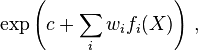Log-linear model
A log-linear model is a mathematical model that takes the form of a function whose logarithm is a linear combination of the parameters of the model, which makes it possible to apply (possibly multivariate) linear regression. That is, it has the general form
in which the fi(X) are quantities that are functions of the variables X, in general a vector of values, while c and the wi stand for the model parameters.
The term may specifically be used for:
- A log-linear plot or graph, which is a type of semi-log plot.
- Poisson regression for contingency tables, a type of generalized linear model.
The specific applications of log-linear models are where the output quantity lies in the range 0 to ∞, for values of the independent variables X, or more immediately, the transformed quantities fi(X) in the range −∞ to +∞. This may be contrasted to logistic models, similar to the logistic function, for which the output quantity lies in the range 0 to 1. Thus the contexts where these models are useful or realistic often depends on the range of the values being modelled.
See also
- Loglinear analysis
- General linear model
- Generalized linear model
- Boltzmann distribution