Luttinger's theorem
In condensed matter physics, Luttinger's theorem[1][2] is a result derived by J. M. Luttinger and J. C. Ward in 1960 that has broad implications in the field of electron transport. It arises frequently in theoretical models of correlated electrons, such as the high-temperature superconductors, and in photoemission, where a metal's Fermi surface can be directly observed.
Definition
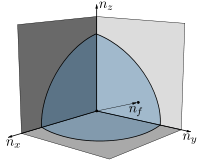
Luttinger's theorem states that the volume enclosed by a material's Fermi surface is directly proportional to the particle density.
While the theorem is an immediate result of the Pauli exclusion principle in the case of noninteracting particles, it remains true even as interactions between particles are taken into consideration provided that the appropriate definitions of Fermi surface and particle density are adopted. Specifically, in the interacting case the Fermi surface must be defined according to the criteria that
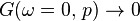 or
or 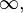
where 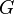 is the single-particle Green function in terms of frequency and momentum. Then Luttinger's theorem can be recast into the form[3]
is the single-particle Green function in terms of frequency and momentum. Then Luttinger's theorem can be recast into the form[3]
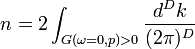 ,
,
where 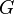 is as above and
is as above and 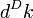 is the differential volume of
is the differential volume of 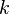 -space in
-space in 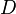 dimensions.
dimensions.
See also
- Fermi liquid
- Fermi surface
References
Inline
- ↑ Luttinger, J. M.; Ward, J. C. (1960). "Ground-State Energy of a Many-Fermion System. II". Physical Review 118 (5): 1417–1427. Bibcode:1960PhRv..118.1417L. doi:10.1103/PhysRev.118.1417.
- ↑ Luttinger, J. M. (1960). "Fermi Surface and Some Smple Equilibrium Properties of a System of Interacting Fermions". Physical Review 119 (4): 1153–1163. Bibcode:1960PhRv..119.1153L. doi:10.1103/PhysRev.119.1153.
- ↑ Alexei M. Tsvelik (2003). Quantum Field Theory in Condensed Matter Physics (2nd ed.). Cambridge University Press. p. 327. ISBN 0-521-82284-X.
General
- Behnam Farid (2007). "On the Luttinger theorem concerning number of particles in the ground states of systems of interacting fermions". arXiv:0711.0952 [cond-mat.str-el].
- Behnam Farid; Tsvelik (2009). "Comment on "Breakdown of the Luttinger sum rule within the Mott-Hubbard insulator", by J. Kokalj and P. Prelovšek, Phys. Rev. B 78, 153103 (2008)". arXiv:0909.2886 [cond-mat.str-el].
- Behnam Farid (2009). "Comment on "Violation of the Luttinger sum rule within the Hubbard model on a triangular lattice", by J. Kokalj and P. Prelovšek, Eur. Phys. J. B 63, 431 (2008)". arXiv:0909.2887 [cond-mat.str-el].
- Kiaran B. Dave; Philip W. Phillips; Charles L. Kane (2012). "Absence of Luttinger's theorem". arXiv:1207.4201 [cond-mat.str-el].
- Behnam Farid (2012). "Comment on "Absence of Luttinger's theorem", by Kiaran B. Dave, Philip W. Phillips and Charles L. Kane, arXiv:1207.4201". arXiv:1211.5612 [cond-mat.str-el].
- M. Oshikawa (2000). "Topological Approach to Luttinger's Theorem and the Fermi Surface of a Kondo Lattice". Physical Review Letters 84 (15): 3370–3373. arXiv:cond-mat/0002392. Bibcode:2000PhRvL..84.3370O. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.84.3370.
- Mastropietro, Vieri; Mattis, Daniel C. (2013). Luttinger Model: The First 50 Years and Some New Directions. World Scientific. ISBN 978-981-4520-71-3.
- F. D. M. Haldane (2005). "Luttinger's Theorem and Bosonization of the Fermi Surface". In R. A. Broglia and J. R. Schrieffer. Proceedings of the International School of Physics "Enrico Fermi", Course CXXI "Perspectives in Many-Particle Physics". North-Holland. pp. 5–29. arXiv:cond-mat/0505529.