List of shipwrecks in 1930
The list of shipwrecks in 1930 includes all ships sunk, foundered, grounded, or otherwise lost during 1930.
January
1 January
- Mapocho (
 Chile): The cargo liner ran aground south of Samanco and was abandoned.[1] She was refloated on 3 January.[2]
Chile): The cargo liner ran aground south of Samanco and was abandoned.[1] She was refloated on 3 January.[2] - Sönderberg (
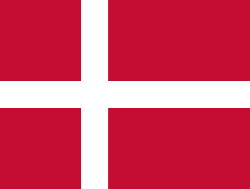 Denmark): The cargo ship ran aground on Harris, Outer Hebrides, United Kingdom. All 27 crew survived.[3]
Denmark): The cargo ship ran aground on Harris, Outer Hebrides, United Kingdom. All 27 crew survived.[3]
4 January
- Edgar Quinet (
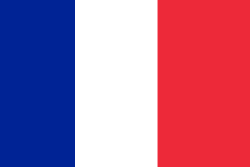 Marine Nationale): The Edgar Quinet-class armoured cruiser ran aground off Oran, Algeria. All crew were rescued. She broke up on 8 January and was a total loss.
Marine Nationale): The Edgar Quinet-class armoured cruiser ran aground off Oran, Algeria. All crew were rescued. She broke up on 8 January and was a total loss.
5 January
- Hofplein (
 Netherlands): The cargo ship ran aground on the Norwegian coast near the Svinøy Lighthouse and broke in two with the loss of five of her 32 crew.[2][4]
Netherlands): The cargo ship ran aground on the Norwegian coast near the Svinøy Lighthouse and broke in two with the loss of five of her 32 crew.[2][4]
6 January
- Albert Morillon (
 France): The cargo ship ran aground off Diégo-Suarez, Madagascar and was wrecked.[5]
France): The cargo ship ran aground off Diégo-Suarez, Madagascar and was wrecked.[5] - Ethel (
 United Kingdom): The salvage vessel sank in the Bristol Channel off Breaksea Point, Glamorgan. The crew were rescued.[6]
United Kingdom): The salvage vessel sank in the Bristol Channel off Breaksea Point, Glamorgan. The crew were rescued.[6] - Miraman (
 Argentina): The cargo ship caught fire at Quequen and was a total loss.[7]
Argentina): The cargo ship caught fire at Quequen and was a total loss.[7]
7 January
- Limpopo (
 Portugal): The coaster ran aground in Luderitz Bay on her maiden voyage and was a total loss.[8]
Portugal): The coaster ran aground in Luderitz Bay on her maiden voyage and was a total loss.[8] - Olga (
 Denmark): The schooner was wrecked in the North Sea during a gale. She was towed into Ålesund being kept afloat by her cargo.[6]
Denmark): The schooner was wrecked in the North Sea during a gale. She was towed into Ålesund being kept afloat by her cargo.[6]
9 January
- Porthmeor (
 United Kingdom): The coaster sprang a leak in the Irish Sea and was beached at Ardglass, County Down.[9] She was refloated on 27 January.[10]
United Kingdom): The coaster sprang a leak in the Irish Sea and was beached at Ardglass, County Down.[9] She was refloated on 27 January.[10]
10 January
- Edward Luckenbach (
 United States): The cargo ship ran aground at Block Island, Rhode Island.[11] She was refloated on 5 March.[12]
United States): The cargo ship ran aground at Block Island, Rhode Island.[11] She was refloated on 5 March.[12]
12 January
- Daiten Maru (
 Japan): The cargo ship ran aground on Rushiri Island, off Hokkaidō.[13] Salvage effors were abandoned on 17 January and she was declared a total loss.[14]
Japan): The cargo ship ran aground on Rushiri Island, off Hokkaidō.[13] Salvage effors were abandoned on 17 January and she was declared a total loss.[14] - The Forester (
 United Kingdom): The coaster broke free from her moorings in Portland Harbour, Dorset. She was driven against a breakwater and sank. All eight people on board survived.[13][15]
United Kingdom): The coaster broke free from her moorings in Portland Harbour, Dorset. She was driven against a breakwater and sank. All eight people on board survived.[13][15] - Katie (
 United Kingdom): The schooner broke free from her moorings in Torbay and drifted into the English Channel. Four crew were rescued by the Padstow Lifeboat.[13]
United Kingdom): The schooner broke free from her moorings in Torbay and drifted into the English Channel. Four crew were rescued by the Padstow Lifeboat.[13] - Reine des Cieux (
 France): The ketch broke free from her moorings in Torbay. Three crew were rescued by the Padstow Lifeboat.[13] She came ashore at Bridport, Dorset and broke up.[16]
France): The ketch broke free from her moorings in Torbay. Three crew were rescued by the Padstow Lifeboat.[13] She came ashore at Bridport, Dorset and broke up.[16] - HMS St. Genny (
 Royal Navy): The tug foundered in the English Channel 32 nautical miles (59 km)) north west of Ouessant, Finistère, France with the loss of 28 of her 33 crew.[17] Survivors were rescued by HMS St. Cyrus (
Royal Navy): The tug foundered in the English Channel 32 nautical miles (59 km)) north west of Ouessant, Finistère, France with the loss of 28 of her 33 crew.[17] Survivors were rescued by HMS St. Cyrus ( Royal Navy).[16]
Royal Navy).[16]
13 January
- Skauts (
 Latvia): The cargo ship was driven ashore on Texel, North Holland, Netherlands.[13] She was refloated on 21 January.[18]
Latvia): The cargo ship was driven ashore on Texel, North Holland, Netherlands.[13] She was refloated on 21 January.[18] - Thyra (
 Sweden): The cargo ship's propeller shaft fractured. She was driven ashore on the Norwegian coast and was a total loss.[13]
Sweden): The cargo ship's propeller shaft fractured. She was driven ashore on the Norwegian coast and was a total loss.[13] - Valentino Coda (
.svg.png) Italy): The cargo ship was abandoned in the North Sea (53°28′N 4°22′E / 53.467°N 4.367°E). She came ashore on Vlieland, Friesland, Netherlands.[15] Valentino Coda was refloated on 19 January.[19]
Italy): The cargo ship was abandoned in the North Sea (53°28′N 4°22′E / 53.467°N 4.367°E). She came ashore on Vlieland, Friesland, Netherlands.[15] Valentino Coda was refloated on 19 January.[19]
14 January
- Bradfyne (
 United Kingdom): The cargo ship was beached at Houston, Texas, United States in order to avoid a collision with South American towing barge Tampico (both
United Kingdom): The cargo ship was beached at Houston, Texas, United States in order to avoid a collision with South American towing barge Tampico (both  United States).[16] She was refloated on 24 January.[20]
United States).[16] She was refloated on 24 January.[20] - Gulfqueen (
 United States): The cargo ship was driven ashore at Philadelphia, Pennsylvania.[16] She was refloated on 17 January.[14]
United States): The cargo ship was driven ashore at Philadelphia, Pennsylvania.[16] She was refloated on 17 January.[14]
16 January
- Ko Chow (
 United Kingdom): The cargo ship struck rocks off Wuchow, China and was beached.[21]
United Kingdom): The cargo ship struck rocks off Wuchow, China and was beached.[21] - Marietta Nomikou (
 Greece): The cargo ship was holed in the Corinth Canal and was beached.[21] She was refloated on 20 January.[22]
Greece): The cargo ship was holed in the Corinth Canal and was beached.[21] She was refloated on 20 January.[22] - Romanie (
.svg.png) Belgium): The cargo ship was wrecked in Pridmouth Bay, English Channel. The crew were rescued.[21][23]
Belgium): The cargo ship was wrecked in Pridmouth Bay, English Channel. The crew were rescued.[21][23]
17 January
- Telegraaf 6 (
 Netherlands): The cargo ship collided with Main (
Netherlands): The cargo ship collided with Main (.svg.png) Germany) in the Scheldt at Liefkenshoek, Antwerp, Belgium and was beached.[14] She was refloated the next day.[19]
Germany) in the Scheldt at Liefkenshoek, Antwerp, Belgium and was beached.[14] She was refloated the next day.[19]
21 January
- Ibero (
.svg.png) Spain): The cargo ship departed Cardiff, Glamorgan, United Kingdom for Barcelona. She passed Penarth Head that day. No further trace, presumed foundered with the loss of all hands.[24]
Spain): The cargo ship departed Cardiff, Glamorgan, United Kingdom for Barcelona. She passed Penarth Head that day. No further trace, presumed foundered with the loss of all hands.[24]
22 January
- Monte Cervantes (
.svg.png) Germany): The passenger ship struck a rock off Ushuaia, Chile and sank with the loss of her captain. Nearly 1,500 people were rescued by Vincente Fidel Lopez (
Germany): The passenger ship struck a rock off Ushuaia, Chile and sank with the loss of her captain. Nearly 1,500 people were rescued by Vincente Fidel Lopez ( Argentina.
Argentina.
26 January
- Daksa (
 Yugoslavia): The cargo ship issued an SOS in the Atlantic Ocean (42°30′N 9°35′W / 42.500°N 9.583°W). No further trace, presumed foundered with the loss of all hands.[25]
Yugoslavia): The cargo ship issued an SOS in the Atlantic Ocean (42°30′N 9°35′W / 42.500°N 9.583°W). No further trace, presumed foundered with the loss of all hands.[25] - W. H. Libby (
 United States: The cargo ship ran aground at Port Eads, Louisiana.[10] She was refloated on 31 January.[26]
United States: The cargo ship ran aground at Port Eads, Louisiana.[10] She was refloated on 31 January.[26]
27 January
- Grace Hankinson (
 United Kingdom): The coaster was towing Ruby L II (
United Kingdom): The coaster was towing Ruby L II ( United Kingdom). Both vessels were wrecked in the Petit Passage, Nova Scotia, Canada.[10]
United Kingdom). Both vessels were wrecked in the Petit Passage, Nova Scotia, Canada.[10] - Knebworth (
 United Kingdom): The cargo ship was wrecked near Biarritz, Pyrénées-Atlantiques, France.[27]
United Kingdom): The cargo ship was wrecked near Biarritz, Pyrénées-Atlantiques, France.[27]
29 January
- Braaland (
 Norway): The cargo ship ran aground on the Bombay Reef, Paracel Islands and the crew abandoned ship.[28][29] She was declared a total loss on 4 February.[30]
Norway): The cargo ship ran aground on the Bombay Reef, Paracel Islands and the crew abandoned ship.[28][29] She was declared a total loss on 4 February.[30]
31 January
- Tyrienne S (
 United Kingdom): The schooner was destroyed by fire at Harbour Le Cou, Newfoundland.[26]
United Kingdom): The schooner was destroyed by fire at Harbour Le Cou, Newfoundland.[26]
February
1 February
- Edgar F. Coney (
 United States): The tug sank in the Atlantic Ocean off the coast of Florida with the loss of fourteen crew.[26]
United States): The tug sank in the Atlantic Ocean off the coast of Florida with the loss of fourteen crew.[26] - Gatwick (
 United Kingdom): The cargo ship was driven ashore at Methil, Fife. The crew were taken off by breeches buoy.[26] She was refloated on 13 February.[31]
United Kingdom): The cargo ship was driven ashore at Methil, Fife. The crew were taken off by breeches buoy.[26] She was refloated on 13 February.[31]
2 February
- Brioni (
.svg.png) Italy): The cargo ship foundered in the Adriatic Sea off Vis, Yugoslavia with the loss of two crew.[32]
Italy): The cargo ship foundered in the Adriatic Sea off Vis, Yugoslavia with the loss of two crew.[32] - Hans Maersk (
 Denmark): The cargo ship collided with Emsland (
Denmark): The cargo ship collided with Emsland (.svg.png) Germany) in the Kaiser Wilhelm Canal and was beached.[26]
Germany) in the Kaiser Wilhelm Canal and was beached.[26]
3 February
- Scheldesop (
.svg.png) Belgium) : Ran aground on the Goodwin Sands, English Channel. Refloated but leaking, cargo discharged at Ramsgate the ship sailed to Antwerp where she was declared a constructive total loss. Later repaired and returned to service.[33]
Belgium) : Ran aground on the Goodwin Sands, English Channel. Refloated but leaking, cargo discharged at Ramsgate the ship sailed to Antwerp where she was declared a constructive total loss. Later repaired and returned to service.[33] - Diva (
.svg.png) Italy): The barque came ashore at Saint-Raphaël, Var, France. The crew were rescued.[32]
Italy): The barque came ashore at Saint-Raphaël, Var, France. The crew were rescued.[32]
4 February
- Albert Second (
 United Kingdom): The schooner was driven ashore on Isla Contoy, Quintana Roo, Mexico and was wrecked.[34]
United Kingdom): The schooner was driven ashore on Isla Contoy, Quintana Roo, Mexico and was wrecked.[34]
5 February
- Hav (
 Norway): The cargo ship broke free from her tow in the Atlantic Ocean off the coast of Portugal. She came ashore at Cape Roca and was wrecked.[35]
Norway): The cargo ship broke free from her tow in the Atlantic Ocean off the coast of Portugal. She came ashore at Cape Roca and was wrecked.[35]
7 February
- Tatsuta Maru (
 Japan): The almost-completed ocean liner was severely damaged by fire at Nagasaki.[36]
Japan): The almost-completed ocean liner was severely damaged by fire at Nagasaki.[36]
8 February
- Hartfield (
 United Kingdom): The cargo ship struck a rock and was holed in the Dardanelles. She was beached at Çanakkale, Turkey but was refloated the next day.[37]
United Kingdom): The cargo ship struck a rock and was holed in the Dardanelles. She was beached at Çanakkale, Turkey but was refloated the next day.[37] - Oranje (
 Netherlands): The auxiliary schooner sprang a leak and sank in the Thames Estuary off Southend Pier with the loss of two of her three crew.[38] She was raised on 20 February.[39]
Netherlands): The auxiliary schooner sprang a leak and sank in the Thames Estuary off Southend Pier with the loss of two of her three crew.[38] She was raised on 20 February.[39]
9 February
- Elcano (
.svg.png) Spain): The cargo ship sank at her moorings at Valencia, Spain during a gale.[40]
Spain): The cargo ship sank at her moorings at Valencia, Spain during a gale.[40] - Sveti Duje (
 Yugoslavia): The cargo ship was driven ashore in Mazarrón Bay.[40] She was refloated on 16 February.[41]
Yugoslavia): The cargo ship was driven ashore in Mazarrón Bay.[40] She was refloated on 16 February.[41]
10 February
- Dorothy Baird (
 Dominion of Newfoundland): The schooner sprang a leak in the Atlantic Ocean (39°42′N 53°07′W / 39.700°N 53.117°W) and was abandoned. She was set on fire as salvage was impossible and she was a danger to navigation. The crew were rescued by British Valour (
Dominion of Newfoundland): The schooner sprang a leak in the Atlantic Ocean (39°42′N 53°07′W / 39.700°N 53.117°W) and was abandoned. She was set on fire as salvage was impossible and she was a danger to navigation. The crew were rescued by British Valour ( United Kingdom).[42][43]
United Kingdom).[42][43]
11 February
- München (
.svg.png) Germany): The ocean liner caught fire and sank at New York, United States. She was subsequently salvaged, repaired and returned to service as General von Steuben.
Germany): The ocean liner caught fire and sank at New York, United States. She was subsequently salvaged, repaired and returned to service as General von Steuben. - Vineyard (
 United Kingdom): The auxiliary sailing vessel was sunk at Irvine, Ayrshire when a railway wagon overran coal drops and fell through the ship.[42]
United Kingdom): The auxiliary sailing vessel was sunk at Irvine, Ayrshire when a railway wagon overran coal drops and fell through the ship.[42]
15 February
- Admiral Benson (
 United States): The cargo ship ran aground at the mouth of the Columbia River.[44] She was abandoned as a total loss.[45]
United States): The cargo ship ran aground at the mouth of the Columbia River.[44] She was abandoned as a total loss.[45]
16 February
- Beauport (
 United Kingdom): The cargo ship was wrecked off Guernsey.[46]
United Kingdom): The cargo ship was wrecked off Guernsey.[46] - Henry A. McLellan (
 United Kingdom): The four-masted schooner broke free from here moorings at Meteghan, Nova Scotia, Canada. She was driven into the auxiliary schooners Avon Queen and Edwin G. Farrar (both
United Kingdom): The four-masted schooner broke free from here moorings at Meteghan, Nova Scotia, Canada. She was driven into the auxiliary schooners Avon Queen and Edwin G. Farrar (both  United Kingdom). All three vessels were beached. Henry A. McLellan was a total loss.[47]
United Kingdom). All three vessels were beached. Henry A. McLellan was a total loss.[47]
17 February
- Bullmouth (
 United Kingdom): The tanker collided with Fiumana (
United Kingdom): The tanker collided with Fiumana (.svg.png) Italy) at Istanbul, Turkey and was beached. She was later refloated.[48]
Italy) at Istanbul, Turkey and was beached. She was later refloated.[48] - El Paraguayo (
 United Kingdom): The cargo ship ran aground at Santos, São Paulo, Brazil.[41] She was refloated on 23 February.[49]
United Kingdom): The cargo ship ran aground at Santos, São Paulo, Brazil.[41] She was refloated on 23 February.[49] - Mahone (
 United Kingdom): The schooner was driven ashore at St. John's, Newfoundland.[48] She was refloated on 22 February.[49]
United Kingdom): The schooner was driven ashore at St. John's, Newfoundland.[48] She was refloated on 22 February.[49]
19 February
- John Blumer (
 Norway): The cargo ship caught fire at Rufisque, French West Africa and was beached.[45] She was a total loss.[50]
Norway): The cargo ship caught fire at Rufisque, French West Africa and was beached.[45] She was a total loss.[50]
21 February
- Alabama Maru (
 Japan): The cargo ship ran aground near Cape Inubō.[51] She broke in two on 7 March and was a total loss.[52]
Japan): The cargo ship ran aground near Cape Inubō.[51] She broke in two on 7 March and was a total loss.[52] - Kohshun Maru (
 Japan): The cargo ship ran aground at the Scotch Cap Lighthouse, Unimak Island, Alaska, United States.[53] She was a total loss.[51]
Japan): The cargo ship ran aground at the Scotch Cap Lighthouse, Unimak Island, Alaska, United States.[53] She was a total loss.[51] - Sembilan (
 Netherlands): The cargo ship collided with Halle (
Netherlands): The cargo ship collided with Halle (.svg.png) Germany) at Port Said, Egypt and was beached in the Suez Roads.[53] She was refloated on 23 February.[51]
Germany) at Port Said, Egypt and was beached in the Suez Roads.[53] She was refloated on 23 February.[51]
23 February
- Batitu (
 Argentina): The tug collided with Vauban (
Argentina): The tug collided with Vauban ( United Kingdom in the Point India Channel and sank. The crew were rescued by Vauban.[51]
United Kingdom in the Point India Channel and sank. The crew were rescued by Vauban.[51]
25 February
- Fofo (
 Greece): The cargo ship suffered an onboard explosion in the Mediterranean Sea and sank 40 nautical miles (74 km) north east of Oran, Algeria (36°10′N 0°02′W / 36.167°N 0.033°W). All 22 crew were rescued by HMS Nelson (
Greece): The cargo ship suffered an onboard explosion in the Mediterranean Sea and sank 40 nautical miles (74 km) north east of Oran, Algeria (36°10′N 0°02′W / 36.167°N 0.033°W). All 22 crew were rescued by HMS Nelson ( Royal Navy).[54][55]
Royal Navy).[54][55]
27 February
- HMCS Thiepval (
 Royal Canadian Navy): The Battle-class naval trawler struck an uncharted rock in Barkley Sound off the Broken Islands Group, British Columbia and was beached. She sank the next day. Her crew were rescued by HMCS Armentières (
Royal Canadian Navy): The Battle-class naval trawler struck an uncharted rock in Barkley Sound off the Broken Islands Group, British Columbia and was beached. She sank the next day. Her crew were rescued by HMCS Armentières ( Royal Canadian Navy).
Royal Canadian Navy).
28 February
March
2 March
- Kohlenimport (
.svg.png) Germany): The cargo ship collided with Gudur (
Germany): The cargo ship collided with Gudur ( Sweden) in the North Sea off Terschelling, Friesland, Netherlands and sank. The crew were rescued by Gudur.[57]
Sweden) in the North Sea off Terschelling, Friesland, Netherlands and sank. The crew were rescued by Gudur.[57]
3 March
- Cornwall (
 United Kingdom): The cargo ship ran aground on the south shore of Curaçao, Netherlands Antilles.[58] She was refloated on 17 March.[59]
United Kingdom): The cargo ship ran aground on the south shore of Curaçao, Netherlands Antilles.[58] She was refloated on 17 March.[59] - Ulf (
 Denmark): The cargo ship collided with Iceland (
Denmark): The cargo ship collided with Iceland ( United Kingdom) in the North Sea off Norderney, Lower Saxony, Germany and sank. Her crew were rescued by Iceland.[57]
United Kingdom) in the North Sea off Norderney, Lower Saxony, Germany and sank. Her crew were rescued by Iceland.[57]
4 March
- Fukuju Maru (
 Japan): The cargo ship was driven ashore at Shiriyasaki and was wrecked with the loss of all hands.[60]
Japan): The cargo ship was driven ashore at Shiriyasaki and was wrecked with the loss of all hands.[60]
5 March
- Capable (
 United Kingdom): The coaster was driven ashore at Atherfield Point, Isle of Wight. All six crew were rescued.[12] She was refloated on 13 March.[61]
United Kingdom): The coaster was driven ashore at Atherfield Point, Isle of Wight. All six crew were rescued.[12] She was refloated on 13 March.[61] - Mars (
 Latvia): The cargo ship ran aground at Ystad, Skåne County, Sweden.[12] She was refloated on 13 March and found to be severely damaged.[61]
Latvia): The cargo ship ran aground at Ystad, Skåne County, Sweden.[12] She was refloated on 13 March and found to be severely damaged.[61]
7 March
- Manfred (
 Sweden): The coaster ran aground at Steabjerg.[52] She was refloated on 18 March and found to be extensively damaged.[62]
Sweden): The coaster ran aground at Steabjerg.[52] She was refloated on 18 March and found to be extensively damaged.[62] - Tyne Maru (
 Japan): The cargo ship ran aground in the Kurushima Strait.[52] She was refloated on 26 March.[63]
Japan): The cargo ship ran aground in the Kurushima Strait.[52] She was refloated on 26 March.[63] - Urajio Maru (
 Japan): The cargo ship ran aground in the Ryukyu Islands.[52] She was refloated on 11 March.[64]
Japan): The cargo ship ran aground in the Ryukyu Islands.[52] She was refloated on 11 March.[64]
8 March
- Lavinia M. Snow (
 United States): The four-masted schooner was driven ashore at Cape Hatteras, North Carolina and was wrecked.[65]
United States): The four-masted schooner was driven ashore at Cape Hatteras, North Carolina and was wrecked.[65]
10 March
- General Plumer (
 United Kingdom): The schooner departed Barbados for Port aux Basques, Newfoundland. No further trace, presumed foundered in the Atlantic Ocean with the loss of all hands.[66]
United Kingdom): The schooner departed Barbados for Port aux Basques, Newfoundland. No further trace, presumed foundered in the Atlantic Ocean with the loss of all hands.[66] - Shimzu Maru (
 Japan): The cargo ship collided with Eurypylus (
Japan): The cargo ship collided with Eurypylus ( United Kingdom) in the Astraea Channel and was beached.[67]
United Kingdom) in the Astraea Channel and was beached.[67]
11 March
- Munaires (
 United States): The cargo ship was severely damaged at New Orleans, Louisiana when a dockside fire spread to the ship.[68] Having sank, she was refloated on 16 March.[59]
United States): The cargo ship was severely damaged at New Orleans, Louisiana when a dockside fire spread to the ship.[68] Having sank, she was refloated on 16 March.[59]
12 March
- Geneva Kathleen (
 United States): The schooner was driven ashore in the Cayman Islands and was wrecked.[68]
United States): The schooner was driven ashore in the Cayman Islands and was wrecked.[68]
14 March
15 March
- Ament (
 United Kingdom): The cargo ship ran aground in the North Sea off the Longsands Lightship (
United Kingdom): The cargo ship ran aground in the North Sea off the Longsands Lightship ( United Kingdom) and broke up. Her crew were rescued by Train Ferry No.2 (
United Kingdom) and broke up. Her crew were rescued by Train Ferry No.2 ( United Kingdom).[69]
United Kingdom).[69]
17 March
- Blijdendijk (
 Netherlands): The cargo ship caught fire at Suez, Egypt and was abandoned by her crew.[59]
Netherlands): The cargo ship caught fire at Suez, Egypt and was abandoned by her crew.[59]
20 March
- Nils (
 Norway): The cargo ship ran aground on Sable Island, Nova Scotia, Canada.[70] She was declared a total loss on 26 March.[63]
Norway): The cargo ship ran aground on Sable Island, Nova Scotia, Canada.[70] She was declared a total loss on 26 March.[63]
21 March
- Titoki (
 United Kingdom): The cargo ship ran aground at Motucka, South Island, New Zealand.[71] She was refloated on 28 March.[72]
United Kingdom): The cargo ship ran aground at Motucka, South Island, New Zealand.[71] She was refloated on 28 March.[72]
27 March
- Secundus (
.svg.png) Germany): The galiot sank off Falsterbo, Sweden. The crew were rescued.[73]
Germany): The galiot sank off Falsterbo, Sweden. The crew were rescued.[73] - Wheatplain (
 United Kingdom): The coaster ran aground on Tory Island, County Donegal, Ireland and was wrecked. Her crew were rescued.[73] She broke in three during a gale on 29 March.[74]
United Kingdom): The coaster ran aground on Tory Island, County Donegal, Ireland and was wrecked. Her crew were rescued.[73] She broke in three during a gale on 29 March.[74]
28 March
- Kirsten B (
 Norway): The cargo ship ran aground off Farsund, Vest-Agder.[72] She later broke in two, with the stern section sinking.[75]
Norway): The cargo ship ran aground off Farsund, Vest-Agder.[72] She later broke in two, with the stern section sinking.[75]
29 March
- Kosai Maru (
 Japan): The cargo ship ran aground at Kungtungtau, China and was abandoned in a sinking condition.[74]
Japan): The cargo ship ran aground at Kungtungtau, China and was abandoned in a sinking condition.[74] - HMS L1 (
 Royal Navy): The L-class submarine parted her tow and came ashore at Cape Cornwall, Cornwall.[74]
Royal Navy): The L-class submarine parted her tow and came ashore at Cape Cornwall, Cornwall.[74] - Rambler (
 United Kingdom): The auxiliary schooner was driven ashore in Glasserton Bay and was wrecked. Her crew survived.[74]
United Kingdom): The auxiliary schooner was driven ashore in Glasserton Bay and was wrecked. Her crew survived.[74] - Rhine Maru (
 Japan): The cargo ship was driven ashore at Point Sur, California, United States. Her crew were rescued.[74] She was declared a total loss on 16 April.[76]
Japan): The cargo ship was driven ashore at Point Sur, California, United States. Her crew were rescued.[74] She was declared a total loss on 16 April.[76]
30 March
- Königstein (
.svg.png) Germany): The cargo ship ran aground at Varberg, Halland County, Sweden.[77] She was refloated on 7 April.[78]
Germany): The cargo ship ran aground at Varberg, Halland County, Sweden.[77] She was refloated on 7 April.[78]
April
2 April
- Miguel de Cervantes (
.svg.png) Spanish Navy): The Almirante Cervera-class cruiser broke free from her moorings at Ferrol, Galicia. She collided with the quayside and sank. She was refloated the next day.[79] Later repaired and returned to service.
Spanish Navy): The Almirante Cervera-class cruiser broke free from her moorings at Ferrol, Galicia. She collided with the quayside and sank. She was refloated the next day.[79] Later repaired and returned to service. - Shespoikrabolov (
 Soviet Union): The cargo ship ran aground off Chōsi, Chiba, Japan. Salvage efforts were abandoned on 5 April.[80]
Soviet Union): The cargo ship ran aground off Chōsi, Chiba, Japan. Salvage efforts were abandoned on 5 April.[80]
3 April
- Persiano (
.svg.png) Italy): The cargo ship ran aground at Bokalikale, Turkey.[81] She was refloated on 6 April.[80]
Italy): The cargo ship ran aground at Bokalikale, Turkey.[81] She was refloated on 6 April.[80]
4 April
5 April
- Paradigm (
 Sweden): The cargo ship ran aground in the Lessoe Channel. The crew were rescued by Kattegat (
Sweden): The cargo ship ran aground in the Lessoe Channel. The crew were rescued by Kattegat ( Denmark).[80]
Denmark).[80]
6 April
- Cogandale (
 United Kingdom): The cargo ship sank at Eastern Gut, India. The crew were rescued.[80]
United Kingdom): The cargo ship sank at Eastern Gut, India. The crew were rescued.[80]
8 April
- Colbert (
 France): The cargo ship ran aground at Alexandria, Egypt.[83] She was refloated on 15 April.[84]
France): The cargo ship ran aground at Alexandria, Egypt.[83] She was refloated on 15 April.[84] - General (
 United States): The tug sank at Detour Township, Michigan and was declared a total loss.[85]
United States): The tug sank at Detour Township, Michigan and was declared a total loss.[85]
10 April
- Lila E. D. Young (
 United Kingdom): The schooner sprang a leak in the Atlantic Ocean off the coast of Portugal (40°00′N 9°40′W / 40.000°N 9.667°W). She was abandoned and set on fire. The crew were rescued by Freixall (flag unknown).[86]
United Kingdom): The schooner sprang a leak in the Atlantic Ocean off the coast of Portugal (40°00′N 9°40′W / 40.000°N 9.667°W). She was abandoned and set on fire. The crew were rescued by Freixall (flag unknown).[86] - St. Sunniva (
 United Kingdom): The ferry ran aground on Mousa, Shetland Islands and was wrecked. All on board were rescued.
United Kingdom): The ferry ran aground on Mousa, Shetland Islands and was wrecked. All on board were rescued.
11 April
- Benjamin C. Smith (
 United Kingdom): The schooner was abandoned in the Atlantic Ocean off the coast of Nova Scotia, Canada. The crew were rescued.[87]
United Kingdom): The schooner was abandoned in the Atlantic Ocean off the coast of Nova Scotia, Canada. The crew were rescued.[87] - City of Pekin (
 United Kingdom): The cargo ship struck a submerged rock and sank off Brookes Island, Port Hamilton, Korea. The crew were rescued.[86]
United Kingdom): The cargo ship struck a submerged rock and sank off Brookes Island, Port Hamilton, Korea. The crew were rescued.[86] - Mazeppa (
 United Kingdom): The Thames barge collided with Steingrim (
United Kingdom): The Thames barge collided with Steingrim ( Norway) in the North Sea off the Kentish Knock Lightship (
Norway) in the North Sea off the Kentish Knock Lightship ( United Kingdom). All five crew were rescued by the Walton-on-the-Naze Lifeboat.[87]
United Kingdom). All five crew were rescued by the Walton-on-the-Naze Lifeboat.[87]
15 April
- K. C. Gorden (
 United Kingdom): The schooner caught fire off St. John's, Newfoundland and was a total loss. The crew were rescued.[88]
United Kingdom): The schooner caught fire off St. John's, Newfoundland and was a total loss. The crew were rescued.[88] - Tiziano (
.svg.png) Italy): The cargo ship came ashore at Mazzara, Sicily.[84] She was refloated on 18 April.[89]
Italy): The cargo ship came ashore at Mazzara, Sicily.[84] She was refloated on 18 April.[89]
20 April
- Kamiyoshi Maru (
 Japan): The cargo ship ran aground and sank off Swatow, China.[90]
Japan): The cargo ship ran aground and sank off Swatow, China.[90] - Michalis Pontos (
 Greece): The cargo ship ran aground off Penarth Head, Glamorgan, United Kingdom.[89] She was refloated on 24 April.[91]
Greece): The cargo ship ran aground off Penarth Head, Glamorgan, United Kingdom.[89] She was refloated on 24 April.[91] - Nisshin Maru No.2 (
 Japan): The cargo ship ran aground on Okujiri Island and was a total loss. The crew were rescued.[92]
Japan): The cargo ship ran aground on Okujiri Island and was a total loss. The crew were rescued.[92]
22 April
- Vera E. Himmelman (
 United Kingdom): The schooner sprang a leak in the Atlantic Ocean off North Sydney, Nova Scotia, Canada and was abandoned.[92]
United Kingdom): The schooner sprang a leak in the Atlantic Ocean off North Sydney, Nova Scotia, Canada and was abandoned.[92]
23 April
- Famalicao Terceiro (
 Portugal): The schooner was discovered abandoned in the Atlantic Ocean (approximately 41°N 9°W / 41°N 9°W).[91]
Portugal): The schooner was discovered abandoned in the Atlantic Ocean (approximately 41°N 9°W / 41°N 9°W).[91] - Federico Garolla (
.svg.png) Italy): The cargo ship suffered an explosion of her boilers and sank in the Ionian Sea between Zakynthos and Kephalonia with the loss of twenty of her 23 crew.[93]
Italy): The cargo ship suffered an explosion of her boilers and sank in the Ionian Sea between Zakynthos and Kephalonia with the loss of twenty of her 23 crew.[93]
25 April
- Margit (
 Sweden): The auxiliary three-masted schooner ran aground near Lysekil, Västra Götaland County and sank.[94] She was raised on 7 May.[95]
Sweden): The auxiliary three-masted schooner ran aground near Lysekil, Västra Götaland County and sank.[94] She was raised on 7 May.[95]
26 April
- Kirkwood (
 United Kingdom): The collier was rammed and sunk in the North Sea off the Elbe No.1 Lightship (
United Kingdom): The collier was rammed and sunk in the North Sea off the Elbe No.1 Lightship (.svg.png) Germany) by President Harding (
Germany) by President Harding ( United States) with the loss of a crew member. The survivors were rescued by President Harding.[96][97]
United States) with the loss of a crew member. The survivors were rescued by President Harding.[96][97]
28 April
- Rosa (
 United Kingdom): The Admiralty fuelling craft ran aground at Flamborough Head, Yorkshire and was wrecked. All sixteen crew were rescued by the Flamborough Lifeboat.[98]
United Kingdom): The Admiralty fuelling craft ran aground at Flamborough Head, Yorkshire and was wrecked. All sixteen crew were rescued by the Flamborough Lifeboat.[98]
29 April
- Gairsoppa (
 United Kingdom): The cargo ship ran aground at Fulton Point, India. She was refloated later that day.
United Kingdom): The cargo ship ran aground at Fulton Point, India. She was refloated later that day.
30 April
- Luzon Maru (
 Japan): The cargo ship ran aground at Inuboye-saki.[99] She broke in two, sank, and was declared a total loss.[100]
Japan): The cargo ship ran aground at Inuboye-saki.[99] She broke in two, sank, and was declared a total loss.[100] - Westerner (
 United States): The cargo ship ran aground at Ak-bash-liman, Turkey.[90] She was refloated on 9 May.[101]
United States): The cargo ship ran aground at Ak-bash-liman, Turkey.[90] She was refloated on 9 May.[101]
May
2 May
- Jessie (
.svg.png) Italy): The cargo ship foundered in the Mediterranean Sea off Misrata, Libya.[102]
Italy): The cargo ship foundered in the Mediterranean Sea off Misrata, Libya.[102] - Raven (
 United Kingdom): The cargo ship collided with Cleopatra (
United Kingdom): The cargo ship collided with Cleopatra ( Greece) in the North Sea (53°52′N 6°50′E / 53.867°N 6.833°E) and sank. The crew were rescued by Cleopatra.[103]
Greece) in the North Sea (53°52′N 6°50′E / 53.867°N 6.833°E) and sank. The crew were rescued by Cleopatra.[103]
7 May
- Katiesau (
 Honduras): The auxiliary schooner collided with Copan (
Honduras): The auxiliary schooner collided with Copan ( Honduras) in the Caribbean Sea 5 nautical miles (9.3 km) east of Puerto Cortés and sank.[104]
Honduras) in the Caribbean Sea 5 nautical miles (9.3 km) east of Puerto Cortés and sank.[104]
8 May
- Richfield (
 United States): The tanker was driven ashore at Drake's Bay, California. The crew were rescued.[101]
United States): The tanker was driven ashore at Drake's Bay, California. The crew were rescued.[101]
12 May
- Prima (
 United Kingdom): The dredger capsized in the English Channel off the Owers Lightship (
United Kingdom): The dredger capsized in the English Channel off the Owers Lightship ( United Kingdom).[105]
United Kingdom).[105] - Zia (
 Turkey): The cargo ship caught fire in the Mediterranean Sea (approximately 37°N 26°E / 37°N 26°E) and was abandoned by her crew.[105][106]
Turkey): The cargo ship caught fire in the Mediterranean Sea (approximately 37°N 26°E / 37°N 26°E) and was abandoned by her crew.[105][106]
13 May
- Remenham (
 United Kingdom): The cargo ship struck a submerged object in the Baltic Sea (54°30′N 11°40′E / 54.500°N 11.667°E) and was holed. She was beached on the south coast of Falster, Denmark.[107] She was refloated the next day.[108]
United Kingdom): The cargo ship struck a submerged object in the Baltic Sea (54°30′N 11°40′E / 54.500°N 11.667°E) and was holed. She was beached on the south coast of Falster, Denmark.[107] She was refloated the next day.[108]
15 May
- Azua (
 United States): The schooner collided with City of Atlanta (
United States): The schooner collided with City of Atlanta ( United States in the Atlantic Ocean 47 nautical miles (87 km) south south east of the Barnegat Lighthouse, New Jersey.[109]
United States in the Atlantic Ocean 47 nautical miles (87 km) south south east of the Barnegat Lighthouse, New Jersey.[109] - Motau (
 United Kingdom): The auxiliary schooner foundered in the Pacific Ocean off Suva, fiji.[109]
United Kingdom): The auxiliary schooner foundered in the Pacific Ocean off Suva, fiji.[109] - Principe de Asturias (
.svg.png) Spain): The cargo ship foundered in the Atlantic Ocean off Fernando Pó, French West Africa during a cyclone. The crew survived.[109]
Spain): The cargo ship foundered in the Atlantic Ocean off Fernando Pó, French West Africa during a cyclone. The crew survived.[109]
17 May
- Icarahy (
 Brazil): The cargo ship collided with the breakwater at Rio Grande do Norte and sank with the loss of seven crew.[110]
Brazil): The cargo ship collided with the breakwater at Rio Grande do Norte and sank with the loss of seven crew.[110] - Isobel Moore (
 United Kingdom): The schooner ran aground in Danzig Cove, Newfoundland and was a total loss. The crew survived.[110]
United Kingdom): The schooner ran aground in Danzig Cove, Newfoundland and was a total loss. The crew survived.[110]
18 May
- Josina (
.svg.png) Spain): The cargo ship ran aground on Île d'Aix, Charente-Maritime, France, at the mouth of the Charente.[106] She was refloated on 23 May.[111]
Spain): The cargo ship ran aground on Île d'Aix, Charente-Maritime, France, at the mouth of the Charente.[106] She was refloated on 23 May.[111] - Yonan Maru (
 Japan): The cargo ship was severely damaged by fire at Singapore.[112]
Japan): The cargo ship was severely damaged by fire at Singapore.[112]
19 May
- Maria S. Kastanou (
 Greece): The cargo ship ran aground at Carrumeiro Vejo, Spain.[112] She was declared a total loss on 22 May.[113]
Greece): The cargo ship ran aground at Carrumeiro Vejo, Spain.[112] She was declared a total loss on 22 May.[113]
21 May
- Asia (
 France: The passenger ship caught fire at Jeddah, Nejd and Hejaz and was abandoned with the loss of about 100 lives.[113] She was declared a total loss.[114]
France: The passenger ship caught fire at Jeddah, Nejd and Hejaz and was abandoned with the loss of about 100 lives.[113] She was declared a total loss.[114] - Portgwarra (
 United Kingdom): The cargo ship came ashore at Castle Island, Bermuda. She was refloated on 26 May.[114]
United Kingdom): The cargo ship came ashore at Castle Island, Bermuda. She was refloated on 26 May.[114]
22 May
- Eleftheria (
 Greece): The cargo ship foundered in the Aegean Sea off Skiathos.[111]
Greece): The cargo ship foundered in the Aegean Sea off Skiathos.[111] - Maria Adelia (
 Portugal): The cargo ship was destroyed by fire at Melilla, Spain.[111]
Portugal): The cargo ship was destroyed by fire at Melilla, Spain.[111]
23 May
- Archiduc Rodolphe (
.svg.png) Belgium): The cargo ship ran aground on Lissa Island, Yugoslavia and was wrecked.[33]
Belgium): The cargo ship ran aground on Lissa Island, Yugoslavia and was wrecked.[33] - Normand (
 France): The cargo ship sank at Buncrana, County Donegal, Ireland.[115]
France): The cargo ship sank at Buncrana, County Donegal, Ireland.[115]
25 May
- City of Honolulu (
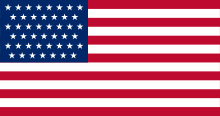 United States): The ocean liner caught fire, burned out and sank in Honolulu Harbour, Hawaii. She was raised on 9 June, patched up and sailed to Los Angeles, California, where she was declared a constructive total loss. City of Honolulu was scrapped at Osaka, Japan in December 1933.
United States): The ocean liner caught fire, burned out and sank in Honolulu Harbour, Hawaii. She was raised on 9 June, patched up and sailed to Los Angeles, California, where she was declared a constructive total loss. City of Honolulu was scrapped at Osaka, Japan in December 1933. - St. Croix (
 United Kingdom): The tug ran aground 6 nautical miles (11 km) north of Walvis Bay, South Africa and was wrecked. The crew were rescued.[115]
United Kingdom): The tug ran aground 6 nautical miles (11 km) north of Walvis Bay, South Africa and was wrecked. The crew were rescued.[115]
28 May
- Kruisschans (
.svg.png) Belgium): The cargo ship struck a submerged object and sank in the English Channel, 20 nautical miles (37 km) west of Beachy Head, East Sussex, United Kingdom. The crew were rescued by the trawler D.L.C. (
Belgium): The cargo ship struck a submerged object and sank in the English Channel, 20 nautical miles (37 km) west of Beachy Head, East Sussex, United Kingdom. The crew were rescued by the trawler D.L.C. ( United Kingdom).[116]
United Kingdom).[116] - Rimula (
 United Kingdom): The cargo ship ran aground on the south shore of Curaçao, Netherlands Antilles. Her crew were rescued.[117] She was refloated on 16 June.[118]
United Kingdom): The cargo ship ran aground on the south shore of Curaçao, Netherlands Antilles. Her crew were rescued.[117] She was refloated on 16 June.[118]
30 May
June
1 June
- Inger (
 Sweden): The cargo ship collided with Literno (
Sweden): The cargo ship collided with Literno (.svg.png) Italy) in the English Channel 7 nautical miles (13 km) south west of Beachy Head, East Sussex, United Kingdom and sank with the loss of fifteen of her eighteen crew. Survivors were rescued by Literno and the Eastbourne Lifeboat.[120][121]
Italy) in the English Channel 7 nautical miles (13 km) south west of Beachy Head, East Sussex, United Kingdom and sank with the loss of fifteen of her eighteen crew. Survivors were rescued by Literno and the Eastbourne Lifeboat.[120][121]
6 June
- Arpha (
 United Kingdom): The yacht ran aground in Moon Sound. She was refloated on 10 June.
United Kingdom): The yacht ran aground in Moon Sound. She was refloated on 10 June. - Chang Wo (
 United Kingdom): The cargo ship ran aground in Tungting Lake, China.[122] She was refloated on 10 June.[123]
United Kingdom): The cargo ship ran aground in Tungting Lake, China.[122] She was refloated on 10 June.[123]
8 June
- Buenos Aires Maru (
 Japan): The cargo ship collided with Kalinin (
Japan): The cargo ship collided with Kalinin ( Soviet Union at Montevideo, Uruguay and was beached.[124]
Soviet Union at Montevideo, Uruguay and was beached.[124] - Masula (
 United Kingdom): The cargo ship arrived at Gibraltar with her cargo on fire. She was beached the next day.[124] The fire was extinguished on 11 June,[125] and she was refloated on 23 June.[126]
United Kingdom): The cargo ship arrived at Gibraltar with her cargo on fire. She was beached the next day.[124] The fire was extinguished on 11 June,[125] and she was refloated on 23 June.[126]
10 June
- Pinthis (
 United States): The tanker was rammed by the passenger ship Fairfax (
United States): The tanker was rammed by the passenger ship Fairfax ( United States) in the Atlantic Ocean off Scituate, Massachusetts. She was set on fire and subsequently sank with the loss of all twenty crew. Twenty-seven people on board Fairfax were killed.[127]
United States) in the Atlantic Ocean off Scituate, Massachusetts. She was set on fire and subsequently sank with the loss of all twenty crew. Twenty-seven people on board Fairfax were killed.[127]
11 June
- Dorothy M. Smart (
 United Kingdom): The schooner foundered in the Atlantic Ocean off Cape Breton, Nova Scotia, Canada.[125]
United Kingdom): The schooner foundered in the Atlantic Ocean off Cape Breton, Nova Scotia, Canada.[125]
13 June
- Miss England II (
 United Kingdom): The speedboat struck a floating tree branch in Lake Windermere during a world speed record attempt. She capsized and sank, killing Sir Henry Segrave and injuring the other two crew.
United Kingdom): The speedboat struck a floating tree branch in Lake Windermere during a world speed record attempt. She capsized and sank, killing Sir Henry Segrave and injuring the other two crew. - Muroran Maru (
 Japan): The cargo ship came ashore on the Kamchatka Peninsula, Soviet Union and was abandoned by her crew.[118]
Japan): The cargo ship came ashore on the Kamchatka Peninsula, Soviet Union and was abandoned by her crew.[118]
16 June
- Thirlby (
 United Kingdom): The cargo ship ran aground on a reef 7 nautical miles (13 km) west of Puerto Padre, Cuba.[118] She was refloated on 23 June.[126]
United Kingdom): The cargo ship ran aground on a reef 7 nautical miles (13 km) west of Puerto Padre, Cuba.[118] She was refloated on 23 June.[126]
17 June
- Dimitrios M. Diacakis (
 Greece): The cargo ship ran aground at Akbashliman, Turkey.[128] She was refloated on 24 June.[129]
Greece): The cargo ship ran aground at Akbashliman, Turkey.[128] She was refloated on 24 June.[129] - N.A.F. (
 United Kingdom): The schooner was wrecked in Bay St. George, Newfoundland. Her crew were rescued.[130]
United Kingdom): The schooner was wrecked in Bay St. George, Newfoundland. Her crew were rescued.[130]
18 June
- Aberdonian (
 United Kingdom): The passenger ship ran aground at Staithes, Yorkshire. Her 55 passengers were taken off by a tug.[128] She was refloated on 22 June.[131]
United Kingdom): The passenger ship ran aground at Staithes, Yorkshire. Her 55 passengers were taken off by a tug.[128] She was refloated on 22 June.[131]
19 June
- Baltic (
 United Kingdom): The four-masted schooner struck rocks in Penrhos Bay and capsized. All five people on board survived.[132]
United Kingdom): The four-masted schooner struck rocks in Penrhos Bay and capsized. All five people on board survived.[132]
21 June
- Keishin Maru (
 Japan): The cargo ship ran aground at Keelung, China.[131] She was refloated on 25 June.[133]
Japan): The cargo ship ran aground at Keelung, China.[131] She was refloated on 25 June.[133] - Towy (
 United Kingdom): The coaster ran aground at Portstewart, County Londonderry.[131] She was refloated on 26 June and taken under tow with the intention of reaching Portrush but she capsized and sank. All crew were rescued.[134]
United Kingdom): The coaster ran aground at Portstewart, County Londonderry.[131] She was refloated on 26 June and taken under tow with the intention of reaching Portrush but she capsized and sank. All crew were rescued.[134]
23 June
- Casablanca (
.svg.png) Germany): The cargo ship was in collision with Henry Stanley (
Germany): The cargo ship was in collision with Henry Stanley ( United Kingdom) in the English Channel (49°36′N 3°00′W / 49.600°N 3.000°W) and sank. All 27 people on board were rescued by Henry Stanley.[131]
United Kingdom) in the English Channel (49°36′N 3°00′W / 49.600°N 3.000°W) and sank. All 27 people on board were rescued by Henry Stanley.[131]
24 June
- Daian Maru (
 Japan): The cargo ship ran aground at Cape Patience, Sakhalin, Soviet Union. Salvage efforts were abandoned on 28 June and she was declared a total loss.[135][136]
Japan): The cargo ship ran aground at Cape Patience, Sakhalin, Soviet Union. Salvage efforts were abandoned on 28 June and she was declared a total loss.[135][136]
25 June
- Mary G. Maynard (
 United States): The schooner was abandoned in the Atlantic Ocean. Her crew were rescued by Evina (
United States): The schooner was abandoned in the Atlantic Ocean. Her crew were rescued by Evina ( Norway). She was later reported derelict at 38°33′N 59°25′W / 38.550°N 59.417°W by Maindy Grange (
Norway). She was later reported derelict at 38°33′N 59°25′W / 38.550°N 59.417°W by Maindy Grange ( United Kingdom).[134]
United Kingdom).[134]
26 June
- Niigata Maru (
 Japan): The cargo ship ran aground in the Oki Islands.[137] She was refloated on 4 July.[138]
Japan): The cargo ship ran aground in the Oki Islands.[137] She was refloated on 4 July.[138]
30 June
July
1 July
- Koyo Maru (
 Japan): The cargo ship came ashore on Sakhalin, Soviet Union.[140] She was refloated on 6 July.[141]
Japan): The cargo ship came ashore on Sakhalin, Soviet Union.[140] She was refloated on 6 July.[141] - Kurdistan (
 United Kingdom): The cargo ship came ashore in the Molyneux Sound.[142] She was refloated on 6 July.[141]
United Kingdom): The cargo ship came ashore in the Molyneux Sound.[142] She was refloated on 6 July.[141]
4 July
- Knight of the Realm (
 United Kingdom): The cargo ship ran aground in the Paraná River 10 nautical miles (19 km) upstream of Rosario, Santa Fe, Argentina.[143] She was refloated on 11 July.[144]
United Kingdom): The cargo ship ran aground in the Paraná River 10 nautical miles (19 km) upstream of Rosario, Santa Fe, Argentina.[143] She was refloated on 11 July.[144]
6 July
- Karagjorgje (
 Yugoslavia): The passenger ship collised with Francesco Morosini (
Yugoslavia): The passenger ship collised with Francesco Morosini (.svg.png) Italy) off Pašman with the loss of four lives. She was beached and all passengers were taken off by Francesco Morosini.[141][145]
Italy) off Pašman with the loss of four lives. She was beached and all passengers were taken off by Francesco Morosini.[141][145]
7 July
- Dampto (
 Norway): The cargo ship collied with Hoten Maru (
Norway): The cargo ship collied with Hoten Maru ( Japan) off the Shangtung Promontory, China and sank. Her crew were rescued.[146]
Japan) off the Shangtung Promontory, China and sank. Her crew were rescued.[146]
8 July
- Greypoint (
 Nicaragua): The cargo ship caught fire at Twelve Mile Island, Alabama, United States.[147] She was a constructive total loss.[133]
Nicaragua): The cargo ship caught fire at Twelve Mile Island, Alabama, United States.[147] She was a constructive total loss.[133] - Iwai Maru (
 Japan): The cargo ship ran aground off Notorosaki.[148] She was refloated on 12 July.[133]
Japan): The cargo ship ran aground off Notorosaki.[148] She was refloated on 12 July.[133] - Mac Hinery (
 United Kingdom): The cargo ship foundered in the Atlantic Ocean off Cape Smokey, Nova Scotia, Canada.[147]
United Kingdom): The cargo ship foundered in the Atlantic Ocean off Cape Smokey, Nova Scotia, Canada.[147]
10 July
- Dolores (
.svg.png) Spain): The auxiliary schooner foundered in the Mediterranean Sea off Portsay. Her crew survived.[149]
Spain): The auxiliary schooner foundered in the Mediterranean Sea off Portsay. Her crew survived.[149] - Yorkton (
 United Kingdom): The cargo ship collided with Mantadoc (
United Kingdom): The cargo ship collided with Mantadoc ( United Kingdom in Whitefish Bay and sank.[144] She was refloated on 9 August.[150]
United Kingdom in Whitefish Bay and sank.[144] She was refloated on 9 August.[150]
11 July
- Evangeline (
 United States): The cargo ship suffered an onboard explosion at Rockaway Point, New York. She was beached in the Rockaway Inlet and was destroyed by the subsequent fire.[149]
United States): The cargo ship suffered an onboard explosion at Rockaway Point, New York. She was beached in the Rockaway Inlet and was destroyed by the subsequent fire.[149] - Lauretta Frances (
 United Kingdom): The schooner sprang a leak and foundered in the Atlantic Ocean 15 nautical miles (28 km) off Cape Anguille, Newfoundland. The crew survived.[144]
United Kingdom): The schooner sprang a leak and foundered in the Atlantic Ocean 15 nautical miles (28 km) off Cape Anguille, Newfoundland. The crew survived.[144]
12 July
- Ascot (
 United Kingdom): The cargo ship ran aground in the Paraná River at Borghi, Argentina.[144] She was refloated on 15 July.[133]
United Kingdom): The cargo ship ran aground in the Paraná River at Borghi, Argentina.[144] She was refloated on 15 July.[133] - Turuna (
 Portugal): The three-masted schooner was abandoned in the Atlantic Ocean (44°30′N 60°55′W / 44.500°N 60.917°W). She was set on fire by her crew, who were rescued by Coiborno (flag unknown).[144]
Portugal): The three-masted schooner was abandoned in the Atlantic Ocean (44°30′N 60°55′W / 44.500°N 60.917°W). She was set on fire by her crew, who were rescued by Coiborno (flag unknown).[144]
14 July
- Fawn (
 United Kingdom): The coaster struck a rock off Portnahaven, Islay and was beached.[151] She was refloated on 18 July.[152]
United Kingdom): The coaster struck a rock off Portnahaven, Islay and was beached.[151] She was refloated on 18 July.[152] - Kohatsu Maru (
 Japan): The cargo ship collided with Aeneas (
Japan): The cargo ship collided with Aeneas ( United Kingdom in the East China Sea off Cape Shantung, China and sank.[151]
United Kingdom in the East China Sea off Cape Shantung, China and sank.[151] - Pengreep (
 United Kingdom): The cargo ship ran aground in the Paraná River 25 nautical miles (46 km) downstream of Rosario, Argentina.[151] She was refloated on 18 July.[153]
United Kingdom): The cargo ship ran aground in the Paraná River 25 nautical miles (46 km) downstream of Rosario, Argentina.[151] She was refloated on 18 July.[153]
19 July
- Aikoku Maru (
 Japan): The cargo ship sank at Nagasaki during a typhoon.[153]
Japan): The cargo ship sank at Nagasaki during a typhoon.[153] - Kalypso Vergotti (
 Greece): The cargo ship ran aground on the English Bank off Uruguay.[153] She was refloated on 1 August.[154]
Greece): The cargo ship ran aground on the English Bank off Uruguay.[153] She was refloated on 1 August.[154] - Ryohi Maru (
 Japan): The cargo ship sank at Nagasaki during a typhoon.[153]
Japan): The cargo ship sank at Nagasaki during a typhoon.[153] - Targis (
.svg.png) Germany): The cargo liner caught fire in the Atlantic Ocean and foundered (33°45′N 50°45′W / 33.750°N 50.750°W). All on board were rescued by Rangitata (
Germany): The cargo liner caught fire in the Atlantic Ocean and foundered (33°45′N 50°45′W / 33.750°N 50.750°W). All on board were rescued by Rangitata ( United Kingdom.[153][155]
United Kingdom.[153][155]
21 July
- Adele Traber (
.svg.png) Germany): The cargo ship ran aground near the Pevna Lighthouse, Oulu, Finland.[156] She was refloated on 24 July.[157]
Germany): The cargo ship ran aground near the Pevna Lighthouse, Oulu, Finland.[156] She was refloated on 24 July.[157] - North Pacific (
 United Kingdom): The cargo ship ran aground in the Paraná River at Arroyo Seco, Santa Fe, Argentina.[156] She was refloated on 25 July.[157]
United Kingdom): The cargo ship ran aground in the Paraná River at Arroyo Seco, Santa Fe, Argentina.[156] She was refloated on 25 July.[157]
22 July
- Saint Hilda (
 United States): The dredger struck a submerged object and foundered at Tampico, Tamaulipas, Mexico, with the loss of two crew.[158]
United States): The dredger struck a submerged object and foundered at Tampico, Tamaulipas, Mexico, with the loss of two crew.[158]
23 July
- Dustu (
 France): The schooner struck a rock in the Bay of Biscay 5 nautical miles (9.3 km) off Lochtudy, Finistère and foundered.[159]
France): The schooner struck a rock in the Bay of Biscay 5 nautical miles (9.3 km) off Lochtudy, Finistère and foundered.[159] - Raymond (
.svg.png) Belgium): The coaster ran aground at Warkworth, Northumberland, United Kingdom.[159] She was refloated on 29 July.[160]
Belgium): The coaster ran aground at Warkworth, Northumberland, United Kingdom.[159] She was refloated on 29 July.[160]
28 July
- Kronprins Gustav Adolf (
 Sweden): The cargo ship caught fire in the Atlantic Ocean 82 nautical miles (152 km) off Vitória, Brazil. She was consequently abandoned 14 nautical miles (26 km) south east of the Rio Doce Lighthouse.[161] The crew were rescued by Alphacea (
Sweden): The cargo ship caught fire in the Atlantic Ocean 82 nautical miles (152 km) off Vitória, Brazil. She was consequently abandoned 14 nautical miles (26 km) south east of the Rio Doce Lighthouse.[161] The crew were rescued by Alphacea ( Netherlands) and Vandyck (
Netherlands) and Vandyck ( United Kingdom). She drifted ashore 60 nautical miles (110 km) north of Vitória and was a total loss.[160][162]
United Kingdom). She drifted ashore 60 nautical miles (110 km) north of Vitória and was a total loss.[160][162]
29 July
- George J. Whalen (
 United States): The dredger foundered in Lake Erie off Dunkirk, New York. There was heavy loss of life.[162]
United States): The dredger foundered in Lake Erie off Dunkirk, New York. There was heavy loss of life.[162]
30 July
- Biyo Maru (
 Japan): The cargo ship ran aground off the Shiriyazaki Lighthouse, Honshu.[163] She was refloated on 24 August.[164]
Japan): The cargo ship ran aground off the Shiriyazaki Lighthouse, Honshu.[163] She was refloated on 24 August.[164] - Heijun Maru (
 Japan): The cargo ship ran aground off the Shiriyazaki Lighthouse.[163] She was refloated on 19 August.[165]
Japan): The cargo ship ran aground off the Shiriyazaki Lighthouse.[163] She was refloated on 19 August.[165]
31 July
- Nerbudda (
 United Kingdom): The cargo ship collided with Legazpi (
United Kingdom): The cargo ship collided with Legazpi (.svg.png) Spain) in the Atlantic Ocean (36°22′N 3°24′W / 36.367°N 3.400°W) and was holed.[166] She was taken in tow by Nankin (
Spain) in the Atlantic Ocean (36°22′N 3°24′W / 36.367°N 3.400°W) and was holed.[166] She was taken in tow by Nankin ( United Kingdom) and beached at Castle Ferro, Spain.[154][167] Nerbudda was refloated on 4 August and towed to Gibraltar.[168]
United Kingdom) and beached at Castle Ferro, Spain.[154][167] Nerbudda was refloated on 4 August and towed to Gibraltar.[168]
August
1 August
- Eastborough (
 United Kingdom): The cargo ship ran aground in the Paraná River, Argentina.[169] She was refloated on 7 August.[170]
United Kingdom): The cargo ship ran aground in the Paraná River, Argentina.[169] She was refloated on 7 August.[170] - Feltore (
 United States): The cargo ship ran aground at Cruz Grande, Mexico and was abandoned.[154][169]
United States): The cargo ship ran aground at Cruz Grande, Mexico and was abandoned.[154][169]
2 August
- Thyland (
.svg.png) Germany): The cargo ship collided with Hedwigshütte (
Germany): The cargo ship collided with Hedwigshütte (.svg.png) Germany) in the Kaiser Wilhelm Canal and was beached.[169]
Germany) in the Kaiser Wilhelm Canal and was beached.[169]
7 August
- August Thyssen (
.svg.png) Germany): The cargo ship came ashore at Alligator Pond, Jamaica.[170] She was refloated on 10 August.[150]
Germany): The cargo ship came ashore at Alligator Pond, Jamaica.[170] She was refloated on 10 August.[150] - Svea (
 Estonia): The sailing ship collided with Jupiter (
Estonia): The sailing ship collided with Jupiter ( Estonia) at Stockholm, Sweden and sank with the loss of a crew member.[171]
Estonia) at Stockholm, Sweden and sank with the loss of a crew member.[171] - Tregenna (
 United Kingdom): The cargo ship ran aground at San Pedro de Macorís, Dominican Republic.[171] She was refloated on 15 August.[172]
United Kingdom): The cargo ship ran aground at San Pedro de Macorís, Dominican Republic.[171] She was refloated on 15 August.[172]
8 August
- Avgy (
 Greece): The cargo ship caught fire in the Atlantic Ocean and put into Leixões, Portugal and was beached.[173][174] She was refloated on 29 August.[175]
Greece): The cargo ship caught fire in the Atlantic Ocean and put into Leixões, Portugal and was beached.[173][174] She was refloated on 29 August.[175] - Hochelaga (
 United Kingdom): The cargo ship was beached on one of the Magdalen Islands, Quebec, Canada having previously ran aground in the Bird Islands, Northwest Territories.[173] Following storm damage on August 18, she was a total loss.[176]
United Kingdom): The cargo ship was beached on one of the Magdalen Islands, Quebec, Canada having previously ran aground in the Bird Islands, Northwest Territories.[173] Following storm damage on August 18, she was a total loss.[176]
9 August
- Sir Stafford Northcote (
 United Kingdom: The cargo ship collided with City of London (
United Kingdom: The cargo ship collided with City of London ( United Kingdom) in the River Thames and sank.[177]
United Kingdom) in the River Thames and sank.[177]
10 August
- Caribou (
 United Kingdom): The passenger ship ran aground on Muse Island, Newfoundland. All passengers and crew took to the lifeboats.[174] She was a total loss.[150]
United Kingdom): The passenger ship ran aground on Muse Island, Newfoundland. All passengers and crew took to the lifeboats.[174] She was a total loss.[150]
12 August
- Baltic (
 Danzig): The tanker ran aground at Punta Indio, Argentina.[178] She was refloated on 16 August.[179]
Danzig): The tanker ran aground at Punta Indio, Argentina.[178] She was refloated on 16 August.[179] - Dalila (
 France): The cargo ship ran aground in the Charente at Tonnay-Charente, Charente-Maritime.[178]
France): The cargo ship ran aground in the Charente at Tonnay-Charente, Charente-Maritime.[178] - Halley's Comet (
 United Kingdom): The schooner foundered off Bell Island, Newfoundland.[180]
United Kingdom): The schooner foundered off Bell Island, Newfoundland.[180] - Taitsu Maru (
 Japan): The cargo ship ran aground at Urusan, Korea.[172] She was still aground on 22 October.[181]
Japan): The cargo ship ran aground at Urusan, Korea.[172] She was still aground on 22 October.[181]
13 August
- Ryuho Maru No.1 (
 Japan): The cargo ship ran aground at Lopatka, Soviet Union.[180] She was refloated on 29 August.[175]
Japan): The cargo ship ran aground at Lopatka, Soviet Union.[180] She was refloated on 29 August.[175]
16 August
- RMS Tahiti (
 United Kingdom): The ocean liner suffered a fractured starboard propeller shaft in the Pacific Ocean (460 nautical miles (850 km) off Rarotonga, Cook Islands. Her hull was holed and she was abandoned on 18 August. All 128 passengers and 148 crew were rescued by Ventura (
United Kingdom): The ocean liner suffered a fractured starboard propeller shaft in the Pacific Ocean (460 nautical miles (850 km) off Rarotonga, Cook Islands. Her hull was holed and she was abandoned on 18 August. All 128 passengers and 148 crew were rescued by Ventura ( United States).[179][182]
United States).[179][182]
17 August
- Angele (
 France): The sailing ship departed Cardiff, Glamorgan, United Kingdom for Pont-l'Abbé, Finistère. No further trace, presumed foundered with the loss of all hands.[183]
France): The sailing ship departed Cardiff, Glamorgan, United Kingdom for Pont-l'Abbé, Finistère. No further trace, presumed foundered with the loss of all hands.[183]
18 August
- Brilliant (
 United States): The coastal tanker suffered an onboard explosion and fire at Jacksonville, Florida and was a constructive total loss. Five crew were killed.[165][184]
United States): The coastal tanker suffered an onboard explosion and fire at Jacksonville, Florida and was a constructive total loss. Five crew were killed.[165][184]
21 August
- Ba (
 Norway): The cargo ship struck rocks at Guardiana, Portugal and sank. Her crew were rescued.[185]
Norway): The cargo ship struck rocks at Guardiana, Portugal and sank. Her crew were rescued.[185] - Izaro (
.svg.png) Spain): The cargo ship struck a rock and sank in the Mediterranean Sea off Cape Palos, Murcia.[186]
Spain): The cargo ship struck a rock and sank in the Mediterranean Sea off Cape Palos, Murcia.[186] - Tami Maru (
 Japan): The cargo ship ran aground on the Shiretoko Peninsula.[186] She was refloated on 31 August.[187]
Japan): The cargo ship ran aground on the Shiretoko Peninsula.[186] She was refloated on 31 August.[187]
23 August
- Guine (
 Portugal): The cargo ship was wrecked at Bissau, Portuguese Guinea.[188]
Portugal): The cargo ship was wrecked at Bissau, Portuguese Guinea.[188]
26 August
- Daring (
 United Kingdom): The tug caught fire and sank in the Pacific Ocean off Vancouver Island, Canada with the loss of six crew.[189]
United Kingdom): The tug caught fire and sank in the Pacific Ocean off Vancouver Island, Canada with the loss of six crew.[189]
27 August
- Argentum (
 United Kingdom): The cargo ship ran aground at Nairn.[189] She was refloated on 23 September.[190]
United Kingdom): The cargo ship ran aground at Nairn.[189] She was refloated on 23 September.[190] - Spica (
 Norway): The cargo ship ran aground on the Cerebus Shoal in the Strait of Canso.[191] She was declared a total loss on 10 September.[192]
Norway): The cargo ship ran aground on the Cerebus Shoal in the Strait of Canso.[191] She was declared a total loss on 10 September.[192]
28 August
- Neches (
 United States): The cargo ship collided with a scow off the Coney Island Lighthouse, New York Harbor and sank, as did the scow.[191]
United States): The cargo ship collided with a scow off the Coney Island Lighthouse, New York Harbor and sank, as did the scow.[191] - Starck (
 Sweden): The cargo ship ran aground at Ulkogrunni, Finland and was beached.[191] She was refloated on 4 September.[193]
Sweden): The cargo ship ran aground at Ulkogrunni, Finland and was beached.[191] She was refloated on 4 September.[193]
31 August
- Claretta (
 United Kingdom): The coaster collided with Borderland (
United Kingdom): The coaster collided with Borderland ( United Kingdom) in the Atlantic Ocean 11 nautical miles (20 km) of the Longships Lighthouse and sank. Her crew were rescued by Borderland.[194]
United Kingdom) in the Atlantic Ocean 11 nautical miles (20 km) of the Longships Lighthouse and sank. Her crew were rescued by Borderland.[194] - Maroussio (
 Greece): The cargo ship ran aground at Injeh Burno, Turkey.[195]
Greece): The cargo ship ran aground at Injeh Burno, Turkey.[195] - Shoreham (
 United Kingdom): The coaster was in collision with Annik (
United Kingdom): The coaster was in collision with Annik ( France) in the Atlantic Ocean 5 nautical miles (9.3 km) off Trevose Head, Cornwall and sank. Her crew were rescued by Annik.[194]
France) in the Atlantic Ocean 5 nautical miles (9.3 km) off Trevose Head, Cornwall and sank. Her crew were rescued by Annik.[194]
September
2 September
- St. Christophe (
 United Kingdom): The cargo ship was wrecked at Los Roques, Venezuela. The crew were rescued.[196] She was a total loss.[197]
United Kingdom): The cargo ship was wrecked at Los Roques, Venezuela. The crew were rescued.[196] She was a total loss.[197]
3 September
- Assimacos (
 Greece): The cargo ship ran aground at Cape Silleiro, Spain.[198] She was declared a total loss on 16 September.[199]
Greece): The cargo ship ran aground at Cape Silleiro, Spain.[198] She was declared a total loss on 16 September.[199] - Corsair (
 United States Coast and Geodetic Survey): The steam yacht ran aground on the Lobster Rocks, Islesboro, Maine.[198]
United States Coast and Geodetic Survey): The steam yacht ran aground on the Lobster Rocks, Islesboro, Maine.[198] - Liny and Mimi (both
.svg.png) Germany): The schooners were in collision with Hero (
Germany): The schooners were in collision with Hero ( United Kingdom) in the Weser and were beached.[193]
United Kingdom) in the Weser and were beached.[193]
8 September
- Innisinver (
 United Kingdom): The cargo ship struck submerged wreckage in the English Channel 5.5 nautical miles (10.2 km) south of Portland Bill, Dorset and sank. All crew survived.[200]
United Kingdom): The cargo ship struck submerged wreckage in the English Channel 5.5 nautical miles (10.2 km) south of Portland Bill, Dorset and sank. All crew survived.[200] - Maria M (
 Greece): The cargo ship was severely damaged by fire at Drapetsona when benzine leaked from the tanker Donax (
Greece): The cargo ship was severely damaged by fire at Drapetsona when benzine leaked from the tanker Donax ( United Kingdom) and caught fire. Seven other sailing vessels were destroyed by fire, and many others were damaged.[200]
United Kingdom) and caught fire. Seven other sailing vessels were destroyed by fire, and many others were damaged.[200] - Mary Patricia (
 United Kingdom): The cargo ship was abandoned in the Atlantic Ocean off Cape Breton Island, Nova Scotia, Canada.[201]
United Kingdom): The cargo ship was abandoned in the Atlantic Ocean off Cape Breton Island, Nova Scotia, Canada.[201]
9 September
10 September
- Malmesbury (
 United Kingdom): The cargo ship ran aground on the Jacob Reef, off the coast of South Africa and was abandoned. The crew were rescued.[192] She broke in tow on 16 September and was a total loss.[202]
United Kingdom): The cargo ship ran aground on the Jacob Reef, off the coast of South Africa and was abandoned. The crew were rescued.[192] She broke in tow on 16 September and was a total loss.[202]
11 September
- Edera (
.svg.png) Italy): The cargo ship ran aground in the North Sea on Bollen Hinder Bank of the coast of the Netherlands.[203] She was refloated on 16 October.[204]
Italy): The cargo ship ran aground in the North Sea on Bollen Hinder Bank of the coast of the Netherlands.[203] She was refloated on 16 October.[204]
13 September

Second Narrows Bridge
- Lorne and Pacific Gatherer (both
 United Kingdom): The tug and barge collided with the Second Narrows Bridge, Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada and jammed under it. The rising tide eventually caused the collapse of the bridge,[205] which took four years to repair.
United Kingdom): The tug and barge collided with the Second Narrows Bridge, Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada and jammed under it. The rising tide eventually caused the collapse of the bridge,[205] which took four years to repair. - Nine (
 United Kingdom): The cargo ship ran aground on the Sealark Reef, Guadalcanal, Solomon Islands and was a total loss. The crew were rescued.[183]
United Kingdom): The cargo ship ran aground on the Sealark Reef, Guadalcanal, Solomon Islands and was a total loss. The crew were rescued.[183]
18 September
- Alma (
.svg.png) Germany): The schooner came ashore at Luleå, Sweden and was wrecked. Her crew were rescued.[206]
Germany): The schooner came ashore at Luleå, Sweden and was wrecked. Her crew were rescued.[206] - Goteborg (
 Sweden): The coaster ran aground north of Lysekil, Västra Götaland County and sank. All passengers and crew were rescued.[206]
Sweden): The coaster ran aground north of Lysekil, Västra Götaland County and sank. All passengers and crew were rescued.[206]
19 September
- Kwalju Maru (
 Japan): The cargo ship ran aground in the Yangtze downstream of Antung, China. She broke in two and was a total loss.[183]
Japan): The cargo ship ran aground in the Yangtze downstream of Antung, China. She broke in two and was a total loss.[183] - Llandilo (
 United Kingdom): The cargo ship ran aground on the Rabbit Islands, Turkey.[183] She was refloated on 29 September but again ran aground.[207] She was refloated again on 1 October.[208]
United Kingdom): The cargo ship ran aground on the Rabbit Islands, Turkey.[183] She was refloated on 29 September but again ran aground.[207] She was refloated again on 1 October.[208] - Tigris (
.svg.png) Belgium): The cargo ship passed Dungeness, Kent, United Kingdom, bound for Alexandria, Egypt. No further trace, presumed foundered with the loss of all hands.[209]
Belgium): The cargo ship passed Dungeness, Kent, United Kingdom, bound for Alexandria, Egypt. No further trace, presumed foundered with the loss of all hands.[209] - Tréport (
 United Kingdom): The cargo ship ran aground on the Girdler Sands, in the North Sea off the Essex coast. The crew were rescued by Queen of Thanet (
United Kingdom): The cargo ship ran aground on the Girdler Sands, in the North Sea off the Essex coast. The crew were rescued by Queen of Thanet ( United Kingdom and the Margate Lifeboat. She was a total loss.[183]
United Kingdom and the Margate Lifeboat. She was a total loss.[183]
20 September
- Madeleine Tristan (
 France): The three-masted schooner was driven ashore at Chesil Beach, Dorset, United Kingdom and was wrecked. All seven crew were rescued.[210]
France): The three-masted schooner was driven ashore at Chesil Beach, Dorset, United Kingdom and was wrecked. All seven crew were rescued.[210] - Theodoros Bulgaris (
 Greece): The cargo ship lost her steering gear in a storm in the Atlantic Ocean (46°48′N 6°43′W / 46.800°N 6.717°W). She was abandoned at 47°15′N 6°20′W / 47.250°N 6.333°W, the crew were rescued by Advocate (
Greece): The cargo ship lost her steering gear in a storm in the Atlantic Ocean (46°48′N 6°43′W / 46.800°N 6.717°W). She was abandoned at 47°15′N 6°20′W / 47.250°N 6.333°W, the crew were rescued by Advocate ( United Kingdom).[210] Theodoris Bulgaris was towed into Brest, Finistère, France on 23 September by Livadia (
United Kingdom).[210] Theodoris Bulgaris was towed into Brest, Finistère, France on 23 September by Livadia (.svg.png) Germany).[190]
Germany).[190]
21 September
- Foxhon (
 Netherlands): The coaster foundered in the Thames Estuary with the loss of three of the five people on board. Survivors were rescued by the trawler Notre Dame des Ardents (
Netherlands): The coaster foundered in the Thames Estuary with the loss of three of the five people on board. Survivors were rescued by the trawler Notre Dame des Ardents ( France).[211]
France).[211]
22 September
- Ida (
.svg.png) Belgium): The coaster ran aground at Prawle Point, Devon, United Kingdom in dense fog. All twelve crew were rescued.[190] She broke in two on 9 October,[212] and had broken up by November.[213]
Belgium): The coaster ran aground at Prawle Point, Devon, United Kingdom in dense fog. All twelve crew were rescued.[190] She broke in two on 9 October,[212] and had broken up by November.[213]
23 September
- City of Osaka (
 United Kingdom): The cargo ship ran aground 6 nautical miles (11 km) south of Buchanness, Aberdeenshire. The crew were rescued by HMS Walker (
United Kingdom): The cargo ship ran aground 6 nautical miles (11 km) south of Buchanness, Aberdeenshire. The crew were rescued by HMS Walker ( Royal Navy) or breeches buoy.[190]
Royal Navy) or breeches buoy.[190] - Deerhound (
.svg.png) Belgium): The cargo ship ran aground in the River Humber, United Kingdom. She was refloated and was then hit by Lakewood (
Belgium): The cargo ship ran aground in the River Humber, United Kingdom. She was refloated and was then hit by Lakewood ( United Kingdom) and sank.[33][190]
United Kingdom) and sank.[33][190] - Matsqui (
 United Kingdom): The cargo ship caught fire off Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada and was beached.[214]
United Kingdom): The cargo ship caught fire off Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada and was beached.[214]
24 September
- Kasugayama Maru (
 Japan): The cargo ship ran aground on Sakhalin, Soviet Union and was wrecked.[215]
Japan): The cargo ship ran aground on Sakhalin, Soviet Union and was wrecked.[215] - Taniwha (
 United Kingdom): The cargo ship sank at Puriri, New Zealand.[214]
United Kingdom): The cargo ship sank at Puriri, New Zealand.[214]
25 September
- Katingo (
 Greece): The cargo ship ran aground at Nagara Point, Turkey.[216] She was refloated on 28 September.[215]
Greece): The cargo ship ran aground at Nagara Point, Turkey.[216] She was refloated on 28 September.[215]
26 September
- Agnesina (
.svg.png) Italy): The brigantine was abandoned in the Mediterranean Sea (36°22′N 19°56′E / 36.367°N 19.933°E). All nine people on board were rescued by Lalandia (
Italy): The brigantine was abandoned in the Mediterranean Sea (36°22′N 19°56′E / 36.367°N 19.933°E). All nine people on board were rescued by Lalandia ( Denmark).[215][217]
Denmark).[215][217] - Doris (
 United Kingdom): The schooner came ashore at the mouth of the River Tees, County Durham. Her crew were rescued.[218] She broke her back the next day and was a total loss.[215]
United Kingdom): The schooner came ashore at the mouth of the River Tees, County Durham. Her crew were rescued.[218] She broke her back the next day and was a total loss.[215] - Margarita (
 United Kingdom): The cargo ship collided with Nueva Señora del Carmen (
United Kingdom): The cargo ship collided with Nueva Señora del Carmen (.svg.png) Spain) in the Strait of Gibraltar and was beached in Gibraltar Bay.[219] She was refloated the next day.[207]
Spain) in the Strait of Gibraltar and was beached in Gibraltar Bay.[219] She was refloated the next day.[207]
28 September
- Vibert T Shave (
 United Kingdom): The schooner collided with Haugarland (
United Kingdom): The schooner collided with Haugarland ( Norway) in the Atlantic Ocean 3 nautical miles (5.6 km) off Ferryland, Newfoundland with the loss of five of the six people on board.[207][215]
Norway) in the Atlantic Ocean 3 nautical miles (5.6 km) off Ferryland, Newfoundland with the loss of five of the six people on board.[207][215]
October
3 October
- Fort McPherson (
 United Kingdom): The cargo ship came ashore in the Richardson Islands, Northwest Territory, Canada and was wrecked.[220]
United Kingdom): The cargo ship came ashore in the Richardson Islands, Northwest Territory, Canada and was wrecked.[220]
5 October
- Lottie May (
 United Kingdom): The schooner was destroyed by fire in the Bay d'Espoir, Newfoundland. The crew survived.[221]
United Kingdom): The schooner was destroyed by fire in the Bay d'Espoir, Newfoundland. The crew survived.[221]
6 October
- Bamfield (
 United Kingdom): The cargo ship collided with Princess Joan (
United Kingdom): The cargo ship collided with Princess Joan ( United Kingdom) in the Pacific Ocean off Discovery Island, British Columbia, Canada and sank.[221]
United Kingdom) in the Pacific Ocean off Discovery Island, British Columbia, Canada and sank.[221]
9 October
- Agnes (
 Norway: The cargo ship broke free from her moorings in a storm at Haugesund, Norway and sank.[212]
Norway: The cargo ship broke free from her moorings in a storm at Haugesund, Norway and sank.[212] - Allende (
 United Kingdom): The cargo ship ran aground at Mokha, Aden Protectorate.[212] She was refloated on 13 October.[209]
United Kingdom): The cargo ship ran aground at Mokha, Aden Protectorate.[212] She was refloated on 13 October.[209]
11 October
- Lutetian (
 United Kingdom): The tanker ran aground on Margarita Island, Venezuela.[222] She was refloated on 16 October.[223]
United Kingdom): The tanker ran aground on Margarita Island, Venezuela.[222] She was refloated on 16 October.[223] - Mersey Rose (
 United Kingdom): The cargo ship collided with Gleneden (
United Kingdom): The cargo ship collided with Gleneden ( United Kingdom)in the English Channel off St. Catherine's Point, Isle of Wight (50°01′N 2°04′W / 50.017°N 2.067°W) and sank. Her crew were rescued by Gleneden.[222]
United Kingdom)in the English Channel off St. Catherine's Point, Isle of Wight (50°01′N 2°04′W / 50.017°N 2.067°W) and sank. Her crew were rescued by Gleneden.[222]
13 October
- Corapeake (
 United States): The schooner collided with a number of scows at Norfolk, Virginia and sank.[209]
United States): The schooner collided with a number of scows at Norfolk, Virginia and sank.[209] - Tiffon (
 Estonia): The schooner came ashore at Sakkijarvi, Finland and was wrecked. Her crew were rescued.[209]
Estonia): The schooner came ashore at Sakkijarvi, Finland and was wrecked. Her crew were rescued.[209]
14 October
- Faustina (
 United Kingdom): The schooner sprang a leak in the Atlantic Ocean and was abandoned (41°42′N 24°51′W / 41.700°N 24.850°W). The crew were rescued by Wearwood (
United Kingdom): The schooner sprang a leak in the Atlantic Ocean and was abandoned (41°42′N 24°51′W / 41.700°N 24.850°W). The crew were rescued by Wearwood ( United Kingdom).[224]
United Kingdom).[224]
15 October
- Demokratia (
 Greece): The cargo ship ran aground off the Leander's Tower, Istanbul, Turkey.[224] She was refloated on 22 October.[225]
Greece): The cargo ship ran aground off the Leander's Tower, Istanbul, Turkey.[224] She was refloated on 22 October.[225]
16 October
- Antonin del Collado (
.svg.png) Italy): The passenger ship collided with Hallmoor (
Italy): The passenger ship collided with Hallmoor ( United Kingdom) in the Atlantic Ocean 10 nautical miles (19 km) off Mariel, Cuba and sank. All on board were rescued by Hallmoor.[223]
United Kingdom) in the Atlantic Ocean 10 nautical miles (19 km) off Mariel, Cuba and sank. All on board were rescued by Hallmoor.[223]
17 October
- Elkhound (
 United Kingdom): The tanker was destroyed by fire at Thameshaven, Essex[226]
United Kingdom): The tanker was destroyed by fire at Thameshaven, Essex[226]
19 October
- Millie (
 United Kingdom): The Thames barge foundered in the Thames Estuary. Both crew were rescued by Baltrader (
United Kingdom): The Thames barge foundered in the Thames Estuary. Both crew were rescued by Baltrader ( United Kingdom).[227]
United Kingdom).[227]
21 October
- Fito (
.svg.png) Spain): The cargo ship collided with another vessel 12 nautical miles (22 km) east of Sálvora, Galicia and sank.[228]
Spain): The cargo ship collided with another vessel 12 nautical miles (22 km) east of Sálvora, Galicia and sank.[228]
22 October
- Zannis Xenios (
 Greece): The cargo ship ran aground on Seeskli Island in the Aegean Sea and sank. Her crew survived.[229]
Greece): The cargo ship ran aground on Seeskli Island in the Aegean Sea and sank. Her crew survived.[229]
24 October
- Kong Ragnar (
 Norway): The cargo ship came ashore at Randøy, Møre og Romsdal and sank with the loss of six crew.[228]
Norway): The cargo ship came ashore at Randøy, Møre og Romsdal and sank with the loss of six crew.[228] - Ortona (
 United Kingdom): The cargo ship ran aground in the River Tees at Middlesbrough, Yorkshire.[228] She was refloated on 8 November.[230]
United Kingdom): The cargo ship ran aground in the River Tees at Middlesbrough, Yorkshire.[228] She was refloated on 8 November.[230]
25 October
- Sonnia (
 United Kingdom): The cargo ship foundered 7 nautical miles (13 km) north east of The Skerries, Isle of Anglesey. The crew took to the lifeboats and landed at Moelfre. Her captain was rescued by the trawler Jeanne (
United Kingdom): The cargo ship foundered 7 nautical miles (13 km) north east of The Skerries, Isle of Anglesey. The crew took to the lifeboats and landed at Moelfre. Her captain was rescued by the trawler Jeanne (.svg.png) Belgium).[231]
Belgium).[231]
28 October
- Andalusia (
.svg.png) Italy): The cargo ship ran aground at Tønsnesskjæret, Troms, Norway.[232] She was refloated on 2 November.[233]
Italy): The cargo ship ran aground at Tønsnesskjæret, Troms, Norway.[232] She was refloated on 2 November.[233]
31 October
- Rahra (
 United Kingdom): The three-masted auxiliary schooner ran aground on Danger Island, Cook Islands and was wrecked.[234]
United Kingdom): The three-masted auxiliary schooner ran aground on Danger Island, Cook Islands and was wrecked.[234]
November
1 November
- Ascot (
 United Kingdom): The cargo ship ran aground at Quequon, Argentina.[235] She was refloated on 9 November.[236]
United Kingdom): The cargo ship ran aground at Quequon, Argentina.[235] She was refloated on 9 November.[236] - Choshun Maru (
 Japan): The passenger ship ran aground on Green Island, Hong Kong. The passengers and crew were taken off.[233]
Japan): The passenger ship ran aground on Green Island, Hong Kong. The passengers and crew were taken off.[233]
2 November
- Commandant Marchand (
 France): The schooner capsized in the Bristol Channel off Cardiff, Glamorgan, United Kingdom.[233]
France): The schooner capsized in the Bristol Channel off Cardiff, Glamorgan, United Kingdom.[233] - Ethel (
 United Kingdom): The cargo ship ran aground at Bideford, Devon.[235] She was refloated on 5 November.[237]
United Kingdom): The cargo ship ran aground at Bideford, Devon.[235] She was refloated on 5 November.[237] - Helmsdale (
 United Kingdom): The cargo ship ran aground on Als, Denmark.[235] She was refloated on 6 November.[238]
United Kingdom): The cargo ship ran aground on Als, Denmark.[235] She was refloated on 6 November.[238] - Julia (
 United Kingdom): The schooner ran aground at The Needles, Isle of Wight. She was refloated on 10 November.[236]
United Kingdom): The schooner ran aground at The Needles, Isle of Wight. She was refloated on 10 November.[236] - Ma Gondole (
 France): The cargo ship foundered in the English Channel off Portland Bill, Dorset, United Kingdom. Three crew were rescued by Josephine Charlotte (
France): The cargo ship foundered in the English Channel off Portland Bill, Dorset, United Kingdom. Three crew were rescued by Josephine Charlotte (.svg.png) Belgium).[233]
Belgium).[233] - Menelaos (
 Greece): The cargo ship was abandoned in the English Channel about 6 nautical miles (11 km) south south west of Selsey Bill, West Sussex, United Kingdom. Her crew were rescued by Canute and Naperian (both
Greece): The cargo ship was abandoned in the English Channel about 6 nautical miles (11 km) south south west of Selsey Bill, West Sussex, United Kingdom. Her crew were rescued by Canute and Naperian (both  United Kingdom).[233]
United Kingdom).[233]
5 November
- Seven Seas Trader (
 United Kingdom): The cargo ship was driven ashore at Trapani, Sicily, Italy.[237] She was refloated on 11 November.[239]
United Kingdom): The cargo ship was driven ashore at Trapani, Sicily, Italy.[237] She was refloated on 11 November.[239]
6 November
- Hakusan Maru (
 Japan): The cargo ship collided with Benmacdhui (
Japan): The cargo ship collided with Benmacdhui ( United Kingdom) at Kobe and was beached.[240] She was refloated on 8 November.[230]
United Kingdom) at Kobe and was beached.[240] She was refloated on 8 November.[230] - Hermione (
 United Kingdom): The tanker ran aground at Kara Point, Greece.[240] She was refloated on 10 November.[239]
United Kingdom): The tanker ran aground at Kara Point, Greece.[240] She was refloated on 10 November.[239] - Seiyo Maru (
 Japan): The cargo ship lost her rudder in the Pacific Ocean (50°30′N 176°48′E / 50.500°N 176.800°E) and was abandoned in a sinking condition. Her crew were rescued by Shiraha Maru (
Japan): The cargo ship lost her rudder in the Pacific Ocean (50°30′N 176°48′E / 50.500°N 176.800°E) and was abandoned in a sinking condition. Her crew were rescued by Shiraha Maru ( Japan).[240]
Japan).[240]
7 November
- Santa Rita (
.svg.png) Italy): The cargo ship ran aground at the mouth of the Adour river, Bayonne, Pyrénées-Atlantiques, France and broke her back. She was a total loss.[230]
Italy): The cargo ship ran aground at the mouth of the Adour river, Bayonne, Pyrénées-Atlantiques, France and broke her back. She was a total loss.[230] - Tamiahua (
 United States): The tanker ran aground off the Pigeon Point Lighthouse, California. She was refloated on 26 November.[241]
United States): The tanker ran aground off the Pigeon Point Lighthouse, California. She was refloated on 26 November.[241]
8 November
- Brooklyn (
 United States): The coaster foundered off Oregon with the loss of all hands.[239][242]
United States): The coaster foundered off Oregon with the loss of all hands.[239][242] - Dunham Wheeler (
 United States): The schooner foundered in the Atlantic Ocean off Cape Canaveral, Florida. Ten crew were rescued by Aztec (
United States): The schooner foundered in the Atlantic Ocean off Cape Canaveral, Florida. Ten crew were rescued by Aztec ( Honduras).[239]
Honduras).[239] - Kenton (
 United Kingdom): The cargo ship ran aground at Akban Liman, Turkey.[230] She was refloated on 16 November.[243]
United Kingdom): The cargo ship ran aground at Akban Liman, Turkey.[230] She was refloated on 16 November.[243] - Olive Moore (
 United Kingdom): The schooner foundered in the Atlantic Ocean (35°35′N 15°50′W / 35.583°N 15.833°W). six crew were rescued by Montello (
United Kingdom): The schooner foundered in the Atlantic Ocean (35°35′N 15°50′W / 35.583°N 15.833°W). six crew were rescued by Montello (.svg.png) Italy).[230][239]
Italy).[230][239]
9 November
- Stralsund (
.svg.png) Germany): The coaster passed Dover, Kent, United Kingdom bound for Gothenburg, Sweden. No further trace. Presumed foundered in the North Sea off Sylt, Schleswig-Holstein, where a lifeboat washed up on 15 November.[244]
Germany): The coaster passed Dover, Kent, United Kingdom bound for Gothenburg, Sweden. No further trace. Presumed foundered in the North Sea off Sylt, Schleswig-Holstein, where a lifeboat washed up on 15 November.[244] - Tanja (
 Sweden): The coaster departed the Free City of Danzig for Trollhattan. No further trace, presumed foundered with the loss of all hands.[245]
Sweden): The coaster departed the Free City of Danzig for Trollhattan. No further trace, presumed foundered with the loss of all hands.[245]
10 November
- Ilford (
 United Kingdom): The cargo ship ran aground at São Vicente, Cape Verde Islands, Portugal.[239] She was refloated on 14 November.[246]
United Kingdom): The cargo ship ran aground at São Vicente, Cape Verde Islands, Portugal.[239] She was refloated on 14 November.[246] - Linkmoor (
 United Kingdom): The cargo ship ran aground at Skarfskerry Head, Caithness. All crew were rescued.[236] She was declared a total loss on 19 November.[247]
United Kingdom): The cargo ship ran aground at Skarfskerry Head, Caithness. All crew were rescued.[236] She was declared a total loss on 19 November.[247] - Teifi (
 United Kingdom): The cargo ship struck a submerged object in the Bristol Channel off Cardiff, Glamorgan and sank. Her crew survived. She may have struck the wreck of the French schooner Commandant Marchand.[236]
United Kingdom): The cargo ship struck a submerged object in the Bristol Channel off Cardiff, Glamorgan and sank. Her crew survived. She may have struck the wreck of the French schooner Commandant Marchand.[236]
11 November
- Moyalla
 United Kingdom): The coaster ran aground at Ballina, County Mayo, Ireland.[239] She was refloated on 10 December.[248]
United Kingdom): The coaster ran aground at Ballina, County Mayo, Ireland.[239] She was refloated on 10 December.[248]
12 November
- Else (
 Denmark): The coaster ran aground in the Kattegat off Hjelm and sank.[234]
Denmark): The coaster ran aground in the Kattegat off Hjelm and sank.[234] - Glenarch (
 United Kingdom): The cargo ship ran aground in the Penfeld at Brest, Finistère, France.[249] She was refloated on 16 November.[243]
United Kingdom): The cargo ship ran aground in the Penfeld at Brest, Finistère, France.[249] She was refloated on 16 November.[243] - Joyce Llewellyn (
 United Kingdom): The cargo ship came ashore on the west coast of Ven, Sweden.[249] She was refloated on 16 November.[250]
United Kingdom): The cargo ship came ashore on the west coast of Ven, Sweden.[249] She was refloated on 16 November.[250] - Sahara (
.svg.png) Spain): The schooner collided with the trawler Santa Eulala (
Spain): The schooner collided with the trawler Santa Eulala (.svg.png) Spain) in the Atlantic Ocean off Las Palmas, Canary Islands and sank. Her crew were rescued by Santa Eulala.[249]
Spain) in the Atlantic Ocean off Las Palmas, Canary Islands and sank. Her crew were rescued by Santa Eulala.[249]
14 November
- Doreena (
 United Kingdom): The Thames barge collided with Camberwell (
United Kingdom): The Thames barge collided with Camberwell ( United Kingdom) in the River Thames and sank with the loss of a crew member.[251]
United Kingdom) in the River Thames and sank with the loss of a crew member.[251] - Laimons (
 Latvia): The cargo ship ran aground on the Curonian Spit, Soviet Union. Her crew were rescued.[250]
Latvia): The cargo ship ran aground on the Curonian Spit, Soviet Union. Her crew were rescued.[250] - Margherita Madre (
_crowned.svg.png) Italy): The schooner was abandoned in the Tyrrhenian Sea 2 nautical miles (3.7 km) off Punta Imperatore, Ischia.[246]
Italy): The schooner was abandoned in the Tyrrhenian Sea 2 nautical miles (3.7 km) off Punta Imperatore, Ischia.[246] - Yero Carras (
 Greece): The cargo ship came ashore at Cape Upright, Chile. She was declared a total loss on 18 November,[246][252] but was refloated on 6 December and beached at Baker Cove.[253][254]
Greece): The cargo ship came ashore at Cape Upright, Chile. She was declared a total loss on 18 November,[246][252] but was refloated on 6 December and beached at Baker Cove.[253][254]
15 November
- Anglesea Rose (
 United Kingdom): The cargo ship ran aground at Yarmouth, Isle of Wight.[250] She was refloated on 18 November.[255]
United Kingdom): The cargo ship ran aground at Yarmouth, Isle of Wight.[250] She was refloated on 18 November.[255] - Laura (
 Chile): The full-rigged ship was wrecked in Cucao Lake, Chiloé Island with the loss of all but eight crew.[250]
Chile): The full-rigged ship was wrecked in Cucao Lake, Chiloé Island with the loss of all but eight crew.[250]
16 November
- Brière (
 France): The cargo ship ran aground north east of Brest, Finistère.[250] She broke in two on 20 November and was a total loss.[244]
France): The cargo ship ran aground north east of Brest, Finistère.[250] She broke in two on 20 November and was a total loss.[244] - Hursley (
 United Kingdom): The coaster ran aground on the Goodwin Sands, Kent and sank. Six crew were rescued by the Ramsgate Lifeboat.
United Kingdom): The coaster ran aground on the Goodwin Sands, Kent and sank. Six crew were rescued by the Ramsgate Lifeboat. - Ronald M. Douglas (
 United Kingdom): The schooner was abandoned in the Atlantic Ocean (33°22′N 49°12′W / 33.367°N 49.200°W). She was set on fire by her crew, who were rescued by Murex (
United Kingdom): The schooner was abandoned in the Atlantic Ocean (33°22′N 49°12′W / 33.367°N 49.200°W). She was set on fire by her crew, who were rescued by Murex ( United Kingdom).[243]
United Kingdom).[243]
17 November
- Trevellas (
 United Kingdom): The auxiliary three masted schooner departed Port Talbot, Glamorgan for New Ross, County Wexford, Ireland. No further trace, presumed foundered with the loss of all hands.[256]
United Kingdom): The auxiliary three masted schooner departed Port Talbot, Glamorgan for New Ross, County Wexford, Ireland. No further trace, presumed foundered with the loss of all hands.[256]
19 November
- Continental Freighter (
 United Kingdom): The cargo ship collided with Hebble (
United Kingdom): The cargo ship collided with Hebble ( United Kingdom in the Scheldt at Antwerp, Belgium and sank.[255] She was refloated on 4 December.[257]
United Kingdom in the Scheldt at Antwerp, Belgium and sank.[255] She was refloated on 4 December.[257] - Highland Hope (
 United Kingdom): The ocean liner ran aground on Farilhões Island, Berlengas, Portugal and was a total loss. All on board were rescued by a Portuguese Navy vessel and Portuguese fishing boats.[244][245][258]
United Kingdom): The ocean liner ran aground on Farilhões Island, Berlengas, Portugal and was a total loss. All on board were rescued by a Portuguese Navy vessel and Portuguese fishing boats.[244][245][258] - J. H. Barrow (
 United Kingdom): The schooner was driven ashore in the River Severn at Oldbury-on-Severn, Gloucestershire.[255] She was refloated on 22 November.[259]
United Kingdom): The schooner was driven ashore in the River Severn at Oldbury-on-Severn, Gloucestershire.[255] She was refloated on 22 November.[259] - Ovidia (
 Sweden): The cargo ship sprang a leak in the Atlantic Ocean 400 nautical miles (740 km) south east of Cape Race, Newfoundland (42°00′N 50°55′W / 42.000°N 50.917°W) and was abandoned. Twenty-eight people and the ship's cat were rescued by Mauretania (
Sweden): The cargo ship sprang a leak in the Atlantic Ocean 400 nautical miles (740 km) south east of Cape Race, Newfoundland (42°00′N 50°55′W / 42.000°N 50.917°W) and was abandoned. Twenty-eight people and the ship's cat were rescued by Mauretania ( United Kingdom).[247][258][260]
United Kingdom).[247][258][260]
20 November
- Dronning Sophie (
 Ireland): The coal hulk sank at Queenstown, County Cork.[244]
Ireland): The coal hulk sank at Queenstown, County Cork.[244] - Kenkon Maru No.8 (
 Japan): The cargo ship ran aground off Dalozaki and broke in two. She was a total loss.[244][261]
Japan): The cargo ship ran aground off Dalozaki and broke in two. She was a total loss.[244][261] - Verena (
 Netherlands): The auxiliary schooner came ashore at Cape Arkona, Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Germany and was wrecked. Her crew were rescued.[244]
Netherlands): The auxiliary schooner came ashore at Cape Arkona, Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Germany and was wrecked. Her crew were rescued.[244]
21 November
- Ruperra (
 United Kingdom): The cargo ship ran aground in Angle Bay, Pembrokeshire.[245] She was refloated on 5 December.[262]
United Kingdom): The cargo ship ran aground in Angle Bay, Pembrokeshire.[245] She was refloated on 5 December.[262] - Sunko Maru (
 Japan): The coaster caught fire and sank off in the Pacific Ocean off Tosa Province.[259]
Japan): The coaster caught fire and sank off in the Pacific Ocean off Tosa Province.[259]
23 November
- Luise Leonhardt (
.svg.png) Germany): The cargo ship was driven on the Grosser Vogel sandbank, in the North Sea off the mouth of the Elbe and sank with the loss of all 31 crew.[263]
Germany): The cargo ship was driven on the Grosser Vogel sandbank, in the North Sea off the mouth of the Elbe and sank with the loss of all 31 crew.[263]
24 November
- Krysanthi Patera (
 Greece): The cargo ship caught fire in the Atlantic Ocean 75 nautical miles (139 km) off Cristóbal, Colón, Panama and was abandoned. All crew were rescued by Trevean (
Greece): The cargo ship caught fire in the Atlantic Ocean 75 nautical miles (139 km) off Cristóbal, Colón, Panama and was abandoned. All crew were rescued by Trevean ( United Kingdom) before she sank.[263]
United Kingdom) before she sank.[263]
25 November
- Citta di Trani (
 United Kingdom): The auxiliary schooner was wrecked in the Abaco Islands.[264]
United Kingdom): The auxiliary schooner was wrecked in the Abaco Islands.[264]
29 November
- Lütt (
.svg.png) Germany): The auxiliary three-masted schooner capsized in the Baltic Sea off Rugenwalde, Western Pomerania.[265] She was towed into Swinemüne on 9 December.[266]
Germany): The auxiliary three-masted schooner capsized in the Baltic Sea off Rugenwalde, Western Pomerania.[265] She was towed into Swinemüne on 9 December.[266]
30 November
- Perez (
.svg.png) Spain): The schooner was driven ashore at Valencia and was wrecked. Her crew were rescued.[265]
Spain): The schooner was driven ashore at Valencia and was wrecked. Her crew were rescued.[265]
December
1 December
- Georges Philippar (
 France): The ocean liner caught fire at Saint-Nazaire, Loire-Atlantique whilst being fitted out. She was completed in January 1932 and was lost on her maiden voyage.
France): The ocean liner caught fire at Saint-Nazaire, Loire-Atlantique whilst being fitted out. She was completed in January 1932 and was lost on her maiden voyage.
2 December
- Asmund (
 Norway): The cargo ship ran aground at Holyhead, Anglesey, United Kingdom.[267] She sank on 7 December.[268]
Norway): The cargo ship ran aground at Holyhead, Anglesey, United Kingdom.[267] She sank on 7 December.[268]
3 December
- Hedwig (
 Netherlands): The cargo ship ran aground in the Pratas Islands (approximately 20°N 116°E / 20°N 116°E) and was wrecked.[269]
Netherlands): The cargo ship ran aground in the Pratas Islands (approximately 20°N 116°E / 20°N 116°E) and was wrecked.[269] - Linton (
 United Kingdom): The coaster was wrecked at West Cape, Prince Edward Island, Canada with the loss of all eight crew.[269]
United Kingdom): The coaster was wrecked at West Cape, Prince Edward Island, Canada with the loss of all eight crew.[269]
4 December
- Alda (
.svg.png) Spain): The cargo ship ran aground at Navia, Asturias.[257] She was refloated on 9 December.[266]
Spain): The cargo ship ran aground at Navia, Asturias.[257] She was refloated on 9 December.[266]
5 December
- Dazzle (
 United Kingdom): The auxiliary schooner was abandoned 8 nautical miles (15 km) off Ramea, Newfoundland. Her crew were rescued.[220]
United Kingdom): The auxiliary schooner was abandoned 8 nautical miles (15 km) off Ramea, Newfoundland. Her crew were rescued.[220] - Yselhaven (
 Netherlands): The cargo ship collided with Oakland (
Netherlands): The cargo ship collided with Oakland ( United Kingdom) in the Weser at Nordenham, Lower Saxony and was beached.[270] She was refloated on 9 December.[266]
United Kingdom) in the Weser at Nordenham, Lower Saxony and was beached.[270] She was refloated on 9 December.[266]
8 December
- Artiglio (
.svg.png) Italy): The salvage vessel was sunk in the Bay of Biscay between Belle Île and Houat, Morbihan, France by the explosion of munitions on board Florence H (
Italy): The salvage vessel was sunk in the Bay of Biscay between Belle Île and Houat, Morbihan, France by the explosion of munitions on board Florence H ( United States), which she was salvaging, with the loss of fourteen of her nineteen crew. Survivors were rescued by Rostro (
United States), which she was salvaging, with the loss of fourteen of her nineteen crew. Survivors were rescued by Rostro (.svg.png) Italy).[271][272]
Italy).[271][272]
10 December
- Don Carlos (
 Argentina): The coaster sank in the Uruguay River, Buenos Aires with the loss of one of her eleven crew.[248][273]
Argentina): The coaster sank in the Uruguay River, Buenos Aires with the loss of one of her eleven crew.[248][273] - Empress of Scotland (
 United Kingdom): The ocean liner was gutted by fire at a shipbreakers' yard in Blyth, Northumberland. She broke in two and sank. Scrapping was completed in 1933.
United Kingdom): The ocean liner was gutted by fire at a shipbreakers' yard in Blyth, Northumberland. She broke in two and sank. Scrapping was completed in 1933. - Hilda (
 United Kingdom): The barquentine collided with the trawler Kudos (
United Kingdom): The barquentine collided with the trawler Kudos ( United Kingdom) in the North Sea 15 nautical miles (28 km) off Hartlepool, County Durham and sank. All six crew were rescued by Kudos.[274]
United Kingdom) in the North Sea 15 nautical miles (28 km) off Hartlepool, County Durham and sank. All six crew were rescued by Kudos.[274] - Vialle Montagne III (
 Sweden): The cargo ship collided with Kresnamn (
Sweden): The cargo ship collided with Kresnamn (.svg.png) Germany) at Gothenburg and sank.[248]
Germany) at Gothenburg and sank.[248]
11 December
- Amy G. McKean (
 United Kingdom): The schooner sprang a leak in the Atlantic Ocean (50°25′N 20°08′W / 50.417°N 20.133°W). She was set on fire and abandoned by her crew, who were rescued by Strasan (
United Kingdom): The schooner sprang a leak in the Atlantic Ocean (50°25′N 20°08′W / 50.417°N 20.133°W). She was set on fire and abandoned by her crew, who were rescued by Strasan ( Sweden).[273]
Sweden).[273] - Saltwick (
 United Kingdom): The cargo ship ran aground in the Paraná River, Argentina.[273] She was refloated on 14 December.[275]
United Kingdom): The cargo ship ran aground in the Paraná River, Argentina.[273] She was refloated on 14 December.[275] - Schlesien (
.svg.png) Germany): The ocean liner ran aground in the Kii Channel.[273] She was refloated on 15 December.[275]
Germany): The ocean liner ran aground in the Kii Channel.[273] She was refloated on 15 December.[275]
13 December
- Nordo (
 Finland): The auxiliary sailing ship ran aground on Svanegrunden, Kattegat. Her crew were rescued.[275]
Finland): The auxiliary sailing ship ran aground on Svanegrunden, Kattegat. Her crew were rescued.[275]
15 December
- Chapel Point (
 United Kingdom): The auxiliary schooner was abandoned in the Pacific Ocean off the coast of British Columbia, Canada and was a total loss.[275]
United Kingdom): The auxiliary schooner was abandoned in the Pacific Ocean off the coast of British Columbia, Canada and was a total loss.[275] - Warren M. Colp (
 United Kingdom): The schooner came ashore at Burnt Point, Newfoundland and was wrecked with the loss of four of her six crew.[276]
United Kingdom): The schooner came ashore at Burnt Point, Newfoundland and was wrecked with the loss of four of her six crew.[276]
16 December
- Gipsy Queen (
 United Kingdom): The schooner was abandoned in the Atlantic Ocean off the coast of Newfoundland. Her crew survived.[277]
United Kingdom): The schooner was abandoned in the Atlantic Ocean off the coast of Newfoundland. Her crew survived.[277] - Thraki (
 Greece): The cargo ship ran aground at Kavala, Yugoslavia.[276] She was refloated on 21 December.[278]
Greece): The cargo ship ran aground at Kavala, Yugoslavia.[276] She was refloated on 21 December.[278]
18 December
- Christos Sigalas (
 Greece): The cargo ship sprang a leak in the Atlantic Ocean (approximately 33°N 69°W / 33°N 69°W) and was abandoned in a sinking condition. Her crew were rescued by Monfiore (
Greece): The cargo ship sprang a leak in the Atlantic Ocean (approximately 33°N 69°W / 33°N 69°W) and was abandoned in a sinking condition. Her crew were rescued by Monfiore (.svg.png) Italy).[279]
Italy).[279] - Cremon (
.svg.png) Germany): The cargo ship was beached at Üto.[279]
Germany): The cargo ship was beached at Üto.[279]
19 December
- Oberon (
 Finland): The ferry collided with Arcturus (
Finland): The ferry collided with Arcturus ( Finland) in the Kattegat off Læsø, Denmark and sank with the loss of 42 of the 82 people on board. Survivors were rescued by Arcturus.[280]
Finland) in the Kattegat off Læsø, Denmark and sank with the loss of 42 of the 82 people on board. Survivors were rescued by Arcturus.[280]
20 December
- Glen Derry (
 United Kingdom): The cargo ship caught fire in the North Sea off Happisburgh, Norfolk and was abandoned. Her crew were rescued by Heworth (
United Kingdom): The cargo ship caught fire in the North Sea off Happisburgh, Norfolk and was abandoned. Her crew were rescued by Heworth ( United Kingdom}). Glen Derry later sank.[281]
United Kingdom}). Glen Derry later sank.[281]
21 December
- Oinoussios (
 Greece): The cargo ship ran aground at Nicolaeff, Turkey.[282] She was refloated on 29 December.[283]
Greece): The cargo ship ran aground at Nicolaeff, Turkey.[282] She was refloated on 29 December.[283] - Rio Azul (
 United Kingdom): The cargo ship collided with Hopatcong (
United Kingdom): The cargo ship collided with Hopatcong ( United States) at Istanbul, Turkey and was beached.[281]
United States) at Istanbul, Turkey and was beached.[281]
22 December
- Malve (
 Finland): The cargo ship ran aground at Knollen Drogden.[278]
Finland): The cargo ship ran aground at Knollen Drogden.[278] - Sonja (
 Norway): The cargo ship ran aground at Ronglevær.[278] She was refloated on 29 December.[282]
Norway): The cargo ship ran aground at Ronglevær.[278] She was refloated on 29 December.[282] - Suffolk Coast (
 United Kingdom): The coaster ran aground at King's Lynn, Norfolk.[278] She was refloated on 5 January 1931.[284]
United Kingdom): The coaster ran aground at King's Lynn, Norfolk.[278] She was refloated on 5 January 1931.[284] - Lucy (
 United Kingdom): The cargo ship ran aground at Kettleness, Yorkshire and was abandoned. The cre were rescued by the Whitby Lifeboat.[285][286]
United Kingdom): The cargo ship ran aground at Kettleness, Yorkshire and was abandoned. The cre were rescued by the Whitby Lifeboat.[285][286]
27 December
- Queenmoor (
 United Kingdom): The cargo ship caught fire in the Indian Ocean and was abandoned by her crew. She was towed into Aden by Preserver (
United Kingdom): The cargo ship caught fire in the Indian Ocean and was abandoned by her crew. She was towed into Aden by Preserver ( United Kingdom.[286]
United Kingdom.[286]
29 December
- Branch Railway (
 United Kingdom): The schooner was driven ashore at Cock's Cove, St. Mary's Bay, Newfoundland and was wrecked.[287]
United Kingdom): The schooner was driven ashore at Cock's Cove, St. Mary's Bay, Newfoundland and was wrecked.[287]
31 December
- Stela (
.svg.png) Egypt): The cargo ship sprang a leak in the Aegean Sea off Levitha, Greece (36°46′N 28°46′E / 36.767°N 28.767°E) and was abandoned.[283][288] She sank 8 nautical miles (15 km) east of Astypalaia.[289]
Egypt): The cargo ship sprang a leak in the Aegean Sea off Levitha, Greece (36°46′N 28°46′E / 36.767°N 28.767°E) and was abandoned.[283][288] She sank 8 nautical miles (15 km) east of Astypalaia.[289] - Theodoris Bulgaris (
 Greece): The cargo ship sprang a leak in the Atlantic Ocean and was abandoned (45°31′N 6°00′W / 45.517°N 6.000°W). Her crew survived.[283]
Greece): The cargo ship sprang a leak in the Atlantic Ocean and was abandoned (45°31′N 6°00′W / 45.517°N 6.000°W). Her crew survived.[283]
Unknown date

The wreck of Baymaud, June 1998
- Baymaud (
 United Kingdom): The auxiliary three-masted schooner sank in Cambridge Bay, Northwest Territories, Canada.
United Kingdom): The auxiliary three-masted schooner sank in Cambridge Bay, Northwest Territories, Canada. - Half Moon (
 United States): the yacht sank in the Atlantic Ocean off Key Biscayne, Florida.
United States): the yacht sank in the Atlantic Ocean off Key Biscayne, Florida.
References
- ↑ "Another wreck off the Pacific coast" The Times (London). Saturday, 4 January 1930. (45402), col C, p. 19.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Monday, 6 January 1930. (45403), col F, p. 22.
- ↑ "Steamers ashore" The Times (London). Friday, 3 January 1930. (45401), col E, p. 10.
- ↑ "Dutch steamer wrecked" The Times (London). Monday, 6 January 1930. (45403), col C, p. 11.
- ↑ "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Monday, 13 January 1930. (45409), col D, p. 22.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Wednesday, 8 January 1930. (45405), col C, p. 22.
- ↑ "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Tuesday, 7 January 1930. (45404), col G, p. 22.
- ↑ "New steamer lost" The Times (London). Wednesday, 8 January 1930. (45405), col C, p. 22.
- ↑ "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Friday, 10 January 1930. (45407), col G, p. 21.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Tuesday, 28 January 1930. (45422), col G, p. 22.
- ↑ "United States steamer stranded" The Times (London). Saturday, 11 January 1930. (45408), col C, p. 19.
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 12.2 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Thursday, 6 March 1930. (45454), col C, p. 25.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 13.2 13.3 13.4 13.5 "The gale at sea" The Times (London). Tuesday, 14 January 1930. (45410), col D, p. 16.
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 14.2 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Saturday, 18 January 1930. (45414), col C, p. 19.
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Tuesday, 14 January 1930. (45410), col F, p. 23.
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 16.2 16.3 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Thursday, 15 January 1930. (45411), col C, p. 24.
- ↑ "The great gale" The Times (London). Tuesday, 14 January 1930. (45410), col D, p. 14.
- ↑ "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Wednesday, 22 January 1930. (45417), col E, p. 25.
- ↑ 19.0 19.1 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Monday, 20 January 1930. (45415), col F, p. 22.
- ↑ "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Monday, 27 January 1930. (45421), col B, p. 20.
- ↑ 21.0 21.1 21.2 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Friday, 17 January 1930. (45413), col F, p. 24.
- ↑ "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Tuesday, 21 January 1930. (45416), col E, p. 20.
- ↑ "Belgian Merchant P-Z". Belgische Koopvaardij. Retrieved 1 December 2010.
- ↑ "Marine insurance" The Times (London). Friday, 14 February 1930. (45437), col E, p. 22.
- ↑ "The Daksa uninsurable" The Times (London). Friday, 7 February 1930. (45431), col F, p. 20.
- ↑ 26.0 26.1 26.2 26.3 26.4 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Monday, 3 February 1930. (45427), col E, p. 20.
- ↑ "WWI STANDARD BUILT SHIPS A-K". Mariners. Retrieved 8 May 2011.
- ↑ "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Thursday, 30 January 1930. (45424), col C, p. 24.
- ↑ "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Tuesday, 4 February 1930. (45428), col E, p. 22.
- ↑ "The Braaland uninsurable" The Times (London). Wednesday, 5 February 1930. (45429), col C, p. 24.
- ↑ "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Friday, 14 February 1930. (45437), col E, p. 22.
- ↑ 32.0 32.1 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Wednesday, 5 February 1930. (45429), col C, p. 24.
- ↑ 33.0 33.1 33.2 "Belgian Merchant A-G". Belgische Koopvaardij. Retrieved 1 October 2010.
- ↑ "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Thursday, 6 February 1930. (45430), col A, p. 24.
- ↑ "Norwegian steamer lost" The Times (London). Thursday, 6 February 1930. (45430), col A, p. 24.
- ↑ "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Saturday, 8 February 1930. (45432), col C, p. 21.
- ↑ "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Monday, 10 February 1930. (45433), col C, p. 22.
- ↑ "Lives lost at sea" The Times (London). Monday, 10 February 1930. (45433), col F, p. 12.
- ↑ "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Friday, 21 February 1930. (45443), col E, p. 20.
- ↑ 40.0 40.1 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Tuesday, 11 February 1930. (45434), col F, p. 24.
- ↑ 41.0 41.1 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Tuesday, 18 February 1930. (45440), col G, p. 26.
- ↑ 42.0 42.1 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Wednesday, 12 February 1930. (45435), col D, p. 23.
- ↑ The London Gazette: no. 33697. p. 1644. 10 March 1931.
- ↑ "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Monday, 17 February 1930. (45439), col C, p. 24.
- ↑ 45.0 45.1 "Marine insurance" The Times (London). Thursday, 20 February 1930. (45442), col F, p. 23.
- ↑ "WWI STANDARD BUILT SHIPS L - W". Mariners. Retrieved 8 May 2011.
- ↑ "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Thursday, 20 February 1930. (45442), col E, p. 23.
- ↑ 48.0 48.1 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Wednesday, 19 February 1930. (45441), col C, p. 23.
- ↑ 49.0 49.1 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Tuesday, 25 February 1930. (45446), col E, p. 20.
- ↑ "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Saturday, 22 February 1930. (45444), col G, p. 22.
- ↑ 51.0 51.1 51.2 51.3 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Monday, 24 February 1930. (45445), col E, p. 21.
- ↑ 52.0 52.1 52.2 52.3 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Saturday, 8 March 1930. (45456), col C, p. 23.
- ↑ 53.0 53.1 "Japanese steamer ashore" The Times (London). Saturday, 22 February 1930. (45444), col G, p. 22.
- ↑ "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Wednesday, 26 February 1930. (45447), col F, p. 25.
- ↑ "British steamer on fire" The Times (London). Thursday, 27 February 1930. (45448), col C, p. 13.
- ↑ "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Saturday, 1 March 1930. (45450), col C, p. 23.
- ↑ 57.0 57.1 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Tuesday, 4 March 1930. (45452), col C, p. 26.
- ↑ "Federal liner stranded" The Times (London). Wednesday, 5 March 1930. (45453), col G, p. 27.
- ↑ 59.0 59.1 59.2 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Tuesday, 18 March 1930. (45464), col E, p. 26.
- ↑ "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Wednesday, 5 March 1930. (45453), col C, p. 27.
- ↑ 61.0 61.1 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Friday, 14 March 1930. (45461), col C, p. 24.
- ↑ "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Wednesday, 19 March 1930. (45464), col F, p. 25.
- ↑ 63.0 63.1 "The Nils uninsurable" The Times (London). Thursday, 27 March 1930. (45472), col C, p. 25.
- ↑ "Urajio Maru refloated" The Times (London). Wednesday, 12 March 1930. (45459), col E, p. 20.
- ↑ "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Monday, 10 March 1930. (45457), col G, p. 23.
- ↑ "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Wednesday, 28 May 1930. (45524), col E, p. 28.
- ↑ "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Tuesday, 11 March 1930. (45458), col D, p. 21.
- ↑ 68.0 68.1 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Thursday, 13 March 1930. (45460), col E, p. 20.
- ↑ 69.0 69.1 "British steamer aground" The Times (London). Monday, 17 March 1930. (45463), col G, p. 12.
- ↑ "Norwegian steamer ashore" The Times (London). Friday, 21 March 1930. (45467), col F, p. 21.
- ↑ "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Saturday, 22 March 1930. (45468), col G, p. 17.
- ↑ 72.0 72.1 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Saturday, 29 March 1930. (45474), col G, p. 22.
- ↑ 73.0 73.1 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Friday, 28 March 1930. (45473), col F, p. 25.
- ↑ 74.0 74.1 74.2 74.3 74.4 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Monday, 31 March 1930. (45475), col G, p. 23.
- ↑ "D/S Kirsten B". Warsailors. Retrieved 6 July 2012.
- ↑ "The Rhine Maru uninsurable" The Times (London). Thursday, 17 April 1930. (45490), col G, p. 7.
- ↑ "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Tuesday, 1 April 1930. (45476), col G, p. 27.
- ↑ "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Tuesday, 8 April 1930. (45482), col E, p. 27.
- ↑ "Spanish cruiser sunk in port" The Times (London). Friday, 4 April 1930. (45479), col B, p. 13.
- ↑ 80.0 80.1 80.2 80.3 80.4 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Monday, 7 April 1930. (45481), col C, p. 23.
- ↑ "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Friday, 4 April 1930. (45479), col F, p. 21.
- ↑ "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Saturday, 5 April 1930. (45480), col F, p. 23.
- ↑ "French steamer ashore" The Times (London). Wednesday, 9 April 1930. (45483), col C, p. 27.
- ↑ 84.0 84.1 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Wednesday, 16 April 1930. (45489), col D, p. 25.
- ↑ "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Thursday, 10 April 1930. (45484), col C, p. 21.
- ↑ 86.0 86.1 "British steamer lost" The Times (London). Saturday, 12 April 1930. (45486), col E, p. 20.
- ↑ 87.0 87.1 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Saturday, 12 April 1930. (45486), col D, p. 9.
- ↑ "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Thursday, 17 April 1930. (45490), col G, p. 7.
- ↑ 89.0 89.1 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Monday, 21 April 1930. (45492), col F, p. 16.
- ↑ 90.0 90.1 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Thursday, 1 May 1930. (45501), col F, p. 28.
- ↑ 91.0 91.1 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Friday, 25 April 1930. (45496), col D, p. 21.
- ↑ 92.0 92.1 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Wednesday, 23 April 1930. (45494), col C, p. 21.
- ↑ "Explosion in Italian steamer" The Times (London). Thursday, 24 April 1930. (45495), col C, p. 11.
- ↑ "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Saturday, 26 April 1930. (45497), col E, p. 19.
- ↑ "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Thursday, 8 May 1930. (45507), col C, p. 28.
- ↑ "British steamer sunk" The Times (London). Monday, 28 April 1930. (45498), col F, p. 13.
- ↑ "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Monday, 28 April 1930. (45497), col F, p. 23.
- ↑ "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Tuesday, 29 April 1930. (45499), col C, p. 26.
- ↑ "Japanese steamers ashore" The Times (London). Thursday, 1 May 1930. (45501), col C, p. 28.
- ↑ "Luzon Maru uninsurable" The Times (London). Friday, 2 May 1930. (45502), col C, p. 25.
- ↑ 101.0 101.1 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Saturday, 10 May 1930. (45509), col C, p. 22.
- ↑ "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Saturday, 3 May 1930. (45503), col C, p. 22.
- ↑ "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Monday, 5 May 1930. (45504), col G, p. 24.
- ↑ "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Friday, 9 May 1930. (45508), col G, p. 21.
- ↑ 105.0 105.1 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Tuesday, 13 May 1930. (45511), col E, p. 22.
- ↑ 106.0 106.1 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Tuesday, 20 May 1930. (45517), col E, p. 22.
- ↑ "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Wednesday, 14 May 1930. (45512), col F, p. 27.
- ↑ "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Thursday, 15 May 1930. (45513), col F, p. 28.
- ↑ 109.0 109.1 109.2 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Friday, 16 May 1930. (45514), col C, p. 29.
- ↑ 110.0 110.1 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Monday, 19 May 1930. (45516), col D, p. 24.
- ↑ 111.0 111.1 111.2 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Saturday, 24 May 1930. (45521), col F, p. 21.
- ↑ 112.0 112.1 "Greek steamer ashore" The Times (London). Tuesday, 20 May 1930. (45517), col E, p. 22.
- ↑ 113.0 113.1 "The Maria S. Kastanou uninsurable" The Times (London). Friday, 23 May 1930. (45520), col F, p. 8.
- ↑ 114.0 114.1 "The Asia uninsurable" The Times (London). Tuesday, 27 May 1930. (45523), col C, p. 28.
- ↑ 115.0 115.1 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Monday, 26 May 1930. (45522), col C, p. 25.
- ↑ "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Thursday, 29 May 1930. (45525), col G, p. 8.
- ↑ "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Friday, 30 May 1930. (45526), col G, p. 21.
- ↑ 118.0 118.1 118.2 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Tuesday, 17 June 1930. (45541), col D, p. 25.
- ↑ "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Saturday, 31 May 1930. (45527), col F, p. 20.
- ↑ "Collision in the Channel" The Times (London). Monday, 2 June 1930. (45528), col G, p. 14.
- ↑ "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Tuesday, 2 June 1930. (45528), col C, p. 25.
- ↑ "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Saturday, 7 June 1930. (45533), col F, p. 22.
- ↑ "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Wednesday, 11 June 1930. (45536), col F, p. 23.
- ↑ 124.0 124.1 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Tuesday, 10 June 1930. (45535), col D, p. 20.
- ↑ 125.0 125.1 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Thursday, 12 June 1930. (45537), col C, p. 25.
- ↑ 126.0 126.1 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Tuesday, 24 June 1930. (45547), col E, p. 19.
- ↑ "U.S. ships in collision" The Times (London). Thursday, 12 June 1930. (45537), col D, p. 14.
- ↑ 128.0 128.1 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Thursday, 19 June 1930. (45543), col E, p. 19.
- ↑ "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Wednesday, 25 June 1930. (45548), col C, p. 28.
- ↑ "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Wednesday, 18 June 1930. (45542), col C, p. 26.
- ↑ 131.0 131.1 131.2 131.3 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Monday, 23 June 1930. (45546), col G, p. 23.
- ↑ "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Friday, 20 June 1930. (45544), col D, p. 27.
- ↑ 133.0 133.1 133.2 133.3 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Wednesday, 16 July 1930. (45566), col E, p. 24.
- ↑ 134.0 134.1 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Friday, 27 June 1930. (45550), col E, p. 21.
- ↑ "Japanese steamer ashore" The Times (London). Wednesday, 25 June 1930. (45548), col E, p. 28.
- ↑ "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Monday, 30 June 1930. (45552), col G, p. 23.
- ↑ "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Saturday, 28 June 1930. (45551), col D, p. 21.
- ↑ "The Niigata Maru refloated" The Times (London). Saturday, 5 July 1930. (45557), col F, p. 23.
- ↑ "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Tuesday, 1 July 1930. (45553), col G, p. 27.
- ↑ "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Friday, 4 July 1930. (45556), col E, p. 27.
- ↑ 141.0 141.1 141.2 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Monday, 7 July 1930. (45558), col F, p. 23.
- ↑ "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Wednesday, 2 July 1930. (45554), col C, p. 25.
- ↑ "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Saturday, 5 July 1930. (45557), col F, p. 23.
- ↑ 144.0 144.1 144.2 144.3 144.4 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Monday, 14 July 1930. (45564), col C, p. 19.
- ↑ "Francesco Morosini (5606895)". Miramar Ship Index. Retrieved 7 July 2012. (subscription required (help)).
- ↑ "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Tuesday, 8 July 1930. (45559), col C, p. 24.
- ↑ 147.0 147.1 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Wednesday, 9 July 1930. (45560), col C, p. 26.
- ↑ "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Friday, 11 July 1930. (45562), col C, p. 26.
- ↑ 149.0 149.1 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Saturday, 12 July 1930. (45563), col C, p. 20.
- ↑ 150.0 150.1 150.2 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Tuesday, 12 August 1930. (45589), col G, p. 15.
- ↑ 151.0 151.1 151.2 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Tuesday, 15 July 1930. (45565), col F, p. 19.
- ↑ "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Saturday, 19 July 1930. (45569), col G, p. 19.
- ↑ 153.0 153.1 153.2 153.3 153.4 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Monday, 21 July 1930. (45570), col C, p. 19.
- ↑ 154.0 154.1 154.2 "News of the Nerbudda" The Times (London). Saturday, 2 August 1930. (45581), col F, p. 12.
- ↑ "German steamer lost" The Times (London). Monday, 21 July 1930. (45570), col C, p. 19.
- ↑ 156.0 156.1 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Tuesday, 22 July 1930. (45571), col G, p. 21.
- ↑ 157.0 157.1 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Saturday, 26 July 1930. (45575), col D, p. 21.
- ↑ "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Thursday, 24 July 1930. (45573), col G, p. 23.
- ↑ 159.0 159.1 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Friday, 25 July 1930. (45574), col G, p. 19.
- ↑ 160.0 160.1 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Wednesday, 30 July 1930. (45578), col G, p. 17.
- ↑ "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Tuesday, 29 July 1930. (45577), col G, p. 24.
- ↑ 162.0 162.1 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Thursday, 31 July 1930. (45579), col C, p. 24.
- ↑ 163.0 163.1 "Two Japanese steamers ashore" The Times (London). Thursday, 31 July 1930. (45579), col D, p. 24.
- ↑ "Biyo Maru refloated" The Times (London). Monday, 25 August 1930. (45600), col D, p. 17.
- ↑ 165.0 165.1 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Thursday, 21 August 1930. (45597), col G, p. 6.
- ↑ "British steamer in collision" The Times (London). Friday, 1 August 1930. (45580), col F, p. 24.
- ↑ "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Friday, 1 August 1930. (45580), col F, p. 24.
- ↑ "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Tuesday, 5 August 1930. (45583), col E, p. 15.
- ↑ 169.0 169.1 169.2 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Monday, 4 August 1930. (45582), col G, p. 17.
- ↑ 170.0 170.1 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Saturday, 9 August 1930. (45587), col F, p. 19.
- ↑ 171.0 171.1 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Friday, 8 August 1930. (45586), col C, p. 18.
- ↑ 172.0 172.1 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Saturday, 16 August 1930. (45593), col F, p. 19.
- ↑ 173.0 173.1 "British steamers ashore" The Times (London). Saturday, 9 August 1930. (45587), col F, p. 19.
- ↑ 174.0 174.1 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Monday, 11 August 1930. (45588), col G, p. 19.
- ↑ 175.0 175.1 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Saturday, 30 August 1930. (45605), col G, p. 16.
- ↑ "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Tuesday, 19 August 1930. (45595), col C, p. 19.
- ↑ "News in Brief" The Times (London). Monday, 11 August 1930. (45588), col G, p. 7.
- ↑ 178.0 178.1 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Wednesday, 13 August 1930. (45590), col E, p. 18.
- ↑ 179.0 179.1 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Monday, 18 August 1930. (45594), col F, p. 17.
- ↑ 180.0 180.1 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Thursday, 14 August 1930. (45591), col G, p. 15.
- ↑ "Reinsurance rates" The Times (London). Wednesday, 22 October 1930. (45650), col E, p. 26.
- ↑ "The Tahiti" The Times (London). Tuesday, 19 August 1930. (45595), col D, p. 10.
- ↑ 183.0 183.1 183.2 183.3 183.4 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Saturday, 20 September 1930. (45623), col E, p. 15.
- ↑ "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Wednesday, 20 August 1930. (45596), col E, p. 12.
- ↑ "Telegrams in Brief" The Times (London). Saturday, 23 August 1930. (45599), col G, p. 9.
- ↑ 186.0 186.1 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Friday, 22 August 1930. (45598), col E, p. 18.
- ↑ "Tami Maru refloated" The Times (London). Monday, 1 September 1930. (45606), col F, p. 17.
- ↑ "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Tuesday, 26 August 1930. (45601), col E, p. 14.
- ↑ 189.0 189.1 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Thursday, 28 August 1930. (45603), col G, p. 6.
- ↑ 190.0 190.1 190.2 190.3 190.4 "Belgian seamen rescued" The Times (London). Wednesday, 24 September 1930. (45626), col E, p. 12.
- ↑ 191.0 191.1 191.2 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Friday, 29 August 1930. (45604), col C, p. 20.
- ↑ 192.0 192.1 "British steamer ashore" The Times (London). Thursday, 11 September 1930. (45615), col F, p. 18.
- ↑ 193.0 193.1 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Friday, 5 September 1930. (45610), col G, p. 20.
- ↑ 194.0 194.1 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Monday, 1 September 1930. (45606), col E-F, p. 17.
- ↑ "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Tuesday, 2 September 1930. (45607), col B-C, p. 17.
- ↑ "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Thursday, 4 September 1930. (45609), col F, p. 15.
- ↑ "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Monday, 15 September 1930. (45618), col G, p. 19.
- ↑ 198.0 198.1 "Greek steamer ashore" The Times (London). Thursday, 4 September 1930. (45609), col F, p. 15.
- ↑ "Italian steamer ashore" The Times (London). Wednesday, 17 September 1930. (45620), col D, p. 18.
- ↑ 200.0 200.1 200.2 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Wednesday, 10 September 1930. (45614), col F, p. 21.
- ↑ "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Tuesday, 9 September 1930. (45613), col G, p. 20.
- ↑ "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Thursday, 18 September 1930. (45621), col D, p. 21.
- ↑ "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Friday, 12 September 1930. (45616), col E, p. 20.
- ↑ "The Edera floated" The Times (London). Friday, 17 October 1930. (45646), col F, p. 23.
- ↑ Heaton, K E (8 July 2004). "Shipwrecks in British Columbia's Waters". Retrieved 21 April 2011.
- ↑ 206.0 206.1 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Friday, 19 September 1930. (45622), col E, p. 4.
- ↑ 207.0 207.1 207.2 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Tuesday, 30 September 1930. (45631), col B, p. 17.
- ↑ "The Llandilo refloated" The Times (London). Thursday, 2 October 1930. (45633), col E, p. 21.
- ↑ 209.0 209.1 209.2 209.3 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Tuesday, 14 October 1930. (45643), col F, p. 19.
- ↑ 210.0 210.1 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Monday, 22 September 1930. (45624), col D, p. 20.
- ↑ "Steamers in distress off French coast" The Times (London). Monday, 22 September 1930. (45624), col F, p. 12.
- ↑ 212.0 212.1 212.2 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Friday, 10 October 1930. (45640), col B, p. 21.
- ↑ "Belgian Merchant H-O". Belgische Koopvaardij. Retrieved 31 October 2010.
- ↑ 214.0 214.1 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Thursday, 15 September 1930. (45627), col D, p. 21.
- ↑ 215.0 215.1 215.2 215.3 215.4 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Monday, 29 September 1930. (45630), col C, p. 22.
- ↑ "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Friday, 26 September 1930. (45628), col F, p. 21.
- ↑ "Lalandia (5606660)". Miramar Ship Index. Retrieved 11 July 2012. (subscription required (help)).
- ↑ "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Saturday, 27 September 1930. (45629), col G, p. 18.
- ↑ "News of the City of Osaka" The Times (London). Saturday, 27 September 1930. (45629), col G, p. 18.
- ↑ 220.0 220.1 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Monday, 8 December 1930. (45690), col G, p. 18.
- ↑ 221.0 221.1 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Wednesday, 8 October 1930. (45638), col E-F, p. 20.
- ↑ 222.0 222.1 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Monday, 13 October 1930. (45642), col G, p. 19.
- ↑ 223.0 223.1 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Friday, 17 October 1930. (45646), col F, p. 23.
- ↑ 224.0 224.1 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Thursday, 16 October 1930. (45645), col E, p. 23.
- ↑ "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Thursday, 23 October 1930. (45651), col C, p. 23.
- ↑ "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Saturday, 18 October 1930. (45647), col F, p. 17.
- ↑ "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Monday, 20 October 1930. (45648), col G, p. 24.
- ↑ 228.0 228.1 228.2 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Saturday, 25 October 1930. (45653), col C, p. 21.
- ↑ "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Friday, 24 October 1930. (45652), col C, p. 23.
- ↑ 230.0 230.1 230.2 230.3 230.4 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Monday, 10 November 1930. (45666), col G, p. 18.
- ↑ "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Monday, 27 October 1930. (45654), col A, p. 21.
- ↑ "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Wednesday, 8 October 1930. (45656), col G, p. 23.
- ↑ 233.0 233.1 233.2 233.3 233.4 "British steamer beached" The Times (London). Tuesday, 4 November 1930. (45661), col B, p. 25.
- ↑ 234.0 234.1 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Friday, 14 November 1930. (45670), col G, p. 23.
- ↑ 235.0 235.1 235.2 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Monday, 3 November 1930. (45660), col G, p. 20.
- ↑ 236.0 236.1 236.2 236.3 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Tuesday, 11 November 1930. (45667), col G, p. 24.
- ↑ 237.0 237.1 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Thursday, 6 November 1930. (45663), col C, p. 24.
- ↑ "Collision between British and Japanese steamers" The Times (London). Friday, 7 November 1930. (45664), col F, p. 22.
- ↑ 239.0 239.1 239.2 239.3 239.4 239.5 239.6 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Wednesday, 12 November 1930. (45668), col G, p. 25.
- ↑ 240.0 240.1 240.2 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Friday, 7 November 1930. (45664), col F, p. 22.
- ↑ "The Tamiahua floated" The Times (London). Thursday, 27 November 1930. (45681), col E, p. 21.
- ↑ "Loss of steamer denied" The Times (London). Wednesday, 12 November 1930. (45668), col G, p. 22.
- ↑ 243.0 243.1 243.2 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Thursday, 18 November 1930. (45673), col G, p. 24.
- ↑ 244.0 244.1 244.2 244.3 244.4 244.5 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Friday, 21 November 1930. (45676), col F, p. 13.
- ↑ 245.0 245.1 245.2 "British steamer ashore" The Times (London). Friday, 21 November 1930. (45676), col F, p. 25.
- ↑ 246.0 246.1 246.2 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Saturday, 15 November 1930. (45671), col D, p. 21.
- ↑ 247.0 247.1 "Swedish steamer in distress" The Times (London). Thursday, 20 November 1930. (45675), col E, p. 20.
- ↑ 248.0 248.1 248.2 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Thursday, 11 December 1930. (45693), col G, p. 22.
- ↑ 249.0 249.1 249.2 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Thursday, 13 November 1930. (45669), col C, p. 24.
- ↑ 250.0 250.1 250.2 250.3 250.4 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Monday, 17 November 1930. (45672), col E, p. 22.
- ↑ "News in Brief" The Times (London). Monday, 17 November 1930. (45672), col G, p. 9.
- ↑ "The Yero Carras uninsurable" The Times (London). Wednesday, 19 November 1930. (45674), col G, p. 20.
- ↑ "The disaster to the Artiglio" The Times (London). Tuesday, 9 December 1930. (45691), col B, p. 24.
- ↑ "Greek steamer beached" The Times (London). Wednesday, 10 December 1930. (45692), col F, p. 26.
- ↑ 255.0 255.1 255.2 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Thursday, 20 November 1930. (45675), col E, p. 16.
- ↑ "Missing vessel" The Times (London). Thursday, 1 January 1931. (45709), col G, p. 20.
- ↑ 257.0 257.1 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Friday, 5 December 1930. (45688), col E, p. 26.
- ↑ 258.0 258.1 "Swedish steamer abandoned" The Times (London). Thursday, 20 November 1930. (45675), col E, p. 16.
- ↑ 259.0 259.1 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Monday, 24 November 1930. (45678), col C, p. 23.
- ↑ "Rescued Swedish crew" The Times (London). Friday, 21 November 1930. (45676), col F, p. 13.
- ↑ "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Monday, 1 December 1930. (45684), col G, p. 24.
- ↑ "The Ruperra floated" The Times (London). Saturday, 6 December 1930. (45689), col E, p. 20.
- ↑ 263.0 263.1 "German Steamer wrecked" The Times (London). Tuesday, 25 November 1930. (45679), col F, p. 14.
- ↑ "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Thursday, 27 November 1930. (45681), col G, p. 21.
- ↑ 265.0 265.1 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Tuesday, 2 December 1930. (45685), col C, p. 25.
- ↑ 266.0 266.1 266.2 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Wednesday, 10 December 1930. (45692), col C, p. 27.
- ↑ "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Wednesday, 3 December 1930. (45686), col B, p. 21.
- ↑ "The Asmund reported sunk" The Times (London). Monday, 9 December 1930. (45690), col G, p. 18.
- ↑ 269.0 269.1 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Thursday, 4 December 1930. (45687), col F, p. 27.
- ↑ "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Saturday, 6 December 1930. (45689), col G, p. 20.
- ↑ "Salvage ship disaster" The Times (London). Tuesday, 9 December 1930. (45691), col A, p. 14.
- ↑ "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Tuesday, 9 December 1930. (45691), col E, p. 24.
- ↑ 273.0 273.1 273.2 273.3 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Friday, 12 December 1930. (45694), col F, p. 20.
- ↑ "Two vessels sunk" The Times (London). Thursday, 11 December 1930. (45693), col B, p. 13.
- ↑ 275.0 275.1 275.2 275.3 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Tuesday, 16 December 1930. (45697), col G, p. 23.
- ↑ 276.0 276.1 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Wednesday, 17 December 1930. (45698), col C, p. 22.
- ↑ "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Thursday, 18 December 1930. (45699), col E, p. 26.
- ↑ 278.0 278.1 278.2 278.3 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Tuesday, 23 December 1930. (45703), col G, p. 19.
- ↑ 279.0 279.1 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Friday, 19 December 1930. (45700), col G, p. 19.
- ↑ "The Oberon disaster" The Times (London). Monday, 22 December 1930. (45702), col D, p. 12.
- ↑ 281.0 281.1 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Monday, 22 December 1930. (45702), col F, p. 21.
- ↑ 282.0 282.1 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Tuesday, 30 December 1930. (45707), col C, p. 19.
- ↑ 283.0 283.1 283.2 "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Thursday, 1 January 1931. (45709), col F-G, p. 20.
- ↑ "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Tuesday, 6 January 1931. (45713), col G, p. 21.
- ↑ "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Saturday, 27 December 1930. (45705), col G, p. 17.
- ↑ 286.0 286.1 "Fire in British steamer" The Times (London). Monday, 29 December 1930. (45706), col F, p. 9.
- ↑ "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Wednesday, 31 December 1930. (45708), col C, p. 21.
- ↑ "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Friday, 2 January 1931. (45710), col G, p. 18.
- ↑ "Casualty reports" The Times (London). Saturday, 3 January 1931. (45711), col C, p. 19.
| Ship events in 1930 | |||||||||||
| Ship launches: | 1925 | 1926 | 1927 | 1928 | 1929 | 1930 | 1931 | 1932 | 1933 | 1934 | 1935 |
| Ship commissionings: | 1925 | 1926 | 1927 | 1928 | 1929 | 1930 | 1931 | 1932 | 1933 | 1934 | 1935 |
| Ship decommissionings: | 1925 | 1926 | 1927 | 1928 | 1929 | 1930 | 1931 | 1932 | 1933 | 1934 | 1935 |
| Shipwrecks: | 1925 | 1926 | 1927 | 1928 | 1929 | 1930 | 1931 | 1932 | 1933 | 1934 | 1935 |