaf interchange – It is more popular in Malaysia to link two overlapping expressways because of its relatively cheaper cost. The biggest cloverleaf highway interchange in Malaysia is Bulatan Darul Ehsan a.k.a. Shah Alam Cloverleaf Interchange of Federal Highway in Shah Alam, Selangor.
- Diamond Interchange – It is more popular in Malaysia to join the expressway crossing over municipal roads.
- Multi-Level Stacked Diamond Interchange – It is a diamond interchange upgraded into a multi-level interchange. Examples include the Bandar Sunway Interchange between Damansara-Puchong Expressway and New Pantai Expressway in Petaling Jaya.
- Diverging diamond interchange – This is a rare type of diamond interchange which involves temporary lane changes, i.e. from left-hand traffic to right and then back to the left. Like SPUI, it allows traffic from two opposite directions to turn right at the same time but does not allow traffic to go straight ahead. Examples include the Freescale Interchange at Damansara-Puchong Expressway.
- Single-point urban interchange (SPUI) – A SPUI interchange is nearly similar with a typical diamond interchange but it allows traffic from two opposite directions to turn right at the same time; however, it does not allow traffic to go straight. Examples include the Danga City Mall interchange at Skudai Highway / Johor Bahru Inner Ring Road.
- Roundabout interchange – Very popular in Malaysia.
- Parclo interchange – An example of this is the Port Dickson Interchange on the North-South Expressway and Kapar Interchange on the New North Klang Straits Bypass.
- Directional T interchange – These interchanges are found at Nilai North and Nilai Interchanges of North-South Expressway and also Setia Alam Interchange and Bukit Lanjan Interchange on New Klang Valley Expressway.
- Stacked Interchange – Examples of these are the Penchala Interchange on the Damansara-Puchong Expressway and Penchala Link of the Sprint Expressway.
- Multi-Level Stacked Interchange – Examples of these are the Ampang Interchange on the Jalan Ampang and the Ampang flyover of the Kuala Lumpur Middle Ring Road 2.
- Multi-Level Stacked Roundabout – There are three-level and four-level roundabouts found in Malaysia. Examples of four-level roundabouts include the Segambut Interchange of Kuala Lumpur-Rawang Highway and Kewajipan Interchange of New Pantai Expressway.
- Double U-Turn Interchange – These interchanges found at Tampoi North interchange on the Skudai Highway and Pasir Gudang Highway.
- Left in/left out (LILO) junction – These junctions restrict the ingress and egress of the minor roads; they only permit left-turn entries. To turn to opposite direction, motorists may need to make a U-turn on the expressway. These junctions are very common in urban expressways such as in Sungai Besi Expressway and Damansara-Puchong Expressway.
Safety
Speed limits
The default National Speed Limit on Malaysian expressways is 110 km/h (70 mph), but in certain areas a lower speed limit (such as 90 km/h (55 mph) or 80 km/h (50 mph)) is applied, especially in single carriageway expressway, large urban areas, crosswinds, heavy traffic and in dangerous mountainous routes and 60 km/h is applied 1 km before the toll plaza Speed traps are also deployed by the Malaysian police at many places along the expressways.
Types of vehicles not allowed to enter an expressway
PLUS Expressways networks and East Coast Expressway (ECE)
- Bicycles
- Steam roller
- Tractors
- Excavators and backhoes
North-South Expressway Northern Route (Sungai Buloh - Bukit Lanjan), New Klang Valley Expressway (Shah Alam - Jalan Duta), Federal Highway (Sungai Rasau - Batu Tiga): Monday to Friday (Except Public Holidays) from 6.30am to 9.30am
- Heavy vehicles weighing 10,000 kg or more
Ampang-Kuala Lumpur Elevated Highway (AKLEH)
- Bicycles
Maju Expressway (MEX) (Kuala Lumpur-Putrajaya Expressway (KLPE))
- Bicycles
SMART Tunnel
- Motorcycles and bicycles
- Bus
- Steam roller
- Heavy vehicles like lorries, trailers, etc.
- Tractors
- Excavators and backhoes
Accidents
Malaysian expressways are potential sites of fatal highway accidents in Malaysia, especially during festive seasons. However, accidents in Malaysia happen on federal, state, and municipal roads. Most road accidents are caused by the attitude of certain road users who drive dangerously over the speed limit.
List of accident-prone areas in Malaysian tolled expressways and highways
- km 25 of Gunung Pulai near Kulai, Johor on North-South Expressway Southern Soute
- km 171 to 141 of Tangkak - Pagoh stretch on North-South Expressway Southern Soute
- km of Jalan Duta toll plaza, Kuala Lumpur on North-South Expressway Northern Route
- km 293 to 310 of North-South Expressway Northern Route from Gopeng Interchange to Tapah Interchange (Gua Tempurung stretch)
- km 256 of old Jelapang toll plaza, Perak on North-South Expressway Northern Route
- km --- to --- of North-South Expressway Northern Route from Menora Tunnel to Sungai Perak Rest and Service Area, Perak
- km 31 of Gombak, Selangor on Karak Expressway (not far from Genting Sempah Tunnel).
- Sungai Besi sharp corner flyover bridge from Jalan Dewan Bahasa (formerly Jalan Lapangan Terbang) on Kuala Lumpur Middle Ring Road 1 towards Kuala Lumpur-Seremban Expressway.
- km of Kelana Jaya on Damansara-Puchong Expressway near Kelana Jaya LRT stations.
- km of Puchong on Damansara-Puchong Expressway near Tractors Malaysia.
- km of Damansara Utama-Section 14 on Sprint Expressway.
- Subang Jaya aka Persiaran Tujuan Interchange on the railway bridge corner (from Kuala Lumpur to Subang Jaya) at the exit of Federal Highway.
During workdays/peak hours
During workdays or peak hours. There are many restricted routes on the expressways especially in the Klang Valley to ease congestion during peak hours in the morning such as Federal Highway (Sungai Rasau - Subang), New Klang Valley Expressway (Shah Alam - Jalan Duta) and North-South Expressway Northern Route (Rawang - Bukit Lanjan). Heavy vehicles (except buses and tankers) with laden and unladen heavy vehicles weighing 10,000 kg or more are not allowed to enter the expressway between 6:30 am until 9:30 am on Monday to Friday (except public holidays). A compound fines will be issued to heavy vehicles which flouted the rule.
During festive seasons
During festive seasons such as Chinese New Year, Deepavali, Christmas and Hari Raya, activities such as construction, road repairs and maintenance works have been temporarily stopped to ensure a smoother traffic flow on the expressways. Meanwhile, heavy goods vehicles such as logging trucks, cement trucks, container trucks, construction materials trucks and other heavy goods vehicles (except tanker lorry, provision goods truck, crane, tow truck, fire engine, ambulance, etc.) are banned from using roads, highways and expressways during festive seasons. A massive nationwide operation known as Ops Selamat (Previously named as Ops Sikap) is held annually by the Malaysian police to ensure safety on all roads in Malaysia during festive seasons. To smoother traffic flow during peak periods in the festive seasons, a Travel Time Advisory (TTA) has been set up at all interstate expressways such as PLUS Expressways network and East Coast Expressway.
Automated Enforcement System (AES)
The Automated Enforcement System (AES) is the road safety enforcement system to monitored all federal roads, highways and expressways in Malaysia. This system came into effect on 22 September 2012.
Type of AES
- Speed light camera
- Red light camera
Natural hazards
Other hazardous conditions on expressways include landslides, crosswinds, fog, storms, road damages, paddy (jerami) burning activities and flash floods.
List of landslide-prone areas
- km of Bukit Lanjan-Jalan Duta on North-South Expressway Northern route
- km of Bukit Lanjan between Kota Damansara-Bukit Lanjan on New Klang Valley Expressway
- km of Gua Tempurung between Gopeng-Tapah on North-South Expressway Northern route
- km of Bukit Merah between Bukit Merah-Taiping (Utara) on North-South Expressway Northern route
- km of Sungai Perak-Jelapang Toll Plaza on North-South Expressway Northern route
- km of Bukit Berapit between Changkat Jering-Kuala Kangsar on North-South Expressway Northern route
- km of Gombak-Genting Sempah on Karak Expressway
- km of Bukit Tinggi-Bentong on Karak Expressway
- km of Gunung Ma'okil between Pagoh-Yong Peng on North-South Expressway Southern route
- km of Puchong-Seri Kembangan on Damansara-Puchong Expressway near Puchong Selatan toll plaza.
- km 15 of Skudai-Senai (North) on North-South Expressway Southern route near Skudai toll plaza.
List of crosswind-prone areas
- km of Senawang-Pedas/Linggi on North-South Expressway Southern route
- km of Alor Gajah-Ayer Keroh on North-South Expressway Southern route
- km along East Coast Expressway
List of flash flood-prone areas
- km 15 of Batu Tiga Interchange on Federal Highway
- km of Shah Alam Interchange on New Klang Valley Expressway
- km of Sungai Besi on Sungai Besi Expressway near Razak Mansion
- km of Seberang Jaya Interchange underpass on Butterworth-Kulim Expressway near Carrefour Seberang Jaya
- km of Alor Star - Jitra of the North-South Expressway Northern Route
- km 173.9 - 171.9 of Jasin, Melaka and Tangkak, Johor on North-South Expressway Southern Route
Controversial issues
There are several controversial issues regarding the construction of expressways. The main issue is the increase of toll rates, which can be a huge burden especially for residents of Kuala Lumpur and the surrounding Klang Valley conurbation.[11]
There are also various parties who question the capability of the numerous expressways in Klang Valley to overcome traffic congestion, which does not show signs of improvement with the construction of new expressways. Three chief factors were blamed for the urban expressway congestion, namely the short-sighted policies by the authorities, greedy property developers, and the failure of local municipal councils to control the development in the Klang Valley.[12]
There are also several protests being held by residents of some housing areas being affected by several planned expressways, such as the Sungai Besi – Ulu Kelang Expressway (SUKE) and the Damansara-Shah Alam Highway (DASH). Environmental issues such as road noise and worsening congestion became the chief reasons of those protests.[11]
Other controversial issues include the following:
- The cracks found on beams on the Kepong Flyover in Kuala Lumpur Middle Ring Road 2 (MRR2) on 10 August 2004.
- The flyover which collapsed on Setia Alam Interchange in New Klang Valley Expressway during construction on 10 July 2005, where, tragically, about 4 lives were lost.
- The 8 fallen I-beams at the Pajam Interchange in Negri Sembilan during the construction of the Kajang-Seremban Highway (LEKAS Highway) on the night of 27 September 2007.
- The ramp collapse at the Batu Maung Interchange at Batu Maung side of the Penang Second Bridge during construction on 6 June 2013 killing one person.
Interesting facts
- The Tanjung Malim-Slim River tolled road (Federal Route
 ) is the first tolled highway in Malaysia.
) is the first tolled highway in Malaysia. - The Sultan Yahya Petra Bridge (Federal Route
 ) is the first tolled bridge in Malaysia.
) is the first tolled bridge in Malaysia. - PLUS Expressways is the largest highway concessionaries operator company in Malaysia, also the largest listed toll expressway operator in Southeast Asia, Asia, and the eighth largest in the world. The second largest is Prolintas.
- The longest bridge in Malaysia is Sultan Abdul Halim Muadzam Shah Bridge (Penang Second Bridge)
 with a total length 24 km (15 mi). The second longest bridge is Penang Bridge
with a total length 24 km (15 mi). The second longest bridge is Penang Bridge  with a total length 13.5 km (8.4 mi).
with a total length 13.5 km (8.4 mi). - The longest expressway in Malaysia is North-South Expressway

 with a total length 966 km (600 mi).
with a total length 966 km (600 mi). - The longest expressway river bridge in Malaysia is the Sungai Johor Bridge on Senai-Desaru Expressway
 with a total length 1.7 km (1.708 m). The bridge also the longest single plane cable-stayed bridge in Malaysia.
with a total length 1.7 km (1.708 m). The bridge also the longest single plane cable-stayed bridge in Malaysia. - The section between Cahaya Baru and Penawar of the Senai-Desaru Expressway
 is built as a two-lane single carriageway making the first two-lane controlled-access expressway in Malaysia.
is built as a two-lane single carriageway making the first two-lane controlled-access expressway in Malaysia. - The first cable-stayed land bridge in Malaysia is the LDP cable stayed bridge at the Freescale interchange on Damansara-Puchong Expressway
 with a total length 1.1 km (0.68 mi)
with a total length 1.1 km (0.68 mi) - The most expensive section of the expressway is the Gopeng-Tapah section on the North-South Expressway Northern Route
 . At RM200 million, it translates to RM 20 million per kilometre. Embankment strengthening is the major contributor for this escalating cost.
. At RM200 million, it translates to RM 20 million per kilometre. Embankment strengthening is the major contributor for this escalating cost. - The largest toll plaza in Malaysia is Bandar Cassia-PLUS Toll Plaza (Gateway Arch Toll Plaza) in Penang Second Bridge
 with over 28 lanes (excluding additional motorcycle toll plaza). The second largest toll plaza is Sungai Besi Toll Plaza in North-South Expressway Southern Route
with over 28 lanes (excluding additional motorcycle toll plaza). The second largest toll plaza is Sungai Besi Toll Plaza in North-South Expressway Southern Route  with over 18 lanes (excluding additional toll booths).
with over 18 lanes (excluding additional toll booths). - The highest toll plaza in Malaysia is Setul Toll Plaza in Kajang-Seremban Highway
 located at the hilly top of Gunung Mantin-Seremban at 258 metres above sea level.
located at the hilly top of Gunung Mantin-Seremban at 258 metres above sea level. - Bandar Saujana Putra Interchange on North-South Expressway Central Link
 and South Klang Valley Expressway
and South Klang Valley Expressway  is the only expressway interchange in Malaysia to have two toll plazas.
is the only expressway interchange in Malaysia to have two toll plazas. - The North-South Expressway

 is the first expressway in Malaysia that provided an Overhead Bridge Restaurant (OBR).
is the first expressway in Malaysia that provided an Overhead Bridge Restaurant (OBR). - The busiest expressway in Malaysia is Federal Highway route
 from Klang to Kuala Lumpur
from Klang to Kuala Lumpur - Federal Highway route
 is the first highway in Malaysia to have a motorcycle lane.
is the first highway in Malaysia to have a motorcycle lane. - The first highway tunnel in Malaysia is Genting Sempah Tunnel on Kuala Lumpur-Karak Expressway
 .
. - The first elevated highway in Malaysia is Ampang-Kuala Lumpur Elevated Highway (AKLEH)
 .
. - The longest flyover bridge in Malaysia is Batu Tiga Flyover on North-South Expressway Central Link
 .
. - SMART Tunnel
 (4 km (2.5 miles)) is the longest motorway tunnel, as well as the first double-decked tunnel and the first tunnel that has a stormwater tunnel and a motorway tunnel in Malaysia.
(4 km (2.5 miles)) is the longest motorway tunnel, as well as the first double-decked tunnel and the first tunnel that has a stormwater tunnel and a motorway tunnel in Malaysia. - The widest tunnel in Malaysia is Penchala Tunnel on Penchala Link of Sprint Expressway
 .
. - The first expressway with double-decked carriageway in Malaysia is Kerinchi Link on Sprint Expressway
 .
. - The Kuala Lumpur-Karak Expressway
 is the only expressway in Malaysia has a separate carriageway at Genting Sempah in Selangor-Pahang border (one for Selangor side and one for Pahang side) due to their geographical locations.
is the only expressway in Malaysia has a separate carriageway at Genting Sempah in Selangor-Pahang border (one for Selangor side and one for Pahang side) due to their geographical locations. - The biggest cloverleaf highway interchange in Malaysia is Bulatan Darul Ehsan Interchange of Federal Highway route
 and Kemuning-Shah Alam Highway
and Kemuning-Shah Alam Highway  in Shah Alam, Selangor.
in Shah Alam, Selangor. - The largest highway interchange in Malaysia is Gelugor Complex Interchange at Penang Bridge
 .
. - The PLUS Speedway (formerly ELITE Speedway), is the first go-kart circuit in the Malaysian expressways. The circuit is located near the USJ Rest and Service Area on North-South Expressway Central Link
 .
. - Tapah Rest and Service Area (both bound) on North-South Expressway Northern Route
 in Perak is the first rest and service area in the Malaysian expressway to have wireless broadband internet facilities.
in Perak is the first rest and service area in the Malaysian expressway to have wireless broadband internet facilities. - The PLUS Art Gallery in Ayer Keroh Overhead Bridge Restaurant (OBR) North-South Expressway Southern Route
 is the first highway art gallery in Malaysia.
is the first highway art gallery in Malaysia. - The Perasing Rest and Service Area on the East Coast Expressway
 is the biggest Rest and Service Area on the ECE network. It is only accessible by the directional T interchange to R&R in which it is probably the only one of its type in Malaysia.
is the biggest Rest and Service Area on the ECE network. It is only accessible by the directional T interchange to R&R in which it is probably the only one of its type in Malaysia. - The largest advertising board on the Malaysian expressways is the Giant Wau Kite Spectacular Advertising Board on the North-South Expressway Southern Route
 near Sungai Besi and the North-South Expressway Central Link
near Sungai Besi and the North-South Expressway Central Link  near Putrajaya.
near Putrajaya. - While most toll expressways in Malaysia use green signboards with white letters, the MetaCorp expressway networks (East-West Link Expressway and Kuala Lumpur-Seremban Expressway)
 use blue signboards instead, as if they are municipal expressways.
use blue signboards instead, as if they are municipal expressways. - Before 2007, all federally funded expressways have no exit numbering system; however, the exit number system similar to toll expressways was introduced in 2007 exclusively for Federal Highway route
 (then followed by the Putrajaya-Cyberjaya Expressway route
(then followed by the Putrajaya-Cyberjaya Expressway route  ); thus making the Federal Highway as the first federal expressway with expressway exit numbering system.
); thus making the Federal Highway as the first federal expressway with expressway exit numbering system. - Tun Salahuddin Bridge
 is the first and currently the only toll expressway in the East Malaysia, while almost all toll expressways are built in the Peninsular Malaysia. The Tun Salahuddin Bridge is also the only toll expressway without any grade-separated interchanges.
is the first and currently the only toll expressway in the East Malaysia, while almost all toll expressways are built in the Peninsular Malaysia. The Tun Salahuddin Bridge is also the only toll expressway without any grade-separated interchanges. - The Machap Rest and Service Area (north bound) at the North-South Expressway Southern Route
 is the first fully air-conditioned rest area in Malaysia.
is the first fully air-conditioned rest area in Malaysia. - The Sungai Perak Rest and Service Area (south bound) at the North-South Expressway Northern Route
 in Perak is the first rest and service area in the Malaysian expressway to have an eco-management theme known as "The Green Trail" or "Jejak Hijau".
in Perak is the first rest and service area in the Malaysian expressway to have an eco-management theme known as "The Green Trail" or "Jejak Hijau". - Putrajaya-Cyberjaya Expressway route
 is the first future federal highway on Multimedia Super Corridor (MSC).
is the first future federal highway on Multimedia Super Corridor (MSC). - PLUSMiles is the first and only toll rebate loyalty programme in the Malaysian expressways.
- Shah Alam is the first and currently the only city in Malaysia to have its own municipal route numbering system, while other municipal routes in Malaysia do not bear any route numbering scheme.
- The longest closed toll collection system coverage in Malaysia is from Juru toll plaza to Skudai toll plaza (previously Ipoh South toll plaza to Skudai toll plaza), which runs through the North-South Expressway Northern Route
 , New Klang Valley Expressway
, New Klang Valley Expressway  , North-South Expressway Central Link
, North-South Expressway Central Link  and North-South Expressway Southern Route
and North-South Expressway Southern Route  .
. - The North-South Expressway Northern Route
 is the first and currently the only expressway in Malaysia to have a runaway truck ramp near Jelapang, Ipoh.
is the first and currently the only expressway in Malaysia to have a runaway truck ramp near Jelapang, Ipoh. - There is one semi tunnel on the East-West Highway (Route
 ) from Gerik, Perak to Jeli, Kelantan. It is probably the only one of its type in Malaysia.
) from Gerik, Perak to Jeli, Kelantan. It is probably the only one of its type in Malaysia. - The first true two-lane expressway with full access control in Malaysia is the Cahaya Baru-Penawar section of the Senai-Desaru Expressway
 .[10]
.[10] - The Johor Bahru Eastern Dispersal Link Expressway
 is the only expressway in Malaysia has a controlled-access toll free expressway.
is the only expressway in Malaysia has a controlled-access toll free expressway. - The Kota Bharu-Kuala Krai Expressway, currently under construction, will be the first state-owned controlled-access expressway once completed.[13]
Malaysian expressways in popular culture
Films
These films were filmed mainly on Malaysian expressways:
| Films | Types of film | Expressway locations |
|---|---|---|
| Tragedi Oktober | Local Malay film starring Awie | Along New Klang Valley Expressway |
| Sembilu | Local Malay film starring Awie | Along North-South Expressway Northern Route |
| Remp-It | Local Malay film | Along Shah Alam Expressway |
| KL Menjerit | Local Malay film starring Rosyam Nor | Along KL IRR, KL MRR1 and North-South Expressway Southern Route |
| KL Menjerit 1 | Local Malay film, prequel of KL Menjerit | Along North-South Expressway Southern Route |
| Don - The Chase Begins Again | Bollywood film starring Shah Rukh Khan | Bukit Kiara interchange Sprint Expressway |
| Skyline Cruisers | Hong Kong Cantonese film | Putra Mahkota interchange North-South Expressway Southern Route |
| Evolusi KL Drift | Local Malay film starring Fasha Sandha | Along streets, roads and highways in Kuala Lumpur Along roads and highways in Putrajaya |
| Evolusi KL Drift 2 | Local Malay film starring Fasha Sandha | Along streets, roads and highways in Kuala Lumpur Along roads and highways in Putrajaya |
| Karak | Local Malay film | EXIT 813 Karak Interchange near Kuala Lumpur – Karak Expressway |
| Kongsi | Local Malay film | Along streets, roads and highways in Kuala Lumpur SMART Tunnel |
| PE3 | Local Malay film | North-South Expressway Southern Route to Penang Bridge |
Televisions
Dramas
| TV series | Types of TV series | Expressway locations |
|---|---|---|
| Dari Fail Peronda Lebuhraya | Malay drama | North-South Expressway |
| Impak Maksima, the series | Malay drama | Sprint Expressway |
Documentary
| TV series | Types of TV series | Expressway locations |
|---|---|---|
| Discovery Channel's Extreme Engineering | Documentary | SMART Tunnel |
| National Geographic Channel's Truly Malaysia | Documentary | SMART Tunnel |
| Science Channel's Man Made Marvels | Documentary | SMART Tunnel |
| National Geographic Channel's Megastructures | Documentary | SMART Tunnel Sultan Abdul Halim Muadzam Shah Bridge (Penang Second Bridge) |
Video games
- Burnout Dominator - The Spiritual City track is based on the real-life Kuala Lumpur city, with signboards leading to some expressways such as
 North-South Expressway Southern Route and
North-South Expressway Southern Route and  Sprint Expressway.
Sprint Expressway.
Gallery
-
Linkedua Expressway in Malaysia after the Singapore-Malaysia Second Link Bridge, in the northbound direction.
-

The Ampang-Kuala Lumpur Elevated Highway's interchange with Kuala Lumpur Middle Ring Road 2 in Ampang.
-
Newer expressways are relatively empty, such as Kajang Dispersial Link Expressway near Bandar Sungai Long, Kajang, Selangor.
-
The cable bridge of Damansara-Puchong Expressway spanning over its intersection with Federal Highway in Petaling Jaya. Kuala Lumpur can be seen in the distant background on the right corner of the picture.
-
The Petaling Jaya stretch of the Federal Highway leading towards Kuala Lumpur.
-

The Titiwangsa Range from the North-South Expressway Northern Route near Slim River.
-

Sentul Link towards Mahameru Highway (MRR1)
See also
- Road signs in Malaysia
- National Speed Limits
- Malaysian Federal Roads system
- Malaysian Highway Authority
- Malaysian State Roads system
- Multi Lane Free Flow
- Electronic Toll Collection
- Teras Teknologi (TERAS)
- Highway
- Driveway
- Freeway
- Motorway
- Autobahn
- Controlled-access highway
- Interstate Highway System
- Expressways of Japan
- Expressways of China
- Asian Highway Network
References
- ↑ Official data from Malaysian Highway Authority
- ↑ Official data from Malaysian Highway Concessionaires Company Association (PSKLM)
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Malaysian Sectional Asian Highway data (XLS) - from the official UNESCAP Asian Highway Network website.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 4.5 ERIA Study Team. "Current Status of ASEAN Transport Sector" (PDF). ASEAN Strategic Transport Plan 2011–2015 (Jakarta: ASEAN Secretariat and ERIA): 3–1 – 3–95. Retrieved 16 November 2013.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 Asian Highway Database: AH Network in Member Countries - The United Nations Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific
- ↑ Singaporean Sectional Asian Highway data (XLS) - from the official UNESCAP Asian Highway Network website.
- ↑ The Genting Sempah Tunnel is adopted from Terowong jalan raya paling panjang - Buku Rekod Malaysia Edisi Kedua, Ghulam Jie M Khan
- ↑ "New highways to KL International Airport". The Star. Retrieved 30 December 2013.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 Arahan Teknik (Jalan) 8/86 - A Guide on Geometric Design of Roads, Jabatan Kerja Raya Malaysia
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 "Reviu eksklusif Lebuhraya Senai-Desaru E22" (in Malay). Blog Jalan Raya Malaysia. 2012-08-23. Retrieved 2014-02-12.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 "Demonstrasi dan bantahan lebuh raya ekspres: Apa puncanya" (in Malay). Blog Jalan Raya Malaysia. 25 September 2013. Retrieved 26 October 2013.
- ↑ Wong, Pauline (10 October 2013). "All roads lead to misery". The Heat. Retrieved 26 October 2013.
- ↑ "Majlis pecah tanah Lebuhraya Kota Bharu-Kuala Krai / Kota Bharu-Kuala Krai Expressway ground-breaking ceremony". Blog Jalan Raya Malaysia. 28 May 2012. Retrieved 1 January 2013.
External links
- Malaysian Highway Authority official page
- Malaysian Highway Authority traffic information page
- "Travel Smarter" - Malaysian Highway Concessionaires Company Association (PSKLM) highway information page
- PLUS Malaysia Berhad - concession holder for:
- North-South Expressway
- Malaysia-Singapore Second Link
- North-South Expressway Central Link
- Seremban-Port Dickson Highway
- Butterworth-Kulim Expressway
- Penang Bridge
- ANIH Berhad - concession holder for:
- Karak Expressway
- East Coast Expressway
- Kuala Lumpur-Seremban Expressway
- East-West Link Expressway
- Gamuda Berhad - concession holder for:
- SPRINT - Sprint Expressway
- LITRAK - Damansara-Puchong Expressway
- KESAS - Shah Alam Expressway
- SMART - SMART Tunnel
- Road Builder - concession holder for:
- Besraya - Sungai Besi Expressway
- NPE - New Pantai Expressway
- LEKAS - Kajang-Seremban Highway
- Grand Saga website
- Propel Berhad - concession holder for highway maintenance in Malaysia
- Motorways Exitlist - Exilist of expressway in Malaysia
- Komuniti PTT Zello Channel Lebuhraya Utara-Selatan
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||






