M129 grenade launcher
| M129 grenade launcher | |
|---|---|
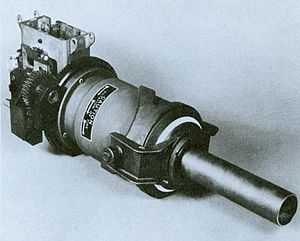 | |
| Type | Automatic grenade launcher |
| Place of origin |
|
| Service history | |
| Used by |
|
| Wars | Vietnam War |
| Production history | |
| Designer | Philco-Ford[1] |
| Designed | 1966[1] |
| Number built | over 1,667[2] |
| Specifications | |
| Length | 597 mm |
| Barrel length | 419 mm |
|
| |
| Cartridge | 40x53mm grenade, 40x46mm grenade |
| Caliber | 40 mm |
| Action | Automatic, motor driven[1] |
| Rate of fire | 400 rpm[2] |
| Muzzle velocity | 850 feet per second (260 m/s)[1] |
| Effective firing range | 2,045 yards (1,870 m)[1] |
| Feed system | belt |
The M129 is a 40 mm automatic grenade launcher that was used as an aircraft weapon in United States service. It was developed from the earlier M75 and was capable of using both the high-velocity 40x53 mm grenade and the lower velocity 40x46 mm grenade.[1]
Overview
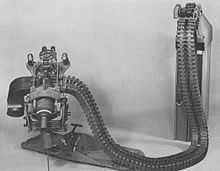
The M129 was a redesign of the M75 grenade launcher that featured reduced recoil and improved mounting and provided an increased rate of fire of up to 400 rpm compared to 225 rpm for the M75. The M129 was used with the chin-mounted M28 series armament subsystem used on the AH-1G, AH-1Q, MOD AH-1S, and production AH-1S Cobra. The M129 was also used on the:
- AH-56 Cheyenne on the XM51
- UH-1H Huey on the XM94
- OH-6A Cayuse on the XM8
- OH-58 Kiowa light observation helicopters on the XM8
Design
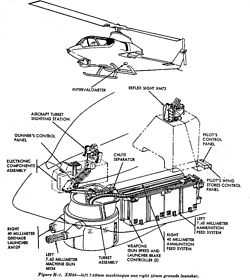
The M129 was effectively a redesign of the older M75 to incorporate a concentric cam and improved mount.[3] The major problem with the M75 was the torque created due to the barrel being below the operating drum. In the M129, the barrel is concentric with the drum and the excessive torque is thus eliminated. Otherwise, operation of the weapon is extremely similar to that of the M75, with the reciprocating barrel and cam assembly still presenting itself, the weapon still being electrically driven and ammunition still fed through a belt system. Some other improvements were made to the M129, most notably that of the addition of special feed tray to permit the firing of low-velocity and high-velocity ammunition, a mechanism to provide instant interchange between electric operation and manual hand-crank operation and a dynamic braking unit to guarantee that the launcher barrel always stopped in the forward (safe) position when the firing trigger is released.
See also
- U.S. helicopter armament subsystems
- List of grenade launchers
- Comparison of automatic grenade launchers
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 Roger Desbois. "GRENADE LAUNCHER M75 40mm". securityarms.som. Retrieved 9 January 2011.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 "M129 40mm Grenade Launcher". globalsecurity.org. Retrieved 9 January 2011.
- ↑ US Army TACOM-RI. 5 October 2005 U.S. ARMY HELICOPTER WEAPONS. Access Date: 25 January 2008