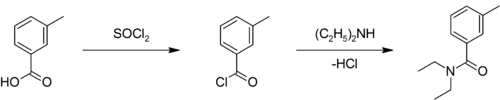m-Toluic acid
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
3-Methylbenzoic acid | |||
| Other names
meta-Toluic acid m-Methylbenzoic acid beta-Methylbenzoic acid | |||
| Identifiers | |||
| 99-04-7 | |||
| ChEBI | CHEBI:10589 | ||
| |||
| Jmol-3D images | Image | ||
| PubChem | 7418 | ||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C8H8O2 | |||
| Molar mass | 136.15 g/mol | ||
| Density | 1.05 g/cm3, solid | ||
| Melting point | 111 to 113 °C (232 to 235 °F; 384 to 386 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 263 °C (505 °F; 536 K) | ||
| Acidity (pKa) | 4.27 (in water)[2] | ||
| Hazards | |||
| MSDS | External MSDS | ||
| Related compounds | |||
| Except where noted otherwise, data is given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |||
| | |||
| Infobox references | |||
m-Toluic acid, (IUPAC: 3-methylbenzoic acid), is an aromatic carboxylic acid, with formula (CH3)C6H4(COOH). It is an isomer of p-toluic acid and o-toluic acid.
It serves, among other purposes, as a precursor to DEET (N,N-diethyl-m-toluamide), the well-known insect repellent:[3][4]
References
- ↑ M-TOLUIC ACID - Compound Summary, PubChem.
- ↑ "Dissociation Constants Of Organic Acids And Bases". Retrieved 11 April 2010.
- ↑ Wang, Benjamin J-S. (1974). "An interesting and successful organic experiment (CEC)". J. Chem. Ed. 51 (10): 631. doi:10.1021/ed051p631.2.
- ↑ Donald L. Pavia (2004). Introduction to organic laboratory techniques (GOOGLE BOOKS EXCERPT). Cengage Learning. pp. 370–376. ISBN 978-0-534-40833-6.