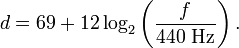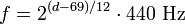MIDI Tuning Standard
MIDI Tuning Standard (MTS) is a specification of precise musical pitch agreed to by the MIDI Manufacturers Association in the MIDI protocol. MTS allows for both a bulk tuning dump message, giving a tuning for each of 128 notes, and a tuning message for individual notes as they are played.
Frequency values
If ƒ is a frequency, then the corresponding frequency data value d may be computed by
The quantity log2 (ƒ / 440 Hz) is the number of octaves above the 440-Hz concert A (it is negative if the frequency is below that pitch). Multiplying it by 12 gives the number of semitones above that frequency. Adding 69 gives the number of semitones above the C five octaves below middle C.
Since 440 Hz is a widely used standard concert A (e.g. USA, UK), and since that is represented in MIDI terms by the integer 69 (nine semitones above middle C, which is 60), this gives a real number which expresses pitch in a manner consistent with MIDI and integer notation, known as the midi note number.
Converting from midi note number (d) to frequency (f) is given by the following formula:
Frequency Data Format
The frequency data format allows for the precise notation of frequencies that differ from equal temperament.
"Frequency data shall be defined in [units] which are fractions of a semitone. The frequency range starts at MIDI note 0, C = 8.1758 Hz, and extends above MIDI note 127, G = 12543.875 Hz. The first byte of the frequency data word specifies the highest equal-tempered semitone not exceeding the frequency. The next two bytes (14 bits) specify the fraction of 100 cents above the semitone at which the frequency lies. Effective resolution = 100 cents / 214 = .0061 cents."[1]
This higher resolution allows a logarithmic representation of pitch in which the semitone is divided into 1282 = 214 = 16384 parts, which means the octave is divided into 196608 (logarithmically) equal parts. These parts are exactly 100/16384 cents (approximately 0.0061 cents) in size, which is far below the threshold of human pitch perception and which therefore allows a very accurate representation of pitch.
Applications
The precision pitch values may be used in microtonal music, just intonation, meantone temperament, or other alternative tunings. Software which supports MTS includes Scala, TiMidity++, alt-tuner, L'il Miss Scale Oven, Tune Smithy, Max Magic Microtuner, Gervill, and Relayer. Software plugin instruments which support MTS include Pianoteq, Native Instruments FM8, Synthogy Ivory, and Xen-Arts' various xenharmonic VSTi plugins, including the FMTS FM synthesizer, Ivor virtual analog synthesizer, and XenFont SoundFont sample player.
See also
References
- ↑ Midi Manufacturers Association, Midi Tuning Specification ( http://www.midi.org/techspecs/midituning.php )