Local government in Wales
 |
| This article is part of a series on the politics and government of Wales |
|
Law and justice |
|
Wales in the EU |
|
Administrative divisions |
|
British politics portal |
For local government purposes, Wales has since 1 April 1996 been divided into 22 single-tier principal areas.[1] The elected councils of these areas are responsible for the provision of all local government services, including education, social work, environmental protection, and most highways. Below these there are also (in most, but not all, parts of the principal areas) elected community councils to which responsibility for specific aspects of the application of local policy may be devolved.
The principal areas are variously styled as "county", "county borough", "city" or "city and county", although this is a distinction not always respected in the media, including the BBC, where all 22 areas are sometimes referred to simply as "counties".[2][3]
The Queen appoints a Lord Lieutenant to represent her in each of the eight preserved counties of Wales – which are combinations of principal areas retained for ceremonial purposes.
Subdivisions of Wales created for such purposes as the provision of police and emergency services and the organization of the National Health Service are made up of combinations of principal areas. The Dyfed-Powys Police force, for example, operates in the area covered by the principal areas of Powys, Pembrokeshire, Ceredigion, and Carmarthenshire – the latter three constituting the preserved county of Dyfed.
In April 2013, it was announced that a major review was to be undertaken into local government organisation in Wales, with a Commission on Public Service Governance and Delivery to be chaired by Sir Paul Williams. The Commission's report was published in January 2014, and recommended a reduction in the number of principal area councils to between 10 and 12.
Cities
There are six cities in total in Wales: in addition to the three principal areas with city status (Cardiff, Swansea and Newport), the communities of Bangor, St David's and St Asaph also have the status. City status is determined by letters patent.
- Bangor - time indeterminate
- Cardiff 1905
- Swansea 1969
- St David's and the Cathedral Close 1994
- Newport 2002
- St Asaph 2012
St Asaph, as the seat of a bishopric, was historically referred to as a city, and was described as such in the 1911 Encyclopædia Britannica. The status was never officially recognised, however. When city status was restored to St David's in 1994, St Asaph town council submitted a petition for the same purpose. The petition was refused as, unlike St David's, there was no evidence of any charter or letters patent in the past conferring the status. Applications for city status in competitions in 2000 and 2002 were unsuccessful.[4] However, city status was finally granted in 2012 when St Asaph won the accolade as part of the Queen's Diamond Jubilee celebrations.[5]
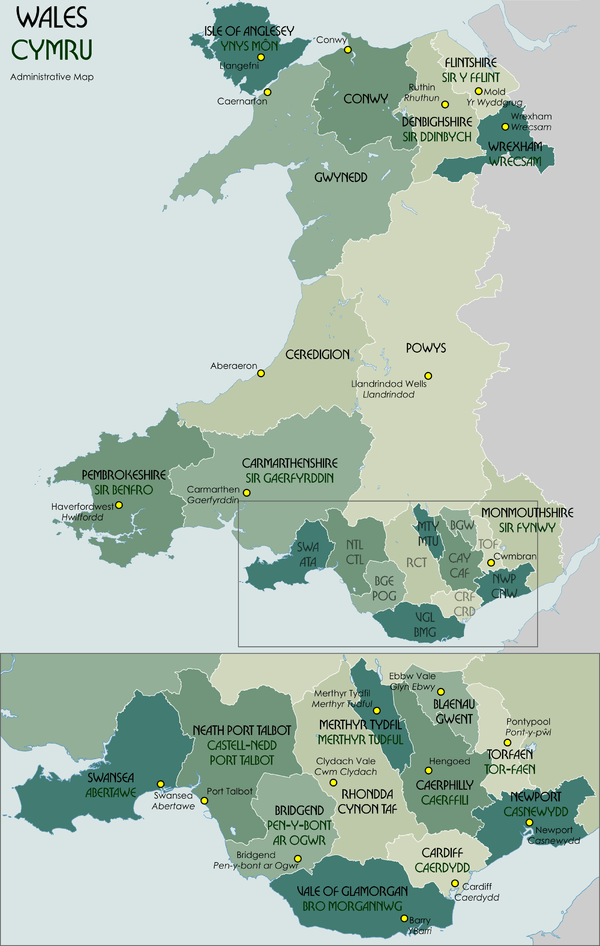
Principal areas of Wales
There are 22 principal areas in Wales. They came into being on 1 April 1996 by virtue of the Local Government (Wales) Act 1994 (1994 c. 19). Eleven are named as counties, including the Cities and Counties of Cardiff and Swansea (marked *), and eleven are styled as county boroughs (marked †).[6] In 2002 Newport was granted city status, and the county borough is now styled as the "City of Newport".[7][8] Welsh language forms are given in parentheses, except where there is no English equivalent.
Locations of each council headquarters are indicated by yellow markers.
 |
|
| ||||||
Name changes
The current names of certain unitary authority areas are different from those specified in the Local Government (Wales) Act 1994. The following changes took place, all with effect from 2 April 1996:[9]
- Conwy from Aberconwy and Colwyn
- Isle of Anglesey from Anglesey
- Gwynedd from Caernarfonshire and Merionethshire
- Ceredigion from Cardiganshire
- Neath Port Talbot from Neath and Port Talbot
Governance
In common with councils throughout the rest of the UK, Welsh councils are run by elected councillors. However because of political in-fighting and a history of poor performance, the executive functions of the Isle of Anglesey Council were temporarily taken over by commissioners appointed by the Welsh Assembly Government.[10] Elections planned for 2012 were delayed until 2013.[11]
Preserved counties of Wales
For ceremonial purposes of Lieutenancy and Shrievalty, Wales is divided into 8 preserved counties which are based on the counties created by the Local Government Act 1972 and used for local government and other purposes between 1974 and their abolition in 1996.
Historic counties of Wales
The historic counties of Wales are ancient subdivisions of Wales, used for various functions for several hundred years. The oldest date from 1138, with further counties created in 1282 and 1535. They were the main administrative subdivisions of Wales from 1889 until the implementation in 1974 of the Local Government Act 1972.
Communities
The lowest level of administrative subdivision in Wales are the communities, into which each principal area is subdivided. They may have elected community councils which perform a number of roles, such as providing local facilities, and representing their communities to larger local government bodies. Community councils are the equivalent of English parish councils. A community council may call itself a "town council" if it so wishes. The councils of three communities with city status – Bangor, St Asaph, and St David's and the Cathedral Close – are known as "city councils". Communities which are too small to have a council may have a community meeting instead: an example of direct democracy.
Police and fire services
Police forces
There are four police forces in Wales. These are:
 |
|
Fire and rescue services
There are three fire and rescue services in Wales. The present Welsh fire services date from 1996. Each covers a number of principal areas. These are:
 |
|
Eurostat NUTS
In the Eurostat Nomenclature of Territorial Units for Statistics (NUTS), Wales is a level-1 NUTS region, coded "UKL", which is subdivided as follows:
| NUTS 1 | Code | NUTS 2 | Code | NUTS 3 | Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wales | UKL | West Wales and The Valleys | UKL1 | Isle of Anglesey | UKL11 |
 |
Gwynedd | UKL12 | |||
| Conwy and Denbighshire | UKL13 | ||||
| South West Wales (Ceredigion, Carmarthenshire, Pembrokeshire) | UKL14 | ||||
| Central Valleys (Merthyr Tydfil, Rhondda Cynon Taff) | UKL15 | ||||
| Gwent Valleys (Blaenau Gwent, Caerphilly, Torfaen) | UKL16 | ||||
| Bridgend and Neath Port Talbot | UKL17 | ||||
| Swansea | UKL18 | ||||
| East Wales | UKL2 | Monmouthshire and Newport | UKL21 | ||
| Cardiff and Vale of Glamorgan | UKL22 | ||||
| Flintshire and Wrexham | UKL23 | ||||
| Powys | UKL24 | ||||
History
Williams Commission
In April 2013, it was announced that a major review was to be undertaken into local government organisation in Wales, with a Commission on Public Service Governance and Delivery being established, to be chaired by Sir Paul Williams. First Minister Carwyn Jones said: "Since public sector budgets are likely to continue to tighten, and demand pressures grow, there is a clear need to examine how services can be sustained and standards of performance raised, so that people in Wales can continue to receive and influence the public services they need and value."[12]
The Commission reported on 20 January 2014. It recommended that the number of councils be reduced, through mergers rather than through boundary changes, from 22 to 10, 11 or 12; and suggested that the cost of merging the councils would be met through savings made within about two years.[13]
Wales' First Minister Carwyn Jones said: "This report addresses many issues that are critical at a time when the need for public services is outstripping the resources available to provide them. I have always been clear that the status quo is not an option. Change is inevitable and essential so that our public services can become more efficient, effective, accessible and responsive." Janet Finch-Saunders AM, shadow minister for local government, said: "What matters to the vast majority of hardworking families is not the intricate structures of local government, but knowing that services will be delivered in an efficient and cost effective way.... We believe that public services are best delivered locally so taxpayers can hold local representatives to account for what happens in their community." Rhodri Glyn Thomas, for Plaid Cymru, commented: "The weight of evidence presented to the Williams Commission shows that if the people of Wales are going to get the services they need and deserve then there has to be a radical improvement in the way public services are delivered.".[13]
See also
- List of Welsh principal areas by population
- List of Welsh principal areas by area
- List of Welsh principal areas by percentage Welsh language
- Welsh Government
- Geography of Wales
- List of communities in Wales
- ISO 3166-2:GB, subdivision codes for the United Kingdom
- Local government in England
- Local government in Northern Ireland
- Local government in Scotland
- Political make-up of local councils in the United Kingdom#Welsh Unitary authorities
External links
- Williams Commission report, January 2014
- LocalGov.co.uk - News updates on UK local government, including reorganisation
- Map of the UK counties and unitary administrations
- Map of all UK local authorities
References
- ↑ Local Government (Wales) Act 1994
- ↑ BBC Wales A listing of "each of the 22 Welsh counties". 23.12.05
- ↑ BBC Wales North West: Conwy County
- ↑ Beckett, J V (2005). City Status in the British isles, 1830 - 2002. Aldershot: Ashgate Publishing. pp. 133–135. ISBN 0-7546-5067-7.
- ↑ "Three towns win city status for Diamond Jubilee". BBC NEWS. 2012-04-18. Retrieved 2012-04-18.
- ↑ Local Government (Wales) Act 1994, Schedule 1
- ↑ The London Gazette: no. 56573. p. 6160. 21 May 2002. Retrieved 5 March 2010.
- ↑ "Newport City Council". Newport City Council. 4 December 2010. Retrieved 5 March 2011.
- ↑ The Residuary Body for Wales (Levies) Regulations 1996
- ↑ Power taken from Anglesey council elected politicians
- ↑ Anglesey council election postponed for year to 2013
- ↑ BBC News, Local councils in Wales could be cut after review, 19 April 2013. Retrieved 19 April 2013
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 BBC News, Williams Commission report calls for fewer councils, 20 January 2014. Retrieved 20 January 2014
- CIA World Factbook 2002
| ||||||||||||||