MACD
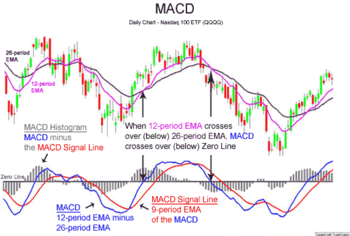
MACD, short for moving average convergence/divergence, is a trading indicator used in technical analysis of stock prices, created by Gerald Appel in the late 1970s.[1] It is supposed to reveal changes in the strength, direction, momentum, and duration of a trend in a stock's price.
The MACD indicator (or "oscillator") is a collection of three time series calculated from historical price data, most often the closing price. These three series are: the MACD series proper, the "signal" or "average" series, and the "divergence" series which is the difference between the two. The MACD series is the difference between a "fast" (short period) exponential moving average (EMA), and a "slow" (longer period) EMA of the price series. The average series is an EMA of the MACD series itself.
The MACD indicator thus depends on three time parameters, namely the time constants of the three EMAs. The notation "MACD(a,b,c)" usually denotes the indicator where the MACD series is the difference of EMAs with characteristic times a and b, and the average series is an EMA of the MACD series with characteristic time c. These parameters are usually measured in days. The most commonly used values are 12, 26, and 9 days, that is, MACD(12,26,9). As true with most of the technical indicators, MACD also finds its period settings from the old days when technical analysis used to be mainly based on the daily charts. The reason was the lack of the modern trading platforms which show the changing prices every moment. As the working week used to be 6-days, the period settings of (12, 26, 9) represent 2 weeks, 1 month and one and a half week. [2] Now when the trading weeks have only 5 days, possibilities of changing the period settings cannot be overruled. However, it is always better to stick to the period settings which are used by the majority of traders as the buying and selling decisions based on the standard settings further push the prices in that direction.
The MACD and average series are customarily displayed as continuous lines in a plot whose horizontal axis is time, whereas the divergence is shown as a bar graph (often called a histogram).
A fast EMA responds more quickly than a slow EMA to recent changes in a stock's price. By comparing EMAs of different periods, the MACD series can indicate changes in the trend of a stock. It is claimed that the divergence series can reveal subtle shifts in the stock's trend.
Since the MACD is based on moving averages, it is inherently a lagging indicator. As a metric of price trends, the MACD is less useful for stocks that are not trending (trading in a range) or are trading with erratic price action.
History
The MACD series proper was invented by Gerald Appel[3] in the 1970s. Thomas Aspray added the divergence bar graph to the MACD in 1986, as a means to anticipate MACD crossovers, an indicator of important moves in the underlying security.
Variations of the MACD include the zero lag MACD[4]
Terminology
Over the years, elements of the MACD have become known by multiple and often over-loaded terms. The common definitions of particularly overloaded terms are:
Divergence: 1. As the D in MACD, "divergence" refers to the two underlying moving averages drifting apart, while "convergence" refers to the two underlying moving averages coming towards each other. 2. Gerald Appel referred to a "divergence" as the situation where the MACD line does not conform to the price movement, e.g. a price low is not accompanied by a low of the MACD.[5] and 3. Thomas Asprey dubbed the difference between the MACD and its signal line the "divergence" series. In practice, definition number 2 above is often preferred.
Histogram:[6] 1. Gerald Appel referred to bar graph plots of the basic MACD time series as "histogram". In Appel's Histogram the height of the bar corresponds to the MACD value for a particular point in time. 2. The difference between the MACD and its Signal line is often plotted as a bar chart and called a "histogram". In practice, definition number 2 above is often preferred.
Mathematical interpretation
In signal processing terms, the MACD series is a filtered measure of the derivative of the input (price) series with respect to time. (The derivative is called "velocity" in technical stock analysis). MACD estimates the derivative as if it were calculated and then filtered by the two low-pass filters in tandem, multiplied by a "gain" equal to the difference in their time constants. It also can be seen to approximate the derivative as if it were calculated and then filtered by a single low pass exponential filter (EMA) with time constant equal to the sum of time constants of the two filters, multiplied by the same gain.[7] So, for the standard MACD filter time constants of 12 and 26 days, the MACD derivative estimate is filtered approximately by the equivalent of a low-pass EMA filter of 38 days. The time derivative estimate (per day) is the MACD value divided by 14.
The average series is also a derivative estimate, with an additional low-pass filter in tandem for further smoothing (and additional lag). The difference between the MACD series and the average series (the divergence series) represents a measure of the second derivative of price with respect to time ("acceleration" in technical stock analysis). This estimate has the additional lag of the signal filter and an additional gain factor equal to the signal filter constant.
Classification
The MACD can be classified as an absolute price oscillator (APO), because it deals with the actual prices of moving averages rather than percentage changes. A percentage price oscillator (PPO), on the other hand, computes the difference between two moving averages of price divided by the longer moving average value.
While an APO will show greater levels for higher priced securities and smaller levels for lower priced securities, a PPO calculates changes relative to price. Subsequently, a PPO is preferred when: comparing oscillator values between different securities, especially those with substantially different prices; or comparing oscillator values for the same security at significantly different times, especially a security whose value has changed greatly.
Another member of the price oscillator family is the detrended price oscillator (DPO), which ignores long term trends while emphasizing short term patterns.
Trading interpretation
Exponential moving averages highlight recent changes in a stock's price. By comparing EMAs of different lengths, the MACD series gauges changes in the trend of a stock. The difference between the MACD series and its average is claimed to reveal subtle shifts in the strength and direction of a stock's trend. It may be necessary to correlate the signals with the MACD to indicators like RSI power.
Some traders attribute special significance to the MACD line crossing the signal line, or the MACD line crossing the zero axis. Significance is also attributed to disagreements between the MACD line or the difference line and the stock price (specifically, higher highs or lower lows on the price series that are not matched in the indicator series).
Signal-line crossover
A "signal-line crossover" occurs when the MACD and average lines cross; that is, when the divergence (the bar graph) changes sign. The standard interpretation of such an event is a recommendation to buy if the MACD line crosses up through the average line (a "bullish" crossover), or to sell if it crosses down through the average line (a "bearish" crossover). These events are taken as indications that the trend in the stock is about to accelerate in the direction of the crossover.
Zero crossover
A "zero crossover" event occurs when the MACD series changes sign, that is, the MACD line crosses the horizontal zero axis. This happens when there is no difference between the fast and slow EMAs of the price series. A change from positive to negative MACD is interpreted as "bearish", and from negative to positive as "bullish". Zero crossovers provide evidence of a change in the direction of a trend but less confirmation of its momentum than a signal line crossover.
Divergence
A "positive divergence" or "bullish divergence" occurs when the price makes a new low but the MACD does not confirm with a new low of its own. A "negative divergence" or "bearish divergence" occurs when the price makes a new high but the MACD does not confirm with a new high of its own. A divergence with respect to price may occur on the MACD line and/or the MACD Histogram.[8]
Timing
The MACD is only as useful as the context in which it is applied. An analyst might apply the MACD to a weekly scale before looking at a daily scale, in order to avoid making short term trades against the direction of the intermediate trend.[9] Analysts will also vary the parameters of the MACD to track trends of varying duration. One popular short-term set-up, for example, is the (5,35,5).
False signals
Like any forecasting algorithm, the MACD can generate false signals. A false positive, for example, would be a bullish crossover followed by a sudden decline in a stock. A false negative would be a situation where there was no bullish crossover, yet the stock accelerated suddenly upwards.
A prudent strategy may be to apply a filter to signal line crossovers to ensure that they have held up. An example of a price filter would be to buy if the MACD line breaks above the signal line and then remains above it for three days. As with any filtering strategy, this reduces the probability of false signals but increases the frequency of missed profit.
Analysts use a variety of approaches to filter out false signals and confirm true ones.
A MACD crossover of the signal line indicates that the direction of the acceleration is changing. The MACD line crossing zero suggests that the average velocity is changing direction.
See also
References
- ↑ Appel, Gerald (2005). Technical Analysis Power Tools for Active Investors. Financial Times Prentice Hall. p. 166. ISBN 0-13-147902-4.
- ↑ "Why MACD (12, 26, 9)?" section of the page "Moving Average Convergence-Divergence (MACD) - The Complete Guide". ForexAbode.com.
- ↑ Gerald Appel (), INO TV
- ↑ http://www.forexo.co.uk/macd-moving-average-convergence-divergence
- ↑ Appel, Gerald (2005). Technical Analysis Power Tools for Active Investors. Financial Times Prentice Hall. ISBN 0-13-147902-4.
- ↑ Patterson, Jackie Ann (2014). Truth About MACD: What Worked, What Didn't Work, and How to Avoid Mistakes Even Experts Make. Own Mountain Trading Company. pp. 19–21. ISBN 1492749842.
- ↑ The MACD Approach to Derivative (Rate of Change) Estimation
- ↑ Patterson, Jackie Ann (2014). Truth About MACD: What Worked, What Didn't Work, and How to Avoid Mistakes Even Experts Make. Own Mountain Trading Company. pp. 45–99. ISBN 1492749842.
- ↑ Murphy, John (1999). Technical Analysis of the Financial Markets. Prentice Hall Press. pp. 252–255. ISBN 0-7352-0066-1.
External links
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||