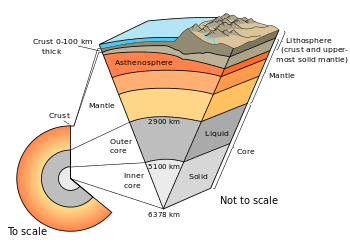
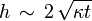Lithosphere
A lithosphere (Ancient Greek: λίθος [lithos] for "rocky", and σφαῖρα [sphaira] for "sphere") is the rigid,[1] outermost shell of a rocky planet, and can be identified on the basis of its mechanical properties. On Earth, it comprises the crust and the portion of the upper mantle that behaves elastically on time scales of thousands of years or greater. The outermost shell of a rocky planet, the crust, is defined on the basis of its chemistry and mineralogy.
Earth's lithosphere
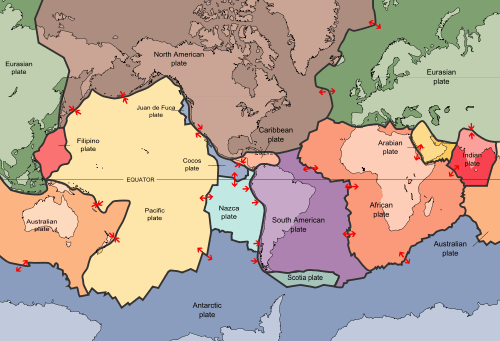
Earth's lithosphere includes the crust and the uppermost mantle, which constitute the hard and rigid outer layer of the Earth. The lithosphere is subdivided into tectonic plates. The uppermost part of the lithosphere that chemically reacts to the atmosphere, hydrosphere and biosphere through the soil forming process is called the pedosphere. The lithosphere is underlain by the asthenosphere which is the weaker, hotter, and deeper part of the upper mantle. The boundary between the lithosphere and the underlying asthenosphere is known as the Lithosphere-Asthenosphere boundary and is defined by a difference in response to stress: the lithosphere remains rigid for very long periods of geologic time in which it deforms elastically and through brittle failure, while the asthenosphere deforms viscously and accommodates strain through plastic deformation. The study of past and current formations of landscapes is called geomorphology.
History
The concept of the lithosphere as Earth’s strong outer layer was described by A.E.H. Love in his 1911 monograph "Some problems of Geodynamics" and further developed by Joseph Barrell, who wrote a series of papers about the concept.[2][3][4][5] The concept was based on the presence of significant gravity anomalies over continental crust, from which he inferred that there must exist a strong upper layer (which he called the lithosphere) above a weaker layer which could flow (which he called the asthenosphere). These ideas were expanded by Harvard geologist Reginald Aldworth Daly in 1940 with his seminal work "Strength and Structure of the Earth"[6] and have been broadly accepted by geologists and geophysicists. Although these ideas about lithosphere and asthenosphere were developed long before plate tectonic theory was articulated in the 1960s, the concepts that a strong lithosphere exists and that this rests on a weak asthenosphere are essential to that theory.
Types
There are two types of lithosphere:
- Oceanic lithosphere, which is associated with oceanic crust and exists in the ocean basins (mean density of about 2.9 grams per cubic centimeter)
- Continental lithosphere, which is associated with continental crust (mean density of about 2.7 grams per cubic centimeter)
The thickness of the lithosphere is considered to be the depth to the isotherm associated with the transition between brittle and viscous behavior.[7] The temperature at which olivine begins to deform viscously (~1000 °C) is often used to set this isotherm because olivine is generally the weakest mineral in the upper mantle. Oceanic lithosphere is typically about 50–140 km thick [8](but beneath the mid-ocean ridges is no thicker than the crust), while continental lithosphere has a range in thickness from about 40 km to perhaps 280 km;[8] the upper ~30 to ~50 km of typical continental lithosphere is crust. The mantle part of the lithosphere consists largely of peridotite. The crust is distinguished from the upper mantle by the change in chemical composition that takes place at the Moho discontinuity.
Oceanic lithosphere
Oceanic lithosphere consists mainly of mafic crust and ultramafic mantle (peridotite) and is denser than continental lithosphere, for which the mantle is associated with crust made of felsic rocks. Oceanic lithosphere thickens as it ages and moves away from the mid-ocean ridge. This thickening occurs by conductive cooling, which converts hot asthenosphere into lithospheric mantle and causes the oceanic lithosphere to become increasingly thick and dense with age. The thickness of the mantle part of the oceanic lithosphere can be approximated as a thermal boundary layer that thickens as the square root of time.
Here, 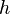 is the thickness of the oceanic mantle lithosphere,
is the thickness of the oceanic mantle lithosphere, 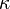 is the thermal diffusivity (approximately 10−6 m2/s) for silicate rocks, and
is the thermal diffusivity (approximately 10−6 m2/s) for silicate rocks, and 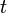 is the age of the given part of the lithosphere. The age is often equal to L/V, where L is the distance from the spreading centre of mid-oceanic ridge, and V is velocity of the lithospheric plate.
is the age of the given part of the lithosphere. The age is often equal to L/V, where L is the distance from the spreading centre of mid-oceanic ridge, and V is velocity of the lithospheric plate.
Oceanic lithosphere is less dense than asthenosphere for a few tens of millions of years but after this becomes increasingly denser than asthenosphere. This is because the chemically differentiated oceanic crust is lighter than asthenosphere, but thermal contraction of the mantle lithosphere makes it more dense than the asthenosphere. The gravitational instability of mature oceanic lithosphere has the effect that at subduction zones, oceanic lithosphere invariably sinks underneath the overriding lithosphere, which can be oceanic or continental. New oceanic lithosphere is constantly being produced at mid-ocean ridges and is recycled back to the mantle at subduction zones. As a result, oceanic lithosphere is much younger than continental lithosphere: the oldest oceanic lithosphere is about 170 million years old, while parts of the continental lithosphere are billions of years old. The oldest parts of continental lithosphere underlie cratons, and the mantle lithosphere there is thicker and less dense than typical; the relatively low density of such mantle "roots of cratons" helps to stabilize these regions.[9][10]
Subducted lithosphere
Geophysical studies in the early 21st century posit that large pieces of the lithosphere have been subducted into the mantle as deep as 2900 km to near the core-mantle boundary,[11] while others "float" in the upper mantle,[12][13] while some stick down into the mantle as far as 400 km but remain "attached" to the continental plate above,[10] similar to the extent of the "tectosphere" proposed by Jordan in 1988.[14]
Mantle xenoliths
Geoscientists can directly study the nature of the subcontinental mantle by examining mantle xenoliths[15] brought up in kimberlite, lamproite, and other volcanic pipes. The histories of these xenoliths have been investigated by many methods, including analyses of abundances of isotopes of osmium and rhenium. Such studies have confirmed that mantle lithospheres below some cratons have persisted for periods in excess of 3 billion years, despite the mantle flow that accompanies plate tectonics.[16]
See also
References
- ↑ Skinner, B.J. & Porter, S.C.: Physical Geology, page 17, chapt. The Earth: Inside and Out, 1987, John Wiley & Sons, ISBN 0-471-05668-5
- ↑ Barrell, J (1914). "The strength of the Earth's crust". Journal of Geology 22 (4): 289–314. Bibcode:1914JG.....22..289B. doi:10.1086/622155. JSTOR 30056401.
- ↑ Barrell, J (1914). "The strength of the Earth's crust". Journal of Geology 22 (5): 441–468. Bibcode:1914JG.....22..441B. doi:10.1086/622163. JSTOR 30067162.
- ↑ Barrell, J (1914). "The strength of the Earth's crust". Journal of Geology 22 (7): 655–683. Bibcode:1914JG.....22..655B. doi:10.1086/622181. JSTOR 30060774.
- ↑ Barrell, J (1914). "The strength of the Earth's crust". Journal of Geology 22 (6): 537–555. Bibcode:1914JG.....22..537B. doi:10.1086/622170. JSTOR 30067883.
- ↑ Daly, R. (1940) Strength and structure of the Earth. New York: Prentice-Hall.
- ↑ Parsons, B. and McKenzie, D. (1978). "Mantle Convection and the thermal structure of the plates" (PDF). Journal of Geophysical Research 83 (B9): 4485. Bibcode:1978JGR....83.4485P. doi:10.1029/JB083iB09p04485.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Pasyanos M. E. (2008-05-15). "Lithospheric Thickness Modeled from Long Period Surface Wave Dispersion" (PDF). Retrieved 2014-04-25.
- ↑ Jordan, Thomas H. (1978). "Composition and development of the continental tectosphere". Nature 274 (5671): 544. Bibcode:1978Natur.274..544J. doi:10.1038/274544a0.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 O'Reilly, Suzanne Y.; Zhang, Ming; Griffin, William L.; Begg, Graham; Hronsky, Jon (2009). "Ultradeep continental roots and their oceanic remnants: A solution to the geochemical "mantle reservoir" problem?". Lithos 112: 1043. Bibcode:2009Litho.112.1043O. doi:10.1016/j.lithos.2009.04.028.
- ↑ Burke, Kevin; Torsvik, Trond H. (2004). "Derivation of Large Igneous Provinces of the past 200 million years from long-term heterogeneities in the deep mantle". Earth and Planetary Science Letters 227 (3–4): 531. Bibcode:2004E&PSL.227..531B. doi:10.1016/j.epsl.2004.09.015.
- ↑ Replumaz, Anne; Kárason, Hrafnkell; Van Der Hilst, Rob D; Besse, Jean; Tapponnier, Paul (2004). "4-D evolution of SE Asia's mantle from geological reconstructions and seismic tomography". Earth and Planetary Science Letters 221: 103. Bibcode:2004E&PSL.221..103R. doi:10.1016/S0012-821X(04)00070-6.
- ↑ Li, Chang; Van Der Hilst, Robert D.; Engdahl, E. Robert; Burdick, Scott (2008). "A new global model for P wave speed variations in Earth's mantle". Geochemistry Geophysics Geosystems 9 (5). Bibcode:2008GGG.....905018L. doi:10.1029/2007GC001806.
- ↑ "Structure and formation of the continental tectosphere". doi:10.1093/petrology/Special_Volume.1.11.
- ↑ Nixon, P.H. (1987) Mantle xenoliths J. Wiley & Sons, 844 p. ISBN 0-471-91209-3
- ↑ Carlson, Richard W. (2005). "Physical, chemical, and chronological characteristics of continental mantle" (PDF). Reviews of Geophysics 43. Bibcode:2005RvGeo..43.1001C. doi:10.1029/2004RG000156.
Further reading
- Chernicoff, Stanley; Whitney, Donna (1990). Geology. An Introduction to Physical Geology (4th ed.). Pearson. ISBN 0131751247.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Lithospheres. |
| ||||||||||||||